Abstract
Purpose
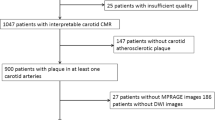
Covert brain infarctions (CBIs) and cerebral microbleeds (CMBs) represent subclinical sequelae of ischemic and hemorrhagic cerebral small vessel disease, respectively. In addition to thromboembolic stroke, carotid atherosclerosis has been associated with downstream vascular brain injury, including inflammation and small vessel disease. The specific plaque features responsible for this are unknown. We aimed to determine the association of specific vulnerable carotid plaque features to CBIs and CMBs to better understand the relation of large and small vessel disease in a single-center retrospective observational study.
Methods
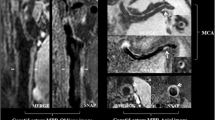
Intraplaque hemorrhage (IPH) and plaque ulceration were recorded on carotid MRA and total, cortical, and lacunar CBIs and CMBs were recorded on brain MR in 349 patients (698 carotid arteries). Multivariable Poisson regression was performed to relate plaque features to CBIs and CMBs. Within-subject analysis in those with unilateral IPH and ulceration was performed with Poisson regression.
Results
Both IPH and plaque ulceration were associated with total CBI (prevalence ratios (PR) 3.33, 95% CI: 2.16–5.15 and 1.91, 95% CI: 1.21–3.00, respectively), after adjusting for stenosis, demographic, and vascular risk factors. In subjects with unilateral IPH, PR was 2.83, 95% CI: 1.76–4.55, for CBI in the ipsilateral hemisphere after adjusting for stenosis. Among those with unilateral ulceration, PR was 1.82, 95% CI: 1.18–2.81, for total CBI ipsilateral to ulceration after adjusting for stenosis. No statistically significant association was seen with CMBs.
Conclusion
Both IPH and plaque ulceration are associated with total, cortical, and lacunar type CBIs but not CMBs suggesting that advanced atherosclerosis contributes predominantly to ischemic markers of subclinical vascular injury.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- CBI:
-
Covert brain infarction
- CMB:
-
Cerebral microbleed
- IPH:
-
Intraplaque hemorrhage
- PR:
-
Prevalence ratio
References
Gupta A, Giambrone AE, Gialdini G, Finn C, Delgado D, Gutierrez J, Wright C, Beiser AS, Seshadri S, Pandya A (2016) Silent brain infarction and risk of future stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke 47(3):719–725
Vermeer SE, Prins ND, den Heijer T, Hofman A, Koudstaal PJ, Breteler MM (2003) Silent brain infarcts and the risk of dementia and cognitive decline. N Engl J Med 348(13):1215–1222
Baradaran H, Gialdini G, Mtui E, Askin G, Kamel H, Gupta A (2016) Silent brain infarction in patients with asymptomatic carotid artery atherosclerotic disease. Stroke 47(5):1368–1370
van Veluw SJ, Hilal S, Kuijf HJ, Ikram MK, Xin X, Yeow TB, Venketasubramanian N, Biessels GJ, Chen C (2015) Cortical microinfarcts on 3T MRI: clinical correlates in memory-clinic patients. Alzheimers Dement 11(12):1500–1509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2014.12.010
Debette S, Beiser A, DeCarli C, Au R, Himali JJ, Kelly-Hayes M, Romero JR, Kase CS, Wolf PA, Seshadri S (2010) Association of MRI markers of vascular brain injury with incident stroke, mild cognitive impairment, dementia, and mortality. Stroke 41(4):600–606
Finn C, Giambrone AE, Gialdini G, Delgado D, Baradaran H, Kamel H, Gupta A (2017) The association between carotid artery atherosclerosis and silent brain infarction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 26(7):1594–1601
Takasugi J, Miwa K, Watanabe Y, Okazaki S, Todo K, Sasaki T, Sakaguchi M, Mochizuki H (2019) Cortical cerebral microinfarcts on 3T magnetic resonance imaging in patients with carotid artery stenosis. Stroke 50(3):639–644. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.023781
Gupta A, Baradaran H, Schweitzer AD, Kamel H, Pandya A, Delgado D, Dunning A, Mushlin AI, Sanelli PC (2013) Carotid plaque MRI and stroke risk. Stroke 44(11):3071–3077
Saam T, Hetterich H, Hoffmann V, Yuan C, Dichgans M, Poppert H, Koeppel T, Hoffmann U, Reiser MF, Bamberg F (2013) Meta-analysis and systematic review of the predictive value of carotid plaque hemorrhage on cerebrovascular events by magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol 62(12):1081–1091
Hosseini AA, Kandiyil N, MacSweeney ST, Altaf N, Auer DP (2013) Carotid plaque hemorrhage on magnetic resonance imaging strongly predicts recurrent ischemia and stroke. Ann Neurol 73(6):774–784
Romero JR, Preis SR, Beiser A, DeCarli C, D’Agostino RB, Wolf PA, Vasan RS, Polak JF, Seshadri S (2016) Carotid atherosclerosis and cerebral microbleeds: the Framingham Heart Study. J Am Heart Assoc 5(3):e002377
Zhao F-f, Gao H-y, Gao Y, Zhao Z, Li J, Ning F-b, Zhang X-n, Wang Z-g, Yu A-l, Guo Y-y, Sun B-l (2018) A correlational study on cerebral microbleeds and carotid atherosclerosis in patients with ischemic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 27(8):2228–2234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2018.04.009
Ding L, Hong Y, Peng B (2017) Association between large artery atherosclerosis and cerebral microbleeds: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke and vascular neurology 2 (1). https://www.svn.bmj.com/content/2/1/7
Hori S, Hori E, Shibata T, Umemura K, Okamoto S, Kubo M, Horie Y, Kuroda S (2019) Correlation between cerebral microbleeds and vulnerable plaque in patients with severe carotid artery stenosis; comparative magnetic resonance imaging study. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 28(10):104300
Scott McNally J, Yoon HC, Kim SE, Narra KK, McLaughlin MS, Parker DL, Treiman GS (2015) Carotid MRI detection of intraplaque hemorrhage at 3T and 1.5 T. J Neuroimaging 25(3):390–396
Beck MJ, Parker DL, Bolster BD Jr, Kim SE, McNally JS, Treiman GS, Hadley JR (2017) Interchangeable neck shape–specific coils for a clinically realizable anterior neck phased array system. Magn Reson Med 78(6):2460–2468
Eisenmenger LB, Aldred BW, Kim S-E, Stoddard GJ, de Havenon A, Treiman GS, Parker DL, McNally JS (2016) Prediction of carotid intraplaque hemorrhage using adventitial calcification and plaque thickness on CTA. Am J Neuroradiol 37(8):1496–1503. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A4765
McNally JS, McLaughlin MS, Hinckley PJ, Treiman SM, Stoddard GJ, Parker DL, Treiman GS (2015) Intraluminal thrombus, intraplaque hemorrhage, plaque thickness, and current smoking optimally predict carotid stroke. Stroke 46(1):84–90. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.006286
Collaborators* NASCET (1991) Beneficial effect of carotid endarterectomy in symptomatic patients with high-grade carotid stenosis. N Engl J Med 325(7):445–453
Wardlaw JM, Smith EE, Biessels GJ, Cordonnier C, Fazekas F, Frayne R, Lindley RI, T O’Brien J, Barkhof F, Benavente OR (2013) Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease and its contribution to ageing and neurodegeneration. The Lancet Neurology 12(8):822–838
Gregoire S, Chaudhary U, Brown M, Yousry T, Kallis C, Jäger H, Werring D (2009) The Microbleed Anatomical Rating Scale (MARS): reliability of a tool to map brain microbleeds. Neurology 73(21):1759–1766
Van Den Bouwhuijsen Q, Vernooij M, Verhaaren B, Vrooman H, Niessen W, Krestin G, Ikram M, Franco O, van der Lugt A (2017) Carotid plaque morphology and ischemic vascular brain disease on MRI. Am J Neuroradiol 38(9):1776–1782
Etesami M, Hoi Y, Steinman D, Gujar S, Nidecker A, Astor B, Portanova A, Qiao Y, Abdalla W, Wasserman B (2013) Comparison of carotid plaque ulcer detection using contrast-enhanced and time-of-flight MRA techniques. Am J Neuroradiol 34(1):177–184
Regenhardt RW, Das AS, Lo EH, Caplan LR (2018) Advances in understanding the pathophysiology of lacunar stroke: a review. JAMA Neurol 75(10):1273–1281
Azeem F, Durrani R, Zerna C, Smith EE (2020) Silent brain infarctions and cognition decline: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurol 267(2):502–512
Price TR, Manolio TA, Kronmal RA, Kittner SJ, Yue NC, Robbins J, Anton-Culver H, O’Leary DH (1997) Silent brain infarction on magnetic resonance imaging and neurological abnormalities in community-dwelling older adults: the Cardiovascular Health Study. Stroke 28(6):1158–1164
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
This work was supported by a Radiological Society of North America Research Scholar Grant, General Electric Radiology Research Academic Fellowship, and a grant for the Study Design and Biostatistics Center, with funding, in part, from the National Center for Research Resources and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, National Institutes of Health, grant 8UL1TR000105 (formerly UL1RR025764). American Heart Association grant number 17SDG33460420.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Hediyeh Baradaran, Sinead Culleton, Greg Stoddard, and J Scott McNally. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Hediyeh Baradaran and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
This research study was conducted retrospectively from data obtained for clinical purposes at the University of Utah Health Medical Center. The University of Utah Institutional Review Board approved this study.
Consent to participate
All study procedures were approved by the Institutional Review Board at the University of Utah and informed consent was not required given retrospective nature of the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Baradaran, H., Culleton, S., Stoddard, G. et al. Association between high-risk extracranial carotid plaque and covert brain infarctions and cerebral microbleeds. Neuroradiology 65, 287–295 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-022-03062-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-022-03062-0