Abstract
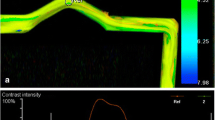
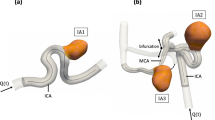
Flow diverters (FDs) are utilized for a wide range of aneurysms, but show safety issues such as adverse interactions with static magnetic fields (displacement force and torque) and radiofrequency-induced heating during magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The present study aimed to assess these adverse interactions in a 7-tesla (7T) static magnetic field and radiofrequency-induced heating during a 7T MRI for two types of FD. Displacement force and magnetically induced torque were assessed using the deflection angle method and low friction surface method, respectively. To assess heating, each FD was set in a phantom filled with gelled-saline mixed with polyacrylic acid and underwent a 7T MRI using a three-dimensional fast spin echo method. Displacement force and magnetically induced torque in the 7T static magnetic field were undetectable, and radiofrequency-induced heating during 7T MRI remained ≤ 0.6 °C for both types of FD, suggesting that magnetic field interactions and heating on FDs during a 7T MRI are acceptable from a safety perspective.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Voelker R (2017) Twice the power in new MRI. JAMA 318:1858. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2017.17120
American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) International: F2052-15 standard test method for measurement of magnetically induced displacement force on medical devices in the magnetic resonance environment. https://www.document-center.com/standards/show/ASTM-F2052. Accessed 30 Apr 2022
Standard test method for measurement of magnetically induced torque on medical devices in the magnetic resonance environment. https://www.astm.org/f2213-17.html. Accessed 30 Apr 2022
American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) International: F2182-19e2. Standard test method for measurement of radio frequency induced heating on or near passive implants during magnetic resonance imaging. https://www.astm.org/f2182-19e02.html. Accessed 30 Apr 2022
Tsutsui S, Matsuda T, Takeda K et al (2022) Assessment of heating on titanium alloy cerebral aneurysm clips during 7T MRI. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 43:972–977. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A7561
Winter L, Seifert F, Zilberti L et al (2021) MRI-related heating of implants and devices: a review. J Magn Reson Imaging 53:1646–1665. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.27194
Ladd ME (2007) High-field-strength magnetic resonance: potential and limits. Top Magn Reson Imaging 18:139–152. https://doi.org/10.1097/RMR.0b013e3180f612b3
Muranaka H, Horiguchi T, Ueda Y et al (2011) Evaluation of RF heating due to various implants during MR procedures. Magn Reson Med Sci 10:11–19. https://doi.org/10.2463/mrms.10.11
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
Since the submitted work does not involve human subject, ethical approval is not required.
Informed consent
Since the submitted work does not involve human subject, informed consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Igarashi, S., Chida, K., Matsuda, T. et al. Assessment of magnetic field interactions and heating for cerebral aneurysm flow diverters during 7T MRI. Neuroradiology 65, 1809–1812 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-023-03208-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-023-03208-8