Abstract
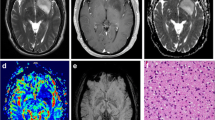
This study aimed to investigate whether arterial spin labeling (ASL) features allow differentiation of oligodendroglioma, IDH-mutant and 1p/19q-codeleted (IDHm-codel) from diffuse glioma with IDH-wildtype (IDHw) or astrocytoma, IDH-mutant (IDHm-noncodel). Participants comprised 71 adult patients with pathologically confirmed diffuse glioma, classified as IDHw, IDHm-noncodel, or IDHm-codel. Subtraction images were generated from paired-control/label images on ASL and used to assess the presence of a cortical high-flow sign. The cortical high-flow sign was defined as increased ASL signal intensity within the tumor-affecting cerebral cortex compared with normal-appearing cortex. Regions without contrast enhancement on conventional MR imaging were targeted. The frequency of the cortical high-flow sign on ASL was compared among IDHw, IDHm-noncodel, and IDHm-codel. As a result, the frequency of the cortical high-flow sign was significantly higher for IDHm-codel than for IDHw or IDHm-noncodel. In conclusion, the cortical high-flow sign could represent a hallmark of oligodendroglioma, IDH-mutant, and 1p/19q-codeleted without intense contrast enhancement.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Change history
30 September 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-023-03228-4
Abbreviations
- ASL:
-
Arterial spin labeling
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- IDH:
-
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
- IDHm-codel:
-
Oligodendroglioma, IDH-mutant and 1p/19q-codeleted
- IDHm-noncodel:
-
Astrocytoma, IDH-mutant
- IDHw:
-
Glioblastoma, IDH-wildtype
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic curve
References
WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board (2021) World Health Organization classification of tumours of the central nervous system, 5th edn. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon
Koeller KK, Rushing EJ (2005) From the archives of the AFIP: Oligodendroglioma and its variants: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics 25:1669–1688
Smits M (2016) Imaging of oligodendroglioma. Br J Radiol 89:20150857
Latysheva A, Emblem KE, Brandal P et al (2019) Dynamic susceptibility contrast and diffusion MR imaging identify oligodendroglioma as defined by the 2016 WHO classification for brain tumors: histogram analysis approach. Neuroradiology 61:545–555
Noguchi T, Yoshiura T, Hiwatashi A et al (2008) Perfusion imaging of brain tumors using arterial spin-labeling: correlation with histopathologic vascular density. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:688–693
Togao O, Hiwatashi A, Yamashita K et al (2017) Grading diffuse gliomas without intense contrast enhancement by amide proton transfer MR imaging: comparisons with diffusion- and perfusion-weighted imaging. Eur Radiol 27:578–588
Hatae R, Hata N, Yoshimoto K et al (2016) Precise Detection of IDH1/2 and BRAF Hotspot Mutations in Clinical Glioma Tissues by a Differential Calculus Analysis of High-Resolution Melting Data. PLoS ONE 11:e0160489
Higa N, Akahane T, Yokoyama S et al (2020) A tailored next-generation sequencing panel identified distinct subtypes of wildtype IDH and TERT promoter glioblastomas. Cancer Sci 111:3902–3911
Ludemann L, Warmuth C, Plotkin M et al (2009) Brain tumor perfusion: comparison of dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging using T1, T2, and T2* contrast, pulsed arterial spin labeling, and H2(15)O positron emission tomography. Eur J Radiol 70:465–474
Saito T, Muragaki Y, Maruyama T et al (2016) Calcification on CT is a simple and valuable preoperative indicator of 1p/19q loss of heterozygosity in supratentorial brain tumors that are suspected grade II and III gliomas. Brain Tumor Pathol 33:175–182
Funding
This work was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant number 22K07657.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the institutional review board of our hospital (Kyushu University Institutional Review Board for Clinical Research).
Informed consent
Informed consent was waived because this study was retrospective nature.
Conflict of interest
MO: Employee of Philips Japan. K.Yamashita, OT, KK, DK, YS, YF, IK, K. Yoshimoto, and KI: Nothing to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yamashita, K., Togao, O., Kikuchi, K. et al. Cortical high-flow sign on arterial spin labeling: a novel biomarker for IDH-mutation and 1p/19q-codeletion status in diffuse gliomas without intense contrast enhancement. Neuroradiology 65, 1415–1418 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-023-03186-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-023-03186-x