Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the usefulness of multiparametric quantitative MRI for myelination quantification in children.
Methods
We examined 22 children (age 0–14 years) with multiparametric quantitative MRI. The total volume of myelin partial volume (Msum), the percentage of Msum within the whole brain parenchyma (Mbpv), and the percentage of Msum within the intracranial volume (Micv) were obtained. Four developmental models of myelin maturation (the logarithmic, logistic, Gompertz, and modified Gompertz models) were examined to find the most representative model of the three parameters. We acquired myelin partial volume values in different brain regions and assessed the goodness of fit for the models.
Results
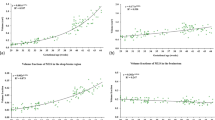
The ranges of Msum, Mbpv, and Micv were 0.8–160.9 ml, 0.2–13%, and 0.0–11.6%, respectively. The Gompertz model was the best fit for the three parameters. For developmental model analysis of myelin partial volume in each brain region, the Gompertz model was the best-fit model for pons (R 2 = 74.6%), middle cerebeller peduncle (R 2 = 76.4%), putamen (R2 = 95.8%), and centrum semiovale (R 2 = 77.7%). The logistic model was the best-fit model for the genu and splenium of the corpus callosum (R 2 = 79.7–93.6%), thalamus (R 2 = 81.7%), and frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital white matter (R 2 = 92.5–96.5%).
Conclusions
Multiparametric quantitative MRI depicts the normal developmental pattern of myelination in children. It is a potential tool for research studies on pediatric brain development evaluation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raine CS (1984) Morphology of myelin and myelination. In: Morell P (ed) Myelin, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, pp 1–50
Barkovich AJ (2000) Concepts of myelin and myelination in neuroradiology. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1099–1109
Johnson MH, Munakata Y (2005) Processes of change in brain and cognitive development. Trends Cogn Sci 9:152–158
Pujol J, Lopez-Sala A, Sebastian-Galles N, Deus J, Cardoner N, Soriano-Mas C, Moreno A, Sans A (2004) Delayed myelination in children with developmental delay detected by volumetric mri. NeuroImage 22:897–903
Courchesne E, Campbell K, Solso S (2011) Brain growth across the life span in autism: age-specific changes in anatomical pathology. Brain Res 1380:138–145
Grossman AW, Churchill JD, McKinney BC, Kodish IM, Otte SL, Greenough WT (2003) Experience effects on brain development: possible contributions to psychopathology. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 44:33–63
Wolff JJ, Gu H, Gerig G et al (2012) Differences in white matter fiber tract development present from 6 to 24 months in infants with autism. Am J Psychiatry 169:589–600
Penner MW, Li KC, Gebarski SS, Allen RJ (1987) MR imaging of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. J Comput Assist Tomogr 11:591–593
Holland BA, Haas DK, Norman D, Brant-Zawadzki M, Newton TH (1986) MRI of normal brain maturation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 7:201–208
Neil J, Miller J, Mukherjee P, Huppi PS (2002) Diffusion tensor imaging of normal and injured developing human brain—a technical review. NMR Biomed 15:543–552
Huppi PS, Dubois J (2006) Diffusion tensor imaging of brain development. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 11:489–497
Kucharczyk W, Macdonald PM, Stanisz GJ, Henkelman RM (1994) Relaxivity and magnetization transfer of white matter lipids at MR imaging: importance of cerebrosides and ph. Radiology 192:521–529
Zhang H, Kang H, Zhao X, Jiang S, Zhang Y, Zhou J, Peng Y (2016) Amide proton transfer (APT) MR imaging and magnetization transfer (MT) MR imaging of pediatric brain development. Eur Radiol 26:3368–3376
Xydis V, Astrakas L, Zikou A, Pantou K, Andronikou S, Argyropoulou MI (2006) Magnetization transfer ratio in the brain of preterm subjects: age-related changes during the first 2 years of life. Eur Radiol 16:215–220
Dean DC III, O'Muircheartaigh J, Dirks H, Waskiewicz N, Lehman K, Walker L, Han M, Deoni SC (2014) Modeling healthy male white matter and myelin development: 3 through 60months of age. NeuroImage 84:742–752
Du YP, Chu R, Hwang D, Brown MS, Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Singel D, Simon JH (2007) Fast multislice mapping of the myelin water fraction using multicompartment analysis of t2* decay at 3t: a preliminary postmortem study. Magn Reson Med 58:865–870
MacKay A, Whittall K, Adler J, Li D, Paty D, Graeb D (1994) In vivo visualization of myelin water in brain by magnetic resonance. Magn Reson Med 31:673–677
Deoni SC, Mercure E, Blasi A, Gasston D, Thomson A, Johnson M, Williams SC, Murphy DG (2011) Mapping infant brain myelination with magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosci 31:784–791
Hagiwara A, Hori M, Yokoyama K et al (2017) Utility of a multiparametric quantitative mri model that assesses myelin and edema for evaluating plaques, periplaque white matter, and normal-appearing white matter in patients with multiple sclerosis: a feasibility study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 38:237–242
Warntjes M, Engstrom M, Tisell A, Lundberg P (2016) Modeling the presence of myelin and edema in the brain based on multi-parametric quantitative MRI. Front Neurol 7:16
Hagiwara A, Warntjes M, Hori M, Andica C, Nakazawa M, Kumamaru KK, Abe O, Aoki S (2017) SyMRI of the brain: rapid quantification of relaxation rates and proton density, with synthetic MRI, automatic brain segmentation, and myelin measurement. Investig Radiol. doi:10.1097/RLI.0000000000000365
Warntjes JB, Leinhard OD, West J, Lundberg P (2008) Rapid magnetic resonance quantification on the brain: optimization for clinical usage. Magn Reson Med 60:320–329
Fabozzi FJ, Focardi SM, Rachev ST, Arshanapalli BG (2014) The basics of financial econometrics: tools, concepts, and asset management applications. Wiley, New Jersey
Gompertz B (1825) On the nature of the function expressive of the law of human mortality, and on a new mode of determining the value of life contingencies. Philos Trans R Soc Lond 115:513–583
Deoni SC, Dean DC III, O'Muircheartaigh J, Dirks H, Jerskey BA (2012) Investigating white matter development in infancy and early childhood using myelin water faction and relaxation time mapping. NeuroImage 63:1038–1053
Granberg T, Uppman M, Hashim F et al (2016) Clinical feasibility of synthetic mri in multiple sclerosis: a diagnostic and volumetric validation study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 37:1023–1029
West H, Leach JL, Jones BV, Care M, Radhakrishnan R, Merrow AC, Alvarado E, Serai SD (2017) Clinical validation of synthetic brain mri in children: initial experience. Neuroradiology 59:43–50
Dubois J, Dehaene-Lambertz G, Kulikova S, Poupon C, Huppi PS, Hertz-Pannier L (2014) The early development of brain white matter: a review of imaging studies in fetuses, newborns and infants. Neuroscience 276:48–71
Courchesne E, Chisum HJ, Townsend J, Cowles A, Covington J, Egaas B, Harwood M, Hinds S, Press GA (2000) Normal brain development and aging: quantitative analysis at in vivo MR imaging in healthy volunteers. Radiology 216:672–682
MacKay A, Laule C, Vavasour I, Bjarnason T, Kolind S, Madler B (2006) Insights into brain microstructure from the t2 distribution. Magn Reson Imaging 24:515–525
Bartzokis G, Lu PH, Tingus K et al (2010) Lifespan trajectory of myelin integrity and maximum motor speed. Neurobiol Aging 31:1554–1562
Glasser MF, Van Essen DC (2011) Mapping human cortical areas in vivo based on myelin content as revealed by t1- and t2-weighted mri. J Neurosci 31:11597–11616
O'Muircheartaigh J, Dean DC III, Dirks H, Waskiewicz N, Lehman K, Jerskey BA, Deoni SC (2013) Interactions between white matter asymmetry and language during neurodevelopment. J Neurosci 33:16170–16177
Levitt JJ, McCarley RW, Dickey CC et al (2002) MRI study of caudate nucleus volume and its cognitive correlates in neuroleptic-naive patients with schizotypal personality disorder. Am J Psychiatry 159:1190–1197
Ali N, Green DW, Kherif F, Devlin JT, Price CJ (2010) The role of the left head of caudate in suppressing irrelevant words. J Cogn Neurosci 22:2369–2386
Adamsbaum C, Pinton F, Rolland Y, Chiron C, Dulac O, Kalifa G (1996) Accelerated myelination in early Sturge-Weber syndrome: MRI-SPECT correlations. Pediatr Radiol 26:759–762
Andica C, Hagiwara A, Nakazawa M, Tsuruta K, Takano N, Hori M, Suzuki H, Sugano H, Arai H, Aoki S (2016) The advantage of synthetic MRI for the visualization of early white matter change in an infant with Sturge-Weber syndrome. Magn Reson Med Sci 15:347–348
van Buchem MA, Steens SC, Vrooman HA, Zwinderman AH, McGowan JC, Rassek M, Engelbrecht V (2001) Global estimation of myelination in the developing brain on the basis of magnetization transfer imaging: a preliminary study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:762–766
Hermoye L, Saint-Martin C, Cosnard G et al (2006) Pediatric diffusion tensor imaging: normal database and observation of the white matter maturation in early childhood. NeuroImage 29:493–504
Lee SM, Choi YH, Cheon JE et al (2017) Image quality at synthetic brain magnetic resonance imaging in children. Pediatr Radiol. doi:10.1007/s00247-017-3913-y
Acknowledgments
We thank Young Ju Lee and Sung-Min Gho of GE Healthcare Korea for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded in part by the National Research Foundation of Korea Grant funded by the Korean Government (2017R1D1A1B03034768).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Informed consent
For this type of retrospective study formal consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, H.G., Moon, WJ., Han, J. et al. Quantification of myelin in children using multiparametric quantitative MRI: a pilot study. Neuroradiology 59, 1043–1051 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-017-1889-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-017-1889-9