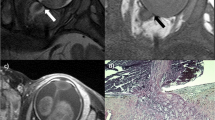
Abstract
Introduction
High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is recommended for the evaluation of metastatic risk factors in children with retinoblastoma according to recent guidelines. The aim of this study was to compare diagnostic accuracy of a new imaging concept with two orbit surface coils to that of an old imaging concept with one orbit surface coil.
Methods
One hundred forty-three patients (148 eyes, 64 girls, 79 boys) underwent high-resolution MRI on 1.5 T scanners using orbit surface coils. The old imaging concept (one orbit surface coil focusing on the (most) effected eye additionally to the standard head coil) was used in 100 patients/103 eye; the new imaging concept (two orbit surface coils (each focusing on one eye) additionally to the standard head coil) in 43 patients/45 eyes. Image analysis was performed by two neuroradiologists in consensus. Histopathology served as gold standard.
Results
Detection rate for choroidal invasion was higher for the new compared to that for the old imaging concept (sensitivity/specificity 87.5/94.6 % vs. 57.1/96.1 % for choroidal invasion and 100/97.5 % vs. 58.3/97.7 % for massive choroidal invasion, respectively). Sensitivity and specificity for the detection of postlaminar optic nerve infiltration, peribulbar fat, and scleral invasion were comparable in both imaging concepts; however positive predictive value was higher in the new imaging concept (new vs. old imaging concept: 60 vs. 31.6 % for postlaminar and deep postlaminar optic nerve infiltration, respectively, and 100 vs. 66.7 % for scleral invasion).
Conclusion
The new imaging concept shows a trend towards improving the accuracy of detecting metastatic risk factors in children with retinoblastoma and is therefore recommended for pretherapeutic imaging and follow-up.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Jong MC, de Graaf P, Noij DP, Goricke S, Maeder P, Galluzzi P, Brisse HJ, Moll AC, Castelijns JA, European Retinoblastoma Imaging Collaboration (ERIC) (2014) Diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography for advanced retinoblastoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology 121:1109–1118
Brisse HJ, de Graaf P, Galluzzi P et al (2014) Assessment of early-stage optic nerve invasion in retinoblastoma using high-resolution 1.5 Tesla MRI with surface coils: a multicentre, prospective accuracy study with histopathological correlation. Eur Radiol. doi:10.1007/s00330-014-3514-1
Chawla B, Sharma S, Sen S, Azad R, Bajaj MS, Kashyap S, Pushker N, Ghose S (2012) Correlation between clinical features, magnetic resonance imaging, and histopathologic findings in retinoblastoma: a prospective study. Ophthalmology 119:850–856
de Graaf P, Goricke S, Rodjan F, Galluzzi P, Maeder P, Castelijns JA, Brisse HJ, on behalf of the European Retinoblastoma Imaging Collaboration (ERIC) (2012) Guidelines for imaging retinoblastoma: imaging principles and MRI standardization. Pediatr Radiol 42:2–14
Khurana A, Eisenhut CA, Wan W, Ebrahimi KB, Patel C, O'Brien JM, Yeom K, Daldrup-Link HE (2012) Comparison of the diagnostic value of MR imaging and ophthalmoscopy for the staging of retinoblastoma. Eur Radiol 23:1271–1280
Rauschecker AM, Patel CV, Yeom KW, Eisenhut CA, Gawande RS, O'Brien JM, Ebrahimi KB, Daldrup-Link HE (2012) High-resolution MR imaging of the orbit in patients with retinoblastoma. Radiographics 32:1307–1326
Sirin S, Schlamann M, Metz KA, Bornfeld N, Schweiger B, Holdt M, Schuendeln MM, Lohbeck S, Krasny A, Goericke SL (2013) Diagnostic image quality of gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted MRI with and without fat saturation in children with retinoblastoma. Pediatr Radiol 43:716–724
Armenian SH, Panigrahy A, Murphree AL, Jubran RF (2008) Management of retinoblastoma with proximal optic nerve enhancement on MRI at diagnosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer 51:479–484
Narang S, Mashayekhi A, Rudich D, Shields CL (2012) Predictors of long-term visual outcome after chemoreduction for management of intraocular retinoblastoma. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 40:736–742
Rodriguez-Galindo C, Chantada GL, Haik BG, Wilson MW (2007) Treatment of retinoblastoma: current status and future perspectives. Curr Treat Options Neurol 9:294–307
Shields CL, Shields JA (2010) Retinoblastoma management: advances in enucleation, intravenous chemoreduction, and intra-arterial chemotherapy. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 21:203–212
Shields CL, Shields JA, Baez K, Cater JR, De Potter P (1994) Optic nerve invasion of retinoblastoma. Metastatic potential and clinical risk factors. Cancer 73:692–698
Chantada GL, Casco F, Fandino AC, Galli S, Manzitti J, Scopinaro M, Schvartzman E, de Davila MT (2007) Outcome of patients with retinoblastoma and postlaminar optic nerve invasion. Ophthalmology 114:2083–2089
Chantada GL, Dunkel IJ, Antoneli CB, de Davila MT, Arias V, Beaverson K, Fandino AC, Chojniak M, Abramson DH (2007) Risk factors for extraocular relapse following enucleation after failure of chemoreduction in retinoblastoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer 49:256–260
Uusitalo MS, Van Quill KR, Scott IU, Matthay KK, Murray TG, O'Brien JM (2001) Evaluation of chemoprophylaxis in patients with unilateral retinoblastoma with high-risk features on histopathologic examination. Arch Ophthalmol 119:41–48
Bosaleh A, Sampor C, Solernou V, Fandino A, Dominguez J, de Davila MT, Chantada GL (2012) Outcome of children with retinoblastoma and isolated choroidal invasion. Arch Ophthalmol 130:724–729
Brisse HJ, Guesmi M, Aerts I et al (2007) Relevance of CT and MRI in retinoblastoma for the diagnosis of postlaminar invasion with normal-size optic nerve: a retrospective study of 150 patients with histological comparison. Pediatr Radiol 37:649–656
Wilson MW, Rodriguez-Galindo C, Billups C, Haik BG, Laningham F, Patay Z (2009) Lack of correlation between the histologic and magnetic resonance imaging results of optic nerve involvement in eyes primarily enucleated for retinoblastoma. Ophthalmology 116:1558–1563
de Graaf P, Barkhof F, Moll AC, Imhof SM, Knol DL, van der Valk P, Castelijns JA (2005) Retinoblastoma: MR imaging parameters in detection of tumor extent. Radiology 235:197–207
Song KD, Eo H, Kim JH, Yoo SY, Jeon TY (2012) Can preoperative MR imaging predict optic nerve invasion of retinoblastoma? Eur J Radiol 81:4041–4045
Lee BJ, Kim JH, Kim DH, Park SH, Yu YS (2012) The validity of routine brain MRI in detecting post-laminar optic nerve involvement in retinoblastoma. Br J Ophthalmol 96:1237–1241
Lemke AJ, Kazi I, Mergner U et al (2007) Retinoblastoma—MR appearance using a surface coil in comparison with histopathological results. Eur Radiol 17:49–60
Schueler AO, Hosten N, Bechrakis NE, Lemke AJ, Foerster P, Felix R, Foerster MH, Bornfeld N (2003) High resolution magnetic resonance imaging of retinoblastoma. Br J Ophthalmol 87:330–335
Linn Murphree A (2005) Intraocular retinoblastoma: the case for a new group classification. Ophthalmol Clin N Am 18:41–53
Shields CL, Mashayekhi A, Au AK, Czyz C, Leahey A, Meadows AT, Shields JA (2006) The International Classification of Retinoblastoma predicts chemoreduction success. Ophthalmology 113:2276–2280
Lee V, Hungerford JL, Bunce C, Ahmed F, Kingston JE, Plowman PN (2003) Globe conserving treatment of the only eye in bilateral retinoblastoma. Br J Ophthalmol 87:1374–1380
Shields CL, Shields JA (2004) Diagnosis and management of retinoblastoma. Cancer Control 11:317–327
Ethical standards and patient consent
We declare that all human and animal studies have been approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of Duisburg-Essen and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. We declare that all patients gave informed consent prior to inclusion in this study.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sirin, S., Schlamann, M., Metz, K.A. et al. High-resolution MRI using orbit surface coils for the evaluation of metastatic risk factors in 143 children with retinoblastoma. Neuroradiology 57, 815–824 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-015-1538-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-015-1538-0