Abstract
Introduction
This study aims to evaluate the impact of iron deposition during aging on the measurement of water diffusion in the brain.
Methods
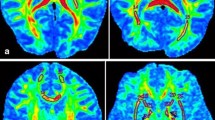
Diffusion tensor images (DTI) and phase images collected from a group of healthy adults from 23 to 72 years old were retrospectively analyzed. The axial diffusivity, radial diffusivity, mean diffusivity (MD), and fractional anisotropy (FA) in the frontal white matter and deep gray matter nuclei were calculated. The phase changes in these regions were used to estimate local iron concentration. Pearson correlation analysis was used to evaluate the age dependence of DTI metrics and iron concentration. Multiple linear regression models were then built to examine the independent effect of age and iron deposition on DTI metrics.
Results
Age-related iron deposition occurred in the putamen (r = 0.680, P < 0.001) and frontal white matter (r = 0.333, P = 0.007). In the putamen, FA increased with elevated iron concentration (P = 0.042) excluding the effect of age, and MD decreased with iron deposition with marginal statistical significance (P = 0.067). In the frontal white matter, increase in iron level was also associated with a decrease in MD and an increase in FA. Moreover, radial diffusivity was more reduced than axial diffusivity as local iron concentration increased.
Conclusion
Iron deposition in the brain during aging decreases water diffusion and increases the degree of anisotropy. Caution is needed when using DTI metrics for diagnosis of various neurological diseases involving abnormal iron deposition.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Le Bihan D, Mangin JF, Poupon C et al (2001) Diffusion tensor imaging: concepts and applications. J Magn Reson Imaging 13:534–546
Sundgren PC, Dong Q, Gómez-Hassan D, Mukherji SK, Maly P, Welsh R (2004) Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain: review of clinical applications. Neuroradiology 46:339–350
Sullivan EV, Pfefferbaum A (2006) Diffusion tensor imaging and aging. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 30:749–761
Sullivan EV, Pfefferbaum A (2007) Neuroradiological characterization of normal adult ageing. Br J Radiol 80:S99–S108
Song SK, Yoshino J, Le TQ et al (2005) Demyelination increases radial diffusivity in corpus callosum of mouse brain. NeuroImage 15(26):132–140
Bhagat YA, Beaulieu C (2004) Diffusion anisotropy in subcortical white matter and cortical gray matter: changes with aging and the role of CSF-suppression. J Magn Reson Imaging 20:216–227
Furutani K, Harada M, Minato M, Morita N, Nishitani H (2005) Regional changes of fractional anisotropy with normal aging using statistical parametric mapping (SPM). J Med Investig 52:186–190
Zhang YT, Zhang CY, Zhang J, Li W (2005) Age related changes of normal adult brain structure: analyzed with diffusion tensor imaging. Chin Med J 118:1059–1065
Abe O, Yamasue H, Aoki S et al (2008) Aging in the CNS: comparison of gray/white matter volume and diffusion tensor data. Neurobiol Aging 29:102–116
Pfefferbaum A, Adalsteinsson E, Rohlfing T, Sullivan EV (2010) Diffusion tensor imaging of deep gray matter brain structures: effects of age and iron concentration. Neurobiol Aging 31:482–493
Pal D, Trivedi R, Saksena S et al (2011) Quantification of age and gender related changes in diffusion tensor imaging indices in deep grey matter of the normal human brain. J Clin Neurosci 18:193–196
Wang Q, Xu X, Zhang M (2010) Normal aging in the basal ganglia evaluated by eigenvalues of diffusion tensor imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:516–520
Hallgren B, Sourander P (1958) The effect of age on the non-haemin iron in the human brain. J Neurochem 3:41–51
Schipper HM (2004) Brain iron deposition and the free radical-mitochondrial theory of ageing. Ageing Res Rev 3:265–301
Xu X, Wang Q, Zhang M (2008) Age, gender, and hemispheric differences in iron deposition in the human brain: an in vivo MRI study. NeuroImage 40:35–42
Awasthi R, Gupta RK, Trivedi R, Singh JK, Paliwal VK, Rathore RK (2010) Diffusion tensor MR imaging in children with pantothenate kinase associated neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation and their siblings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:442–447
Ling HW, Ding B, Wang H, Zhang H, Chen KM (2011) Could iron accumulation be a etiology of the white matter change in Alzheimer’s disease: using phase imaging to detect white matter iron deposition based on diffusion tensor imaging. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 31:300–308
Haacke EM, Muhammad A, Khan A et al (2007) Establishing a baseline phase behavior in magnetic resonance imaging to determine normal vs. abnormal iron content in the brain. J Magn Reson Imaging 26:256–264
Drayer B, Burger P, Darwin R, Riederer S, Herfkens R, Johnson GA (1986) MRI of brain iron. AJR Am J Roentgenol 147:103–110
Haacke EM, Cheng NY, House MJ et al (2005) Imaging iron stores in the brain using magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 23:1–25
Hong X, Dixon TW (1992) Measuring diffusion in inhomogeneous systems in imaging mode using antisymmetric sensitizing gradients. J Magn Reson 99:561–570
Zhong J, Gore JC (1991) Studies of restricted diffusion in heterogeneous media containing variations in susceptibility. Magn Reson Med 19:276–284
Zhong J, Kennan RP, Gore JC (1991) Effects of susceptibility variations on NMR measurement of diffusion. J Magn Reson 95:267–280
Dose MD, Zhong J, Gore JC (1999) In vivo measurement of ADC change due to intravascular susceptibility variation. Magn Reson Med 41:236–240
Trudeau JD, Thomas DW, Hawkins J (1995) The effect of inhomogenerous sample susceptibility on measured diffusion anisotropy using NMR imaging. J Magn Reson B 108:22–30
Beaulieu C, Allen PS (1996) An in vitro evaluation of the effects of local magnetic susceptibility induced gradients on anisotropic water diffusion in nerve. Magn Reson Med 36:39–44
Clark CA, Barker GJ, Tofts PS (1999) An in vivo evaluation of the effects of local magnetic susceptibility-induced gradients on water diffusion measurements in human brain. J Magn Reson 141:52–61
Liu C, Li W, Wu B, Jiang Y, Johnson GA (2012) 3D fiber tractography with susceptibility tensor imaging. NeuroImage 59:1290–1298
Li W, Wu B, Avram AV, Liu C (2012) Magnetic susceptibility anisotropy of human brain in vivo and its molecular underpinnings. NeuroImage 59:2088–2097
Pierpaoli C, Basser PJ (1996) Toward a quantitative assessment of diffusion anisotropy. Magn Reson Med 36:893–906
Anderson AW (2001) Theoretical analysis of the effects of noise on diffusion tensor imaging. Magn Reson Med 46:1174–1188
Haris M, Gupta RK, Husain N, Hasan KM, Husain M, Narayana PA (2006) Measurement of DTI metrics in hemorrhagic brain lesions: possible implication in MRI interpretation. J Magn Reson Imaging 24:1259–1268
Zecca L, Youdim MB, Riederer P, Cornor JR, Crichton RR (2004) Iron, brain ageing and neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:863–873
Yoshikawa K, Nakata Y, Yamada K, Nakagawa M (2004) Early pathological changes in the parkinsonian brain demonstrated by diffusion tensor MRI. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:481–484
Boska MD, Hasan KM, Kibuule D et al (2007) Quantitative diffusion tensor imaging detects dopaminergic neuronal degeneration in a murine model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 26:590–596
Vaillancourt DE, Spraker MB, Prodoehl J et al (2009) High-resolution diffusion tensor imaging in the substantia nigra of de novo Parkinson disease. Neurology 72:1378–1384
Kantarci K, Avula R, Senjem ML et al (2010) Dementia with Lewy bodies and Alzheimer disease: neurodegenerative patterns characterized by DTI. Neurology 74:1814–1821
Rossi C, Boss A, Martirosian P et al (2008) Influence of steady background gradients on the accuracy of molecular diffusion anisotropy measurements. Magn Reson Imaging 26:1250–1258
Zhu WZ, Zhong WD, Wang W et al (2009) Quantitative MR phase-corrected imaging to investigate increased brain iron deposition of patients with Alzheimer disease. Radiology 253:497–504
Zhang J, Zhang Y, Wang J et al (2010) Characterizing iron deposition in Parkinson’s disease using susceptibility-weighted imaging: an in vivo MR study. Brain Res 1330:124–130
Jin L, Wang J, Zhao L et al (2011) Decreased serum ceruloplasmin levels characteristically aggravate nigral iron deposition in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 134:50–58
Zivadinov R, Heininen-Brown M, Schirda CV et al (2012) Abnormal subcortical deep-gray matter susceptibility-weighted imaging filtered phase measurements in patients with multiple sclerosis: a case-control study. Neuroimage 59:331–339
Liu C, Li W, Tong KA et al (2015) Susceptibility-weighted imaging and quantitative susceptibility mapping in the brain. J Magn Reson Imaging 42:23–41
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key Technology R&D Program of China (2012BAI10B04), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81371519), the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LY12H18002), the Medical Scientific Research Foundation of Zhejiang Province (2009QN005), and the Educational Scientific Research Foundation of Zhejiang Province (Y200909841).
Ethical standards and patient consent
We declare that all human studies have been approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. We declare that all patients gave informed consent prior to inclusion in this study.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Wang, Q., Zhong, J. et al. Iron deposition influences the measurement of water diffusion tensor in the human brain: a combined analysis of diffusion and iron-induced phase changes. Neuroradiology 57, 1169–1178 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-015-1579-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-015-1579-4