Abstract
Introduction
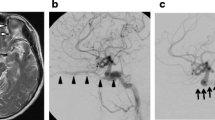
We evaluated the relationship between symptomatic and angiographic changes in untreated cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistulas (CSdAVFs), focusing on venous drainage patterns.
Methods
The clinical and radiologic features of 34 cases of untreated CSdAVF were retrospectively reviewed. We classified venous drainage patterns as type I (only antegrade drainage), type II (combined antegrade drainage and venous reflux), type III (venous reflux without antegrade drainage), or type IV (stasis or occlusion of venous reflux). Symptom changes were categorized as improvement, aggravation of initial symptoms, or symptom pattern change.
Results
Twenty-one patients (61 %) showed symptom changes during follow-up (median, 12; range, 3–151 months). In the symptom improvement group (n = 10), patients who underwent follow-up angiography (n = 4) exhibited spontaneous occlusion. In the symptom aggravation group (n = 4), new venous reflux developed in 2 patients (type I to type II) and spontaneous occlusion in 2 patients (type III to spontaneous occlusion). In the symptom pattern change group (n = 7), 2 patients showed new venous reflux (type I to type II), and 5 showed stasis or occlusion of an engorged ophthalmic vein (type II or III to type IV). Angiographic regression was observed in all type III and IV patients, and cortical venous reflux (CVR) developed in 1 type I patient.
Conclusion
Symptom changes correlated with chronological angiographic changes. Without treatment, most CSdAVFs behaved benignly and had a low incidence of CVR. Therefore, close observation is a possible protocol for managing CSdAVFs that have tolerable symptoms, no CVR, and no antegrade drainage despite aggravation or fluctuation in symptoms.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CSdAVF:
-
Cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula
- CVR:
-
Cortical venous reflux
- IPS:
-
Inferior petrosal sinus
- SPS:
-
Superior petrosal sinus
- OV:
-
Ophthalmic vein
References
Borden JA, Wu JK, Shucart WA (1995) A proposed classification for spinal and cranial dural arteriovenous fistulous malformations and implications for treatment. J Neurosurg 82:166–179
Cognard C, Gobin YP, Pierot L, Bailly AL, Houdart E, Casasco A, Chiras J, Merland JJ (1995) Cerebral dural arteriovenous fistulas: clinical and angiographic correlation with a revised classification of venous drainage. Radiology 194:671–680
Brown RD Jr, Wiebers DO, Nichols DA (1994) Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae: angiographic predictors of intracranial hemorrhage and clinical outcome in nonsurgical patients. J Neurosurg 81:531–538
Soderman M, Pavic L, Edner G, Holmin S, Andersson T (2008) Natural history of dural arteriovenous shunts. Stroke 39:1735–1739
van Dijk JM, terBrugge KG, Willinsky RA, Wallace MC (2002) Clinical course of cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas with long-term persistent cortical venous reflux. Stroke 33:1233–1236
Halbach VV, Higashida RT, Hieshima GB, Reicher M, Norman D, Newton TH (1987) Dural fistulas involving the cavernous sinus: results of treatment in 30 patients. Radiology 163:437–442
Suh DC, Lee JH, Kim SJ, Chung SJ, Choi CG, Kim HJ, Kim CJ, Kook M, Ahn HS, Kwon SU, Kim JS (2005) New concept in cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula: correlation with presenting symptom and venous drainage patterns. Stroke 36:1134–1139
Sasaki H, Nukui H, Kaneko M, Mitsuka S, Hosaka T, Kakizawa T, Kimura R, Nagaseki Y, Naganuma H (1988) Long-term observations in cases with spontaneous carotid-cavernous fistulas. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 90:117–120
Satomi J, Satoh K, Matsubara S, Nakajima N, Nagahiro S (2005) Angiographic changes in venous drainage of cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistulae after palliative transarterial embolization or observational management: a proposed stage classification. Neurosurgery 56:494–502, discussion 494–502
Satomi J, van Dijk JM, Terbrugge KG, Willinsky RA, Wallace MC (2002) Benign cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: outcome of conservative management based on the natural history of the lesion. J Neurosurg 97:767–770
Bujak M, Margolin E, Thompson A, Trobe JD (2010) Spontaneous resolution of two dural carotid-cavernous fistulas presenting with optic neuropathy and marked congestive ophthalmopathy. J Neuroophthalmol 30:222–227
Haugen OH, Sletteberg O, Thomassen L, Krakenes J (1990) Bilateral non-traumatic carotid cavernous sinus fistula with spontaneous closure. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 68:743–747
Pelofsky S, Fisher RG, Stough DR (1972) Carotid cavernous fistula with spontaneous closure of the internal carotid artery. J Trauma 12:1003–1004
Shields CB, Tutt HP (1981) Spontaneous obliteration of carotid-cavernous fistulas. South Med J 74:617–620
Voigt K, Sauer M, Dichgans J (1971) Spontaneous occlusion of a bilateral caroticocavernous fistula studied by serial angiography. Neuroradiology 2:207–211
Cognard C, Houdart E, Casasco A, Gabrillargues J, Chiras J, Merland JJ (1997) Long-term changes in intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae leading to worsening in the type of venous drainage. Neuroradiology 39:59–66
Endo S, Koshu K, Suzuki J (1979) Spontaneous regression of posterior fossa dural arteriovenous malformation. J Neurosurg 51:715–717
Landman JA, Braun IF (1985) Spontaneous closure of a dural arteriovenous fistula associated with acute hearing loss. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 6:448–449
Luciani A, Houdart E, Mounayer C, Saint Maurice JP, Merland JJ (2001) Spontaneous closure of dural arteriovenous fistulas: report of three cases and review of the literature. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:992–996
Awad IA, Little JR, Akarawi WP, Ahl J (1990) Intracranial dural arteriovenous malformations: factors predisposing to an aggressive neurological course. J Neurosurg 72:839–850
Chaudhary MY, Sachdev VP, Cho SH, Weitzner I Jr, Puljic S, Huang YP (1982) Dural arteriovenous malformation of the major venous sinuses: an acquired lesion. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 3:13–19
Kim DJ, terBrugge K, Krings T, Willinsky R, Wallace C (2010) Spontaneous angiographic conversion of intracranial dural arteriovenous shunt: long-term follow-up in nontreated patients. Stroke 41:1489–1494
Phelps CD, Thompson HS, Ossoinig KC (1982) The diagnosis and prognosis of atypical carotid-cavernous fistula (red-eyed shunt syndrome). Am J Ophthalmol 93:423–436
Theaudin M, Saint-Maurice JP, Chapot R, Vahedi K, Mazighi M, Vignal C, Saliou G, Stapf C, Bousser MG, Houdart E (2007) Diagnosis and treatment of dural carotid-cavernous fistulas: a consecutive series of 27 patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78:174–179
Sergott RC, Grossman RI, Savino PJ, Bosley TM, Schatz NJ (1987) The syndrome of paradoxical worsening of dural-cavernous sinus arteriovenous malformations. Ophthalmology 94:205–212
Seeger JF, Gabrielsen TO, Giannotta SL, Lotz PR (1980) Carotid-cavernous sinus fistulas and venous thrombosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:141–148
Hirai T, Korogi Y, Ikushima I, Shigematsu Y, Morishita S, Yamashita Y (2003) Usefulness of source images from three-dimensional time-of-flight MR angiography after treatment of cavernous dural arteriovenous fistulas. Radiat Med 21:205–209
Kwon BJ, Han MH, Kang HS, Chang KH (2005) MR imaging findings of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: relations with venous drainage patterns. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2500–2507
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
We declare that all human and animal studies have been approved by the Institutional Review Board of Samsung Medical Center (No. SMC 2015-02-103-001) and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. We declare that all patients gave informed consent prior to inclusion in this study.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, J.H., Jo, K.I., Kim, K.H. et al. Spontaneous angiographic changes in venous drainage patterns related to symptom changes in patients with untreated cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula. Neuroradiology 57, 1153–1161 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-015-1597-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-015-1597-2