Abstract
Introduction
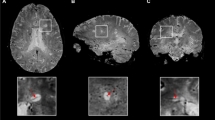
Lesion segmentation plays an important role in the diagnosis and follow-up of multiple sclerosis (MS). This task is very time-consuming and subject to intra- and inter-rater variability. In this paper, we present a new tool for automated MS lesion segmentation using T1w and fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) images.
Methods
Our approach is based on two main steps, initial brain tissue segmentation according to the gray matter (GM), white matter (WM), and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) performed in T1w images, followed by a second step where the lesions are segmented as outliers to the normal apparent GM brain tissue on the FLAIR image.
Results
The tool has been validated using data from more than 100 MS patients acquired with different scanners and at different magnetic field strengths. Quantitative evaluation provided a better performance in terms of precision while maintaining similar results on sensitivity and Dice similarity measures compared with those of other approaches.
Conclusion
Our tool is implemented as a publicly available SPM8/12 extension that can be used by both the medical and research communities.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2005) Unified segmentation. NeuroImage 26(3):839–851
Battaglini M, Rossi F, Grove RA, Stromillo ML, Whitcher B, Matthews PM, De Stefano N (2013) Automated identification of brain new lesions in multiple sclerosis using subtraction images. J Magn Reson Imaging
Boesen K, Rehm K, Schaper K, Stoltzner S, Woods R, Lüders E, Rottenberg D (2004) Quantitative comparison of four brain extraction algorithms. NeuroImage 22(3):1255–1261
Boyes RG, Gunter JL, Frost C, Janke AL, Yeatman T, Hill DL, Bernstein MA, Thompson PM, Weiner MW, Schuff N, Alexander GE, Killiany RJ, DeCarli C, Jack CR, Fox NC (2008) Intensity non-uniformity correction using N3 on 3-T scanners with multichannel phased array coils. NeuroImage 39(4):1752–1762
Cabezas M, Oliver A, Roura E, Freixenet J, Vilanova JC, Ramió-Torrentà L, Rovira À, Lladó X (2014) Automatic multiple sclerosis lesion detection in brain MRI by FLAIR thresholding. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 115(3):147–161
Cabezas M, Oliver A, Valverde S, Freixenet J, Beltran B, Vilanova JC, Ramió-Torrentà L, Rovira À, Lladó X (2014) BOOST: a supervised approach for multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation. J Neurosci Methods 237:108–117
Collignon A, Maes F, Delaere D, Vandermeulen D, Suetens P, Marchal G (1995) Automated multi-modality image registration based on information theory. In: Bizais
Diez Y, Oliver A, Cabezas M, Valverde S, Martí R, Vilanova J, Ramió-Torrentà L, Rovira A, Lladó X (2013) Intensity based methods for brain MRI longitudinal registration. A study on multiple sclerosis patients. Neuroinformatics pp 1–15
Ganiler O, Oliver A, Diez Y, Freixenet J, Vilanova J, Beltran B, Ramió-Torrentà L, Rovira A, Lladó X (2014) A subtraction pipeline for automatic detection of new appearing multiple sclerosis lesions in longitudinal studies. Neuroradiology pp 1–12
García-Lorenzo D, Prima S, Collins DL, Arnold L Douglas, Morrissey SP, Barillot C (2008) Combining robust expectation maximization and mean shift algorithms for multiple sclerosis brain segmentation. In: MICCAI workshop on Medical Image Analysis on Multiple Sclerosis (validation and methodological issues) (MIAMS’2008), New York, United States, pp 82–91
García-Lorenzo D, Lecoeur J, Arnold D, Collins D, Barillot C (2009) Multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation using an automatic multimodal graph cuts. Lect Notes Comput Sci 5762(PART 2):584–591
García-Lorenzo D, Francis S, Narayanan S, Arnold DL, Collins DL (2013) Review of automatic segmentation methods of multiple sclerosis white matter lesions on conventional magnetic resonance imaging. Med Image Anal 17(1):1–18
Geremia E, Clatz O, Menze BH, Konukoglu E, Criminisi A, Ayache N (2011) Spatial decision forests for MS lesion segmentation in multi-channel magnetic resonance images. NeuroImage 57(2):378–390
Lladó X, Oliver A, Cabezas M, Freixenet J, Vilanova JC, Quiles A, Valls L, Ramió-Torrentà L, Rovira A (2012) Segmentation of multiple sclerosis lesions in brain MRI: a review of automated approaches. Inf Sci 186(1):164–185
Love J (2006) Demyelinating diseases. J Clin Pathol 59(11):1151–1159
Mazziotta JC, Toga AW, Evans A, Fox P, Lancaster J (1995) A probabilistic atlas of the human brain: theory and rationale for its development. NeuroImage 2(2A):89–101
Perona P, Malik J (1990) Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion. Pattern Anal Mach Intell IEEE Trans 12(7):629–639
Polman CH, Reingold SC, Banwell B, Clanet M, Cohen JA, Filippi M, Fujihara K, Havrdova E, Hutchinson M, Kappos L, Lublin FD, Montalban X, O’Connor P, Sandberg-Wollheim M, Thompson AJ, Waubant E, Weinshenker B, Wolinsky JS (2011) Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 revisions to the McDonald criteria. Ann Neurol 69(2):292–302
Popescu V, Battaglini M, Hoogstrate W, Verfaillie S, Sluimer I, van Schijndel R, van Dijk B, Cover K, Knol D, Jenkinson M, Barkhof F, de Stefano N, Vrenken H (2012) Optimizing parameter choice for FSL-brain extraction tool (bet) on 3D T1 images in multiple sclerosis. NeuroImage 61(4):1484–1494
Pratt W (1 May 2014) Magnetic resonance in medicine. The basic textbook of the European magnetic resonance forum, 8th edn. Electronic version
Roura E, Oliver A, Cabezas M, Vilanova JC, Rovira A, Ramió-Torrentà L, Lladó X (2014) MARGA: multispectral adaptive region growing algorithm for brain extraction on axial MRI. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 113(2):655–673
Schmidt P, Gaser C, Arsic M, Buck D, Fẗorschler A, Berthele A, Hoshi M, Ilg R, Schmid VJ, Zimmer C, Hemmer B, Mühlau M (2012) An automated tool for detection of FLAIR-hyperintense white-matter lesions in multiple sclerosis. NeuroImage 59(4):3774–3783
Sha DD, Sutton JP (2001) Towards automated enhancement, segmentation and classification of digital brain images using networks of networks. Inf Sci 138(1–4):45–77
Shattuck DW, Sandor-Leahy SR, Schaper KA, Rottenberg DA, Leahy RM (2001) Magnetic resonance image tissue classification using a partial volume model. NeuroImage 13(5):856–876
Sled J, Zijdenbos A, Evans A (1998) A nonparametric method for automatic correction of intensity nonuniformity in MRI data. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 17(1):87–97
Smith SM (2002) Fast robust automated brain extraction. Hum Brain Mapp 17(3):143–155
Souplet JC, Lebrun C, Ayache N, Malandain G (2008) An automatic segmentation of T2-FLAIR multiple sclerosis lesions. In: Multiple Sclerosis Lesion Segmentation Challenge Workshop (MICCAI-2008), New York, NY, USA, United States, pp 1–8
Styner M, Lee J, Chin B, Chin M, Commowick O, Tran H, Jewells V, Warfield S (2008) Editorial: 3D segmentation in the clinic: a grand challenge II: MS lesion segmentation. In: Grand Challenge Workshop: Multiple Sclerosis Lesion Segmentation Challenge, pp 1–8
Sushmita D, Ponnada AN (2013) A comprehensive approach to the segmentation of multichannel three-dimensional MR brain images in multiple sclerosis. NeuroImage Clin 2:184–196
Valverde S, Oliver A, Cabezas M, Roura E, Lladó X (2014) Comparison of 10 brain tissue segmentation methods using revisited IBSR annotations. J Magn Reson Imaging 41(1):93–101
Weiss N, Rueckert D, Rao A (2013) Multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation using dictionary learning and sparse coding. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv MICCAI 8149:735–742
Zheng W, Chee MW, Zagorodnov V (2009) Improvement of brain segmentation accuracy by optimizing non-uniformity correction using N3. NeuroImage 48(1):73–83
Acknowledgments
E. Roura holds a BRUdG2013 grant. S. Valverde holds a FI-DGR2013 grant from the Generalitat de Catalunya. This work has been partially supported by “La Fundació la Marató de TV3” and by Retos de Investigación TIN2014-55710-R.
Ethical standards and patient consent
We declare that all human studies have been approved by the appropriate Ethics Committee and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. We declare that patient consent was waived due to the retrospective nature of this study.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roura, E., Oliver, A., Cabezas, M. et al. A toolbox for multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation. Neuroradiology 57, 1031–1043 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-015-1552-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-015-1552-2