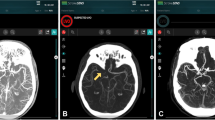
Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the diagnostic performance of AI software in diagnosing intracranial arterial occlusions in the proximal anterior circulation at CT angiography (CTA) and to compare it to manual reading performed in clinical practice.
Methods
Patients with acute ischemic stroke underwent CTA to detect arterial occlusion in the proximal anterior circulation. Retrospective review of CTA scans by two neuroradiologists served as reference standard. Sensitivity and specificity of AI software (StrokeViewer) were compared to those of manual reading using the McNemar test. The proportions of correctly detected occlusions in the distal internal carotid artery and/or M1 segment of the middle cerebral artery (large vessel occlusion [LVO]) and in the M2 segment of the middle cerebral artery (medium vessel occlusion [MeVO]) were calculated.
Results
Of the 474 patients, 75 (15.8%) had an arterial occlusion in the proximal anterior circulation according to the reference standard. Sensitivity of StrokeViewer software was not significantly different compared to that of manual reading (77.3% vs. 78.7%, P = 1.000). Specificity of StrokeViewer software was significantly lower than that of manual reading (88.5% vs. 100%, P < 0.001). StrokeViewer software correctly identified 40 of 42 LVOs (95.2%) and 18 of 33 MeVOs (54.5%). StrokeViewer software detected 8 of 16 (50%) intracranial arterial occlusions which were missed by manual reading.
Conclusion
The current AI software detected intracranial arterial occlusion with moderate sensitivity and fairly high specificity. The AI software may detect additional occlusions which are missed by manual reading. As such, the use of AI software may be of value in clinical stroke care.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berkhemer OA, Fransen PS, Beumer D, van den Berg LA, Lingsma HF, Yoo AJ, Schonewille WJ, Vos JA, Nederkoorn PJ, Wermer MJ, van Walderveen MA, Staals J, Hofmeijer J, van Oostayen JA, Lycklama à Nijeholt GJ, Boiten J, Brouwer PA, Emmer BJ, de Bruijn SF, van Dijk LC, Kappelle LJ, Lo RH, van Dijk EJ, de Vries J, de Kort PL, van Rooij WJ, van den Berg JS, van Hasselt BA, Aerden LA, Dallinga RJ, Visser MC, Bot JC, Vroomen PC, Eshghi O, Schreuder TH, Heijboer RJ, Keizer K, Tielbeek AV, den Hertog HM, Gerrits DG, van den Berg-Vos RM, Karas GB, Steyerberg EW, Flach HZ, Marquering HA, Sprengers ME, Jenniskens SF, Beenen LF, van den Berg R, Koudstaal PJ, van Zwam WH, Roos YB, van der Lugt A, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Majoie CB, Dippel DW (2015) A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 372:11–20
Goyal M, Demchuk AM, Menon BK, Eesa M, Rempel JL, Thornton J, Roy D, Jovin TG, Willinsky RA, Sapkota BL, Dowlatshahi D, Frei DF, Kamal NR, Montanera WJ, Poppe AY, Ryckborst KJ, Silver FL, Shuaib A, Tampieri D, Williams D, Bang OY, Baxter BW, Burns PA, Choe H, Heo JH, Holmstedt CA, Jankowitz B, Kelly M, Linares G, Mandzia JL, Shankar J, Sohn SI, Swartz RH, Barber PA, Coutts SB, Smith EE, Morrish WF, Weill A, Subramaniam S, Mitha AP, Wong JH, Lowerison MW, Sajobi TT, Hill MD, ESCAPE Trial Investigators (2015) Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 372:1019–1030
Fasen BACM, Heijboer RJJ, Hulsmans FH, Kwee RM (2021) Diagnostic performance of single-phase CT angiography in detecting large vessel occlusion in ischemic stroke: a systematic review. Eur J Radiol 134:109458
Fasen BACM, Heijboer RJJ, Hulsmans FH, Kwee RM (2020) CT angiography in evaluating large-vessel occlusion in acute anterior circulation ischemic stroke: factors associated with diagnostic error in clinical practice. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 41:607–611
Salehi L, Jaskolka J, Ossip M, Phalpher P, Valani R, Mercuri M. Utilization of CT angiography of the head and neck in the era of endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke: a retrospective study. Emerg Radiol, in press. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10140-021-02001-5
Fasen BACM, Heijboer RJJ, Hulsmans FH, Kwee RM (2020) Radiology workload in clinical implementation of thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke: experience from The Netherlands. Neuroradiology 62:877–882
van Leeuwen KG, Meijer FJA, Schalekamp S, Rutten MJCM, van Dijk EJ, van Ginneken B, Govers TM, de Rooij M (2021) Cost-effectiveness of artificial intelligence aided vessel occlusion detection in acute stroke: an early health technology assessment. Insights Imaging 12:133
Murray NM, Unberath M, Hager GD, Hui FK (2020) Artificial intelligence to diagnose ischemic stroke and identify large vessel occlusions: a systematic review. J Neurointervent Surg 12:156–164
Bossuyt PM, Reitsma JB, Bruns DE, Gatsonis CA, Glasziou PP, Irwig L, Lijmer JG, Moher D, Rennie D, de Vet HC, Kressel HY, Rifai N, Golub RM, Altman DG, Hooft L, Korevaar DA, Cohen JF, STARD Group (2015) STARD 2015: an updated list of essential items for reporting diagnostic accuracy studies. Radiology 277(826):832
Federaton of Medical Specialists, guideline cerebral infarction and cerenral hemorrhage. Available via https://richtlijnendatabase.nl/richtlijn/herseninfarct_en_hersenbloeding/startpagina_herseninfarct_-bloeding.html. Accessed 29 Jan 2022
Lima FO, Furie KL, Silva GS, Lev MH, Camargo EC, Singhal AB, Harris GJ, Halpern EF, Koroshetz WJ, Smith WS, Nogueira RG (2014) Prognosis of untreated strokes due to anterior circulation proximal intracranial arterial occlusions detected by use of computed tomography angiography. JAMA Neurol 71:151–157
Amukotuwa SA, Straka M, Dehkharghani S, Bammer R (2019) Fast automatic detection of large vessel occlusions on CT angiography. Stroke 50:3431–3438
Fifi JT, Meyers PM, Lavine SD, Cox V, Silverberg L, Mangla S, Pile-Spellman J (2009) Complications of modern diagnostic cerebral angiography in an academic medical center. J Vasc Interv Radiol 20:442–447
Dehkharghani S, Lansberg M, Venkatsubramanian C, Cereda C, Lima F, Coelho H, Rocha F, Qureshi A, Haerian H, Mont’Alverne F, Copeland K, Heit J (2021) High-performance automated anterior circulation CT angiographic clot detection in acute stroke: a multireader comparison. Radiology 298:665–670
Yahav-Dovrat A, Saban M, Merhav G, Lankri I, Abergel E, Eran A, Tanne D, Nogueira RG, Sivan-Hoffmann R (2021) Evaluation of artificial intelligence-powered identification of large-vessel occlusions in a comprehensive stroke center. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 42(2):247–254
Rodrigues G, Barreira CM, Bouslama M, Haussen DC, Al-Bayati A, Pisani L, Liberato B, Bhatt N, Frankel MR, Nogueira RG (2021) Automated large artery occlusion detection in stroke: a single-center validation study of an artificial intelligence algorithm. Cerebrovasc Dis 28:1–6
Rava RA, Peterson BA, Seymour SE, Snyder KV, Mokin M, Waqas M, Hoi Y, Davies JM, Levy EI, Siddiqui AH, Ionita CN (2021) Validation of an artificial intelligence-driven large vessel occlusion detection algorithm for acute ischemic stroke patients. Neuroradiol J 34:408–417
Becks MJ, Manniesing R, Vister J, Pegge SAH, Steens SCA, van Dijk EJ, Prokop M, Meijer FJA (2019) Brain CT perfusion improves intracranial vessel occlusion detection on CT angiography. J Neuroradiol 46:124–129
Klingebiel R, Kentenich M, Bauknecht HC, Masuhr F, Siebert E, Busch M, Bohner G (2008) Comparative evaluation of 64-slice CT angiography and digital subtraction angiography in assessing the cervicocranial vasculature. Vasc Health Risk Manag 4:901–907
Acknowledgements
We thank Razmara Nizak, Alex Puiu, and Merel Boers from NICO.LAB, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, for their technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
This retrospective study was approved by the institutional review board of our hospital (IRB number Z2019102) and patients’ consents were waived.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fasen, B.A.C.M., Berendsen, R.C.M. & Kwee, R.M. Artificial intelligence software for diagnosing intracranial arterial occlusion in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Neuroradiology 64, 1579–1583 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-022-02912-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-022-02912-1