Abstract
Purpose
Myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) is a muscular dystrophy with neurological, cognitive, and radiological abnormalities. The developmental or degenerative nature of these abnormalities, and their progression over time, remains unclear. The aim of this study is to perform a longitudinal assessment of imaging and cognitive performances in a group of patients with DM1.
Methods
A longitudinal observational study was conducted in a group of 33 DM1 patients. All patients underwent cognitive and MRI evaluation, including the use of structural and diffusion tensor imaging techniques, at baseline and follow-up evaluation (4 years). Longitudinal changes in white matter lesion (WML), volumetric analysis, and diffusivity values were assessed and correlated with neuropsychological test findings.
Results
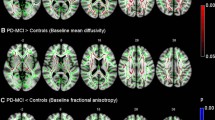
An increase in WML was observed in 16 patients (48.5%). An increase in ventricular system volume and a decrease in volume of the left thalamus, caudates, putamen, and hippocampus were observed (p < 0.001). Global cortical volume showed a significant decrease (p < 0.001), although no changes were observed in white matter volume. A significant increase in mean diffusivity and decrease in fractional anisotropy for the white matter were found (p < 0.001). Neuropsychological evaluation showed a significant deterioration in test performance that measures working memory (Letter-Number Sequencing, p = 0.049) and visuospatial skills (Benton Visual Retention Test, p = 0.001). These findings were significantly associated with WML load (working memory p = 0.002 and visuospatial skills p = 0.021) and mean diffusivity increase (visuospatial skills p = 0.003 in the corpus callosum and working memory p = 0.043 in the right cerebral white matter).
Conclusion
White matter and grey matter involvement in DM1 patients is progressive. Patients experience a worsening in cognitive impairment that correlates with white matter involvement. These findings support the neurodegenerative nature of this disease.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Itoh K, Mitani M, Kawamoto K, Futamura N, Funakawa I, Jinnai K, Fushiki S (2010) Neuropathology does not correlate with regional differences in the extent of expansion of CTG repeats in the brain with myotonic dystrophy type 1. Acta Histochem Cytochem 43:149–156
Jiang H, Mankodi A, Swanson MS, Moxley RT, Thornton CA (2004) Myotonic dystrophy type 1 is associated with nuclear foci of mutant RNA, sequestration of muscleblind proteins and deregulated alternative splicing in neurons. Hum Mol Genet 13:3079–3088
Meola G, Sansone V (2007) Cerebral involvement in myotonic dystrophies. Muscle Nerve 36:294–306
Meola G, Sansone V, Perani D, Scarone S, Cappa S, Dragoni C, Cattaneo E, Cotelli M, Gobbo C, Fazio F, Siciliano G, Mancuso M, Vitelli E, Zhang S, Krahe R, Moxley RT (2003) Executive dysfunction and avoidant personality trait in myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM-1) and in proximal myotonic myopathy (PROMM/DM-2). Neuromuscul Disord 13:813–821
Okkersen K, Buskes M, Groenewoud J, Kessels RPC, Knoop H, van Engelen B, Raaphorst J (2017) The cognitive profile of myotonic dystrophy type 1: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cortex 95:143–155
Weber YG, Roebling R, Kassubek J, Hoffmann S, Rosenbohm A, Wolf M, Steinbach P, Jurkat-Rott K, Walter H, Reske SN, Lehmann-Horn F, Mottaghy FM, Lerche H (2010) Comparative analysis of brain structure, metabolism and cognition in myotonic dystrophy 1 and 2. Neurology 74:1108–1117
Bajrami A, Azman F, Yayla V, Cagirici S, Keskinkiliç C, Sozer N (2017) MRI findings and cognitive functions in a small cohort of myotonic dystrophy type 1: retrospective analyses. Neuroradiol J 30:23–27
Censori B, Provinciali L, Danni M, Provinciali L (1994) Brain involvement in myotonic dystrophy: MRI features and their relationship to clinical and cognitive conditions. Acta Neurol Scand 90:211–217
Di Constanzo A, Di Salle F, Santoro L, Bonavita V, Tedeschi G (2002) Brain MRI features of congenital and adult form myotonic dystrophy type 1: case-control study. Neuromuscul Disord 12:476–483
Huber SJ, Kissel JT, Shuttleworth EC, Chakeres DW, Clapp LE, Brogan MA (1989) Magnetic resonance imaging and clinical correlates of intellectual impairment in myotonic dystrophy. Arch Neurol 46:536–540
Kornblum C, Reul J, Kress W, Grothe C, Amanatidis N, Klockgether T, Schröder R (2004) Cranial magnetic resonance imaging in genetically proven myotonic dystrophy type 1 and 2. J Neurol 251:710–714
Kuo HC, Hsieh YC, Wang HM, Chuang WL, Huang CC (2008) Correlation among subcortical white matter lesions, intelligence and CTG repeat expansion in classic myotonic dystrophy type 1. Acta Neurol Scand 117:101–107
Ogata A, Terae S, Fujita M, Tashiro K (1998) Anterior temporal white matter lesions in myotonic dystrophy with intellectual impairment: an MRI and neuropathological study. Neuroradiology 40:411–415
Romeo V, Pegoraro E, Ferrati C, Squarzanti F, Sorarù G, Palmieri A, Zucchetta P, Antunovic L, Bonifazi E, Novelli G, Trevisan CP, Ermani M, Manara R, Angelini C (2010) Brain involvement in myotonic dystrophies: neuroimaging and neuropsychological comparative study in DM1 and DM2. J Neurol 257:1246–1255
Baldanzi S, Cecchi P, Fabbri S, Pesaresi I, Simoncini C, Angelini C, Bonuccelli U, Cosottini M, Siciliano G (2016) Relationship between neuropsychological impairment and grey and white matter changes in adult-onset myotonic dystrophy type 1. Neuroimage Clin 12:190–197
Cabada T, Iridoy M, Jerico I, Lecumberri P, Seijas R, Gargallo A, Gomez M (2017) Brain involvement in myotonic dystrophy type 1: a morphometric and diffusion tensor imaging study with neuropsychological correlation. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 32:401–412
Caso F, Agosta F, Peric S, Rakocevic-Stojanovic V, Copetti M, Kostic VS, Filippi M (2014) Cognitive impairment in myotonic dystrophy type 1 is associated with white matter damage. PLOS ONE 9:e104697
Franc DT, Muetzel RL, Robinson PR, Rodriguez CP, Dalton JC, Naughton CE, Mueller BA, Wozniak JR, Lim KO, Day JW (2012) Cerebral and muscle MRI abnormalities in myotonic dystrophy. Neuromuscul Disord 22:483–491
Fukuda H, Horiguchi J, Ono C, Ohshita T, Takaba J, Ito K (2005) Diffusion tensor imaging of cerebral white matter in patients with myotonic dystrophy. Acta Radiol 46:643–650
Minnerop M, Weber B, Schoene-Bake JC, Roeske S, Mirbach S, Anspach C, Schneider-Gold C, Betz RC, Helmstaedter C, Tittgemeyer M, Klockgether T, Kornblum C (2011) The brain in myotonic dystrophy 1 and 2: evidence for a predominant white matter disease. Brain 134:3527–3543
Ota M, Sato N, Ohya Y, Aoki Y, Mizukami K, Mori T, Asada T (2006) Relationship between diffusion tensor imaging and brain morphology in patients with myotonic dystrophy. Neurosci Lett 407:234–239
Takaba J, Abe N, Fukuda H (2003) Evaluation of brain in myotonic dystrophy using diffusion tensor MR imaging. Nippon Hoshasen Gijutsu Gakkai Zasshi 59:831–838
van Dorst M, Okkersen K, Kessels RPC, Meijer FJA, Monckton DG, van Engelen BGM, Tuladhar AM, Raaphorst J, OPTIMISTIC consortium (2019) Structural white matter networks in myotonic dystrophy type 1. Neuroimage: Clin 21:101615
Wozniak JR, Mueller BA, Ward EE, Lim KO, Day JW (2011) White matter abnormalities and neurocognitive correlates in children and adolescents with myotonic dystrophy type 1: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Neuromuscul Disord 21:89–96
Wozniak JR, Mueller BA, Lim KO, Hemmy LS, Day JW (2014) Tractography reveals diffuse white matter abnormalities in myotonic dystrophy type 1. J Neurol Sci 341:43–78
Yoo WK, Park YG, Choi YC, Kim SM (2017) Cortical thickness and white matter integrity are associated with CTG expansion size in myotonic dystrophy type I. Yonsei Med J 58:807–815
Zanigni S, Evangelisti S, Giannoccaro MP, Oppi F, Poda R, Giorgio A, Testa C, Manners DN, Avoni P, Gramegna LL, De Stefano N, Lodi R, Tonon C, Liguori R (2016) Relationship of white and gray matter abnormalities to clinical and genetic features in myotonic dystrophy type 1. Neuroimage: Clin 11:678–685
Antonini G, Mainero C, Romano A, Giubilei F, Ceschin V, Gragnani F, Morino S, Fiorelli M, Soscia F, Di Pasquale A, Caramia F (2004) Cerebral atrophy in myotonic dystrophy: a voxel based morphometric study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:1611–1613
Giorgio A, Dotti MT, Battaglini M, Marino S, Mortilla M, Stromillo ML, Bramanti P, Orrico A, Federico A, De Stefano N (2006) Cortical damage in brains of patients with adult form of myotonic dystrophy type 1 and no or minimal MRI abnormalities. J Neurol 253:1471–1477
Schneider-Gold C, Bellenberg B, Prehn C, Krogias C, Schneider R, Klein J, Gold R, Lukas C (2015) Cortical and subcortical grey and white matter atrophy in myotonic dystrophies type 1 and 2 is associated with cognitive impairment, depression and daytime sleepiness. PLoS One 10(6):e0130352
van der Plas E, Hamilton MJ, Miller JN, Koscik TR, Long JD, Cumming S, Povilaikaite J, Farrugia ME, McLean J, Jampana R, Magnotta VA, Gutmann L, Monckton DG, Nopoulos PC (2019) Brain structural features of myotonic dystrophy type 1 and their relationship with CTG repeats. J Neuromusc Disord 6:321–332
Labayru G, Diez I, Sepulcre J, Fernandez E, Zulaica M, Cortes JM, Lopez de Muniain A, Sistiaga A (2019) Regional brain atrophy in gray and white matter is associated with cognitive impairment in myotonic dystrophy type 1. Neuroimage Clin 24:102078
Conforti R, de Cristofaro M, Cristofano A, Brogna B, Sardaro A, Tedeschi G, Cirillo S, Di Costanzo A (2016) Brain MRI abnormalities in the adult form of myotonic dystrophy type 1: a longitudinal case series study. Neuroradiol J 29:36–45
Gliem C, Minnerop M, Roeske S, Gärtner H, Schoene-Bake JC, Adler S, Witt JA, Hoffstaedter F, Schneider-Gold C, Betz RC, Helmstaedter C, Tittgemeyer M, Amunts K, Klockgether T, Weber B, Kornblum C (2019) Tracking the brain in myotonic dystrophies: a 5-year longitudinal follow-up study. PLoS One 14:e0213381
Gagnon C, Heatwole C, Hebert LJ, Hogrel JY, Laberge L, Leone M, Meola G, Richer L, Sansone V, Kierkegaard M (2018) Report of the third outcome measures in myotonic dystrophy type 1 (OMMYD-3) international workshop Paris, France, June 8, 2015. J Neuromusc Dis 5:523–537
Del Ser T, González-Montalvo JI, Martínez-Espinosa S, Delgado-Villapalos C, Bermejo F (1997) Estimation of premorbid intelligence in Spanish people with the word accentuation test and its application to the diagnosis of dementia. Brain Cogn 33:343–356
Tamayo F, Casals-Coll M, Sánchez-Benavides G, Quintana M, Manero RM, Rognoni T, Calvo L, Palomo R, Aranciva F, Peña-Casanova J et al (2012) Estudios normativos españoles en población adulta joven (Proyecto NEURONORMA jóvenes): normas para las pruebas span verbal, span visuoespacial, Letter-Number Sequencing, Trail Making Test y Symbol Digit Modalities Test. Neurologia 27:319–329
Benton A (2002) Test de Retención Visual, Manual. TEA Ediciones, Madrid
Schretlen D (1997) Brief test of attention professional manual. Psychological Assessment Resources, Odessa
Peña-Casanova J (2004) Programa Integrado de Exploración Neuropsicológica (PIEN) – Test Barcelona. Test-Barcelona Workstation, Barcelona
Benedet MJ, Alejandre MA (1998) Test de Aprendizaje verbal España-Complutense, Manual. TEA Ediciones, Madrid
Pedrero-Pérez EJ, Ruiz-Sánchez de León JM, Lozoya-Delgado P, Llanero-Luque M, Rojo-Mota G, Puerta-García C (2011) Evaluación de los síntomas prefrontales: Propiedades psicométricas y datos normativos del cuestionario disejecutivo (DEX) en una muestra de población Española. Rev Neurol 52:394–404
Robles A, Del Ser T, Alom J, Peña-Casanova J, Grupo Asesor del Grupo de Neurología de la Conducta y Demencias de la Sociedad Española de Neurología (2002) Propuesta de criterios para el diagnóstico clínico del deterioro cognitivo ligero, la demencia y la enfermedad de Alzheimer. Neurologia 17:17–32
Wahlund LO, Barkhof F, Fazekas F, Bronge L, Augustin M, Sjögren M, Wallin A, Ader H, Leys D, Pantoni L, Pasquier F, Erkinjuntti T, Scheltens P, European Task Force on Age-Related White Matter Changes (2001) A new rating scale for age-related white matter changes applicable to MRI and CT. Stroke 32:1318–1322
Reuter M, Schmansky NJ, Rosas HD, Fischl B (2012) Within-subject template estimation for unbiased longitudinal image analysis. Neuroimage 61:1402–1418
Reuter M, Fischl B (2011) Avoiding asymmetry-induced bias in longitudinal image processing. Neuroimage 57:19–21
Desikan RS, Segonne F, Fischl B, Quinn BT, Dickerson BC, Blacker D, Buckner RL, Dale AM, Maguire RP, Hyman BT, Albert MS, Killiany RJ (2006) An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuroimage 31:968–980
Yendiki A, Panneck P, Srinivasan P, Stevens A, Zöllei L, Augustinack J, Wang R, Salat D, Ehrlich S, Behrens T, Jbabdi S, Gollub R, Fischl B (2011) Automated probabilistic reconstruction of white-matter pathways in health and disease using an atlas of the underlying anatomy. Front Neuroinformat 5:23
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Woolrich MW, Beckmann CF, Behrens TE, Johansen-Berg H, Bannister PR, De Luca M, Drobnjak I, Flitney DE, Niazy RK, Saunders J, Vickers J, Zhang Y, De Stefano N, Brady JM, Matthews PM (2004) Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. Neuroimage 23:208–219
Buckner RL, Head D, Parker J, Fotenos AF, Marcus D, Morris JC, Snyder AZ (2004) A unified approach for morphometric and functional data analysis in young, old, and demented adults using automated atlas-based head size normalization: reliability and validation against manual measurement of total intracranial volume. NeuroImage 23:724–738
Bernal-Rusiel JL, Greve DN, Reuter M, Fischl B, Sabuncu MR (2013) Statistical analysis of longitudinal neuroimage data with linear mixed effects models. Neuroimage 66:249–260
Cohen JE (1988) Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc, Hillsdale
Okkersen K, Monckton DG, Le N, Tuladhar AM, Raaphorst J, van Engelen BGM (2017) Brain imaging in myotonic dystrophy type 1: a systematic review. Neurology 89:960–969
Minnerop M, Gliem C, Kornblum C (2018) Current progress in CNS imaging of myotonic dystrophy. Front Neurol 9:646
Winblad S, Samuelsson L, Lindberg C, Meola G (2016) Cognition in myotonic dystrophy type 1: a 5-year follow-up study. Eur J Neurol 23:1471–1476
Labayru G, Aliri J, Zulaica M, López de Munain A, Sistiaga A (2020) Age-related cognitive decline in myotonic dystrophy type 1: an 11-year longitudinal follow-up study. J Neuropsychol 14:121–134
Gallais B, Gagnon C, Mathieu J, Richer L (2017) Cognitive decline over time in adults with myotonic dystrophy type 1: a 9-year longitudinal study. Neuromuscul Disord 27:61–72
Sansone V, Gandossini S, Cotelli M, Calabria M, Zanetti O, Meola G (2007) Cognitive impairment in adult myotonic dystrophies: a longitudinal study. Neurol Sci 28:9–15
Modoni A, Silvestri G, Gabriella Vita M, Quaranta D, Tonali PA, Marra C (2008) Cognitive impairment in myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1). A longitudinal follow-up study. J Neurol 255:1737–1742
Angelini C, Pinzan E (2019) Advances in imaging of brain abnormalities in neuromuscular disease. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 12:1756286419845567
Serra L, Silvestri G, Petrucci A, Basile B, Masciullo M, Makovac E, Torso M, Spanò B, Mastropasqua C, Harrison NA, Bianchi ML, Giacanelli M, Caltagirone C, Cercignani M, Bozzali M (2014) Abnormal functional brain connectivity and personality traits in myotonic dystrophy type 1. JAMA Neurol 71:603–611
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from SERAM: 01_TCG_INVESTIGACIÓN_SERAM.INDUSTRIA_18.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This study was reviewed and approved by the local ethics committee.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
Patients signed informed consent regarding publishing their data.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cabada, T., Díaz, J., Iridoy, M. et al. Longitudinal study in patients with myotonic dystrophy type 1: correlation of brain MRI abnormalities with cognitive performances. Neuroradiology 63, 1019–1029 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-020-02611-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-020-02611-9