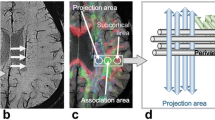
Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to compare the function of the glymphatic system in patients with status epilepticus (SE) with that in healthy controls by diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) method. We also investigated the association between glymphatic system function and the clinical characteristics of SE.
Methods
We retrospectively enrolled 28 patients with SE and 31 healthy controls matched for age and sex. All study participants underwent diffusion tensor imaging using the same 3-T MRI scanner, and the DTI-ALPS index was calculated. We compared the DTI-ALPS index between the SE group and the control group. We also evaluated the associations of the DTI-ALPS index with etiology and type of SE, age, putative duration of seizure, time interval until MRI, seizure-related changes on diffusion-weighted imaging, and any previous structural lesions.
Results
The DTI-ALPS index was significantly lower in the SE group than in the control group (1.462 ± 0.297 vs. 1.632 ± 0.270, p = 0.026) and was negatively correlated with age (r = − 0.280, p = 0.032) in the SE group. However, there were no significant between-group differences in the DTI-ALPS index according to other clinical factors.
Significance
The finding of a significantly lower DTI-ALPS index in the SE group suggests that the glymphatic system is impaired in patients with SE. DTI-ALPS is a useful tool for evaluation of the function of the glymphatic system in these patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data that support the findings of this study are available upon reasonable request.
References
Plog BA, Nedergaard M (2018) The glymphatic system in central nervous system health and disease: past, present, and future. Annu Rev Pathol 13:379–394
Nedergaard M (2013) Garbage truck of the brain. Science 340(6140):1529–1530
Mathiisen TM, Lehre KP, Danbolt NC, Ottersen OP (2010) The perivascular astroglial sheath provides a complete covering of the brain microvessels: an electron microscopic 3D reconstruction. Glia 58(9):1094–1103
Iliff JJ, Wang M, Liao Y, Plogg BA, Peng W, Gundersen GA, Benveniste H, Vates GE, Deane R, Goldman SA (2012) A paravascular pathway facilitates CSF flow through the brain parenchyma and the clearance of interstitial solutes, including amyloid β. Sci Transl Med 4(147):147ra111-147ra111
Verkhratsky A, Sofroniew MV, Messing A, deLanerolle NC, Rempe D, Rodríguez JJ, Nedergaard M (2012) Neurological diseases as primary gliopathies: a reassessment of neurocentrism. ASN Neuro 4(3):e00082. https://doi.org/10.1042/AN20120010
Iliff JJ, Nedergaard M (2013) Is there a cerebral lymphatic system? Stroke 44(6_supp1_1):S93–S95
Kaur J, Davoodi-Bojd E, Fahmy LM, Zhang L, Ding G, Hu J, Zhang Z, Chopp M, Jiang Q (2020) Magnetic resonance imaging and modeling of the glymphatic system. Diagnostics 10(6):344
Iliff JJ, Lee H, Yu M, Feng T, Logan J, Nedergaard M, Benveniste H (2013) Brain-wide pathway for waste clearance captured by contrast-enhanced MRI. J Clin Investig 123(3):1299–1309
Ringstad G, Vatnehol SAS, Eide PK (2017) Glymphatic MRI in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Brain 140(10):2691–2705
Kiviniemi V, Wang X, Korhonen V, Keinänen T, Tuovinen T, Autio J, LeVan P, Keilholz S, Zang Y-F, Hennig J (2016) Ultra-fast magnetic resonance encephalography of physiological brain activity–glymphatic pulsation mechanisms? J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 36(6):1033–1045
Yamada S, Miyazaki M, Kanazawa H, Higashi M, Morohoshi Y, Bluml S, McComb JG (2008) Visualization of cerebrospinal fluid movement with spin labeling at MR imaging: preliminary results in normal and pathophysiologic conditions. Radiology 249(2):644–652
Yamashita S, Isoda H, Hirano M, Takeda H, Inagawa S, Takehara Y, Alley MT, Markl M, Pelc NJ, Sakahara H (2007) Visualization of hemodynamics in intracranial arteries using time-resolved three-dimensional phase-contrast MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 25(3):473–478
Taoka T, Masutani Y, Kawai H, Nakane T, Matsuoka K, Yasuno F, Kishimoto T, Naganawa S (2017) Evaluation of glymphatic system activity with the diffusion MR technique: diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) in Alzheimer’s disease cases. Jpn J Radiol 35(4):172–178
Taoka T, Ito R, Nakamichi R, Kamagata K, Sakai M, Kawai H, Nakane T, Abe T, Ichikawa K, Kikuta J (2022) Reproducibility of diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) for evaluating interstitial fluid diffusivity and glymphatic function: CHanges in Alps index on Multiple conditiON acquIsition eXperiment (CHAMONIX) study. Jpn J Radiol 40(2):147–158
Zhang W, Zhou Y, Wang J, Gong X, Chen Z, Zhang X, Cai J, Chen S, Fang L, Sun J, Lou M (2021) Glymphatic clearance function in patients with cerebral small vessel disease. Neuroimage 238:118257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2021.118257
Taoka T, Ito R, Nakamichi R, Kamagata K, Sakai M, Kawai H, Nakane T, Abe T, Ichikawa K, Kikuta J, Aoki S, Naganawa S (2022) Reproducibility of diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) for evaluating interstitial fluid diffusivity and glymphatic function: CHanges in Alps index on Multiple conditiON acquIsition eXperiment (CHAMONIX) study. Jpn J Radiol 40(2):147–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-021-01187-5
Steward CE, Venkatraman VK, Lui E, Malpas CB, Ellis KA, Cyarto EV, Vivash L, O’Brien TJ, Velakoulis D, Ames D (2021) Assessment of the DTI-ALPS parameter along the perivascular space in older adults at risk of dementia. J Neuroimaging 31(3):569–578
Chen H-L, Chen P-C, Lu C-H, Tsai N-W, Yu C-C, Chou K-H, Lai Y-R, Taoka T, Lin W-C (2021) Associations among cognitive functions, plasma DNA, and diffusion tensor image along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/4034509
Lee H-J, Lee DA, Shin KJ, Park KM (2022) Glymphatic system dysfunction in obstructive sleep apnea evidenced by DTI-ALPS. Sleep Med 89:176–181
Bae YJ, Choi BS, Kim J-M, Choi J-H, Cho SJ, Kim JH (2021) Altered glymphatic system in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 82:56–60
Lee H-J, Lee DA, Shin KJ, Park KM (2021) Glymphatic system dysfunction in patients with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. J Neurol 269:2133–2139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-021-10799-w
Carotenuto A, Cacciaguerra L, Pagani E, Preziosa P, Filippi M, Rocca MA (2021) Glymphatic system impairment in multiple sclerosis: relation with brain damage and disability. Brain. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awab454
Betjemann JP, Lowenstein DH (2015) Status epilepticus in adults. Lancet Neurol 14(6):615–624
Trinka E, Kälviäinen R (2017) 25 years of advances in the definition, classification and treatment of status epilepticus. Seizure 44:65–73
Trinka E, Cock H, Hesdorffer D, Rossetti AO, Scheffer IE, Shinnar S, Shorvon S, Lowenstein DH (2015) A definition and classification of status epilepticus–Report of the ILAE Task Force on Classification of Status Epilepticus. Epilepsia 56(10):1515–1523
Trinka E, Höfler J, Zerbs A (2012) Causes of status epilepticus. Epilepsia 53:127–138
Vargas-Sánchez K, Mogilevskaya M, Rodríguez-Pérez J, Rubiano MG, Javela JJ, González-Reyes RE (2018) Astroglial role in the pathophysiology of status epilepticus: an overview. Oncotarget 9(42):26954
Hirsch LJ, Fong MW, Leitinger M, LaRoche SM, Beniczky S, Abend NS, Lee JW, Wusthoff CJ, Hahn CD, Westover MB (2021) American Clinical Neurophysiology Society’s standardized critical care EEG terminology: 2021 version. J Clin Neurophysiol 38(1):1
Cianfoni A, Caulo M, Cerase A, Della Marca G, Falcone C, Di Lella G, Gaudino S, Edwards J, Colosimo C (2013) Seizure-induced brain lesions: a wide spectrum of variably reversible MRI abnormalities. Eur J Radiol 82(11):1964–1972
Schilling KG, Yeh FC, Nath V, Hansen C, Williams O, Resnick S, Anderson AW, Landman BA (2019) A fiber coherence index for quality control of B-table orientation in diffusion MRI scans. Magn Reson Imaging 58:82–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2019.01.018
Jiang H, van Zijl PC, Kim J, Pearlson GD, Mori S (2006) DtiStudio: resource program for diffusion tensor computation and fiber bundle tracking. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 81(2):106–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2005.08.004
Heo CM, Lee WH, Park BS, Lee YJ, Park S, Kim YW, Lee DA, Yoo BC, Park KM (2021) Glymphatic dysfunction in patients with end-stage renal disease. Front Neurol 12:809438–809438
Lee DA, Park BS, Ko J, Park SH, Park JH, Kim IH, Lee YJ, Park KM (2022) Glymphatic system function in patients with newly diagnosed focal epilepsy. Brain Behav 12(3):e2504. https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.2504
Sutter R, Grize L, Fuhr P, Rüegg S, Marsch S (2013) Acute-phase proteins and mortality in status epilepticus: a 5-year observational cohort study. Crit Care Med 41(6):1526–1533
Seinfeld S, Goodkin HP, Shinnar S (2016) Status epilepticus. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 6(3):a022830
Janigro D, Walker MC (2014) What non-neuronal mechanisms should be studied to understand epileptic seizures? Issues in Clinical Epileptology: A View from the Bench:253–264
Robel S, Buckingham SC, Boni JL, Campbell SL, Danbolt NC, Riedemann T, Sutor B, Sontheimer H (2015) Reactive astrogliosis causes the development of spontaneous seizures. J Neurosci 35(8):3330–3345
Lee DJ, Hsu MS, Seldin MM, Arellano JL, Binder DK (2012) Decreased expression of the glial water channel aquaporin-4 in the intrahippocampal kainic acid model of epileptogenesis. Exp Neurol 235(1):246–255
Marchi N, Banjara M, Janigro D (2016) Blood–brain barrier, bulk flow, and interstitial clearance in epilepsy. J Neurosci Methods 260:118–124
Liu C, Habib T, Salimeen M, Pradhan A, Singh M, Wang M, Wu F, Zhang Y, Gao L, Yang G (2020) Quantification of visible Virchow-Robin spaces for detecting the functional status of the glymphatic system in children with newly diagnosed idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Seizure 78:12–17
Liu K, Zhu J, Chang Y, Lin Z, Shi Z, Li X, Chen X, Lin C, Pan S, Huang K (2021) Attenuation of cerebral edema facilitates recovery of glymphatic system function after status epilepticus. JCI Insight 6(17):e151835. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.151835
Lee DA, Park BS, Ko J, Park SH, Lee YJ, Kim IH, Park JH, Park KM (2022) Glymphatic system dysfunction in temporal lobe epilepsy patients with hippocampal sclerosis. Epilepsia Open 7(2):306–314
Salimeen MSA, Liu C, Li X, Wang M, Singh M, Si S, Li M, Cheng Y, Wang X, Zhao H (2021) Exploring variances of white matter integrity and the glymphatic system in simple febrile seizures and epilepsy. Front Neurol 12:595647. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2021.595647
Jessen NA, Munk ASF, Lundgaard I, Nedergaard M (2015) The glymphatic system: a beginner’s guide. Neurochem Res 40(12):2583–2599
Kress BT, Iliff JJ, Xia M, Wang M, Wei HS, Zeppenfeld D, Xie L, Kang H, Xu Q, Liew JA (2014) Impairment of paravascular clearance pathways in the aging brain. Ann Neurol 76(6):845–861
Christensen J, Yamakawa GR, Shultz SR, Mychasiuk R (2021) Is the glymphatic system the missing link between sleep impairments and neurological disorders? Examining the implications and uncertainties. Prog Neurobiol 198:101917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2020.101917
Lee DA, Lee HJ, Park KM (2022) Glymphatic dysfunction in isolated REM sleep behavior disorder. Acta Neurol Scand 145(4):464–470
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT of the Republic of Korea (NRF-2021R1F1A1049605).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, D.A., Lee, J. & Park, K.M. Glymphatic system impairment in patients with status epilepticus. Neuroradiology 64, 2335–2342 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-022-03018-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-022-03018-4