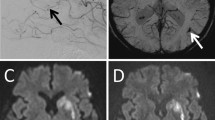
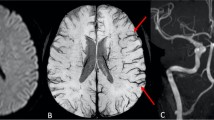
Abstract
Introduction
Microembolic signal (MES) monitoring with transcranial Doppler ultrasonography (TCD) may allow for early prediction of thromboembolisms following endovascular coiling of unruptured intracranial aneurysms (UIAs). However, the method has not gained widespread use and may benefit from correlation with diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) of acute ischemic lesions after coiling. This purposed to evaluate the relationship between MESs and DWI-positive lesions more precisely.
Methods
We conducted a prospective study on 45 consecutive patients. TCD was performed over the artery that is dependent on the site of aneurysm, but seven patients (15.6 %) could not be examined due to the lack of an adequate cranial window. Consequently, 38 patients were available to detect MESs immediately (MES-1) and 24 h (MES-2) after coiling for UIAs. We also checked DWI 1 day after the coiling and analyzed correlations between the TCD and DWI findings.
Results
MES-1 and MES-2 were positive in 25 (65.7 %) and 14 (36.8 %) patients, respectively. DWI-positive lesions were seen in 20 (52.6 %) patients, and only 1 (2.6 %) patient was symptomatic. MES-1 and MES-2 were strongly correlated with the number of DWI-positive lesions (Spearman’s correlation coefficient = 0.79 and 0.70, P < 0.01 and P < 0.01, respectively). Additionally, there was a significant correlation between MES-1 and MES-2 (Spearman’s correlation coefficient = 0.70).
Conclusion
Based upon the significant correlation between MES and DWI findings, MES may have a role for early detection of ischemic complications after coiling of UIAs. In addition, future study for further validation with clinical application seems requiring.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jo KI, Yeon JY, Kim KH et al (2013) Predictors of thromboembolism during coil embolization in patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysm. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 155:1101–1106
Klotzsch C, Nahser HC, Henkes H et al (1998) Detection of microemboli distal to cerebral aneurysms before and after therapeutic embolization. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1315–1318
Rordorf G, Bellon RJ, Budzik RE Jr et al (2001) Silent thromboembolic events associated with the treatment of unruptured cerebral aneurysms by use of Guglielmi detachable coils: prospective study applying diffusion-weighted imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:5–10
Spelle L, Pierot L (2008) Endovascular treatment of non-ruptured intracranial aneurysms: critical analysis of the literature. J Neuroradiol 35:116–120
Droste DW, Ritter M, Kemeny V et al (2000) Microembolus detections at follow-up in 19 patients with acute stroke: correlation with stroke etiology and antithrombotic treatment. Cerebrovasc Dis 10:272–277
Kimura K, Minematsu K, Koga M et al (2001) Microembolic signals and diffusion-weighted MR imaging abnormalities in acute ischemic stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1037–1042
Gass A, Ay H, Szabo K, Koroshetz WJ (2004) Diffusion-weighted MRI for the “small stuff”: the details of acute cerebral ischaemia. Lancet Neurol 3:39–45
Sarkar S, Ghosh S, Ghosh SK, Collier A (2007) Role of transcranial doppler ultrasonography in stroke. Postgrad Med J 83:683–689
King A, Markus HS (2009) Doppler embolic signals in cerebrovascular disease and prediction of stroke risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke 40:3711–3717
Schubert GA, Thome C, Seiz M, Douville C, Eskridge J (2011) Microembolic signal monitoring after coiling of unruptured cerebral aneurysms: an observational analysis of 123 cases. AJNR. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:1386–1391
Roy D, Milot G, Raymond J (2001) Endovascular treatment of unruptured aneurysms. Stroke 32:1998–2004
Alexandrov AV, Demchuk AM, Burgin WS (2002) Insonation method and diagnostic flow signatures for transcranial power motion (M-mode) doppler. J Neuroimaging 12:236–244
Sorensen AG, Buonanno FS, Gonzalez RG et al (1996) Hyperacute stroke: evaluation with combined multisection diffusion-weighted and hemodynamically weighted echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology 199:391–401
Adams HP, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ et al (1993) Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in acute stroke treatment. Stroke 24:35–41
Kang DH, Kim BM, Kim DJ et al (2013) MR-DWI-positive lesions and symptomatic ischemic complications after coiling of unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Stroke 44:789–791
Friendly M (2002) Corrgrams: exploratory displays for correlation matrices. Am Stat 56:316–324
Casasco AE, Aymard A, Gobin YP et al (1993) Selective endovascular treatment of 71 intracranial aneurysms with platinum coils. J Neurosurg 79:3–10
Graves VB, Strother CM, Rappe AH (1993) Treatment of experimental canine carotid aneurysms with platinum coils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 14:787–793
Nichols DA, Brown RD Jr, Thielen KR et al (1997) Endovascular treatment of ruptured posterior circulation aneurysms using electrolytically detachable coils. J Neurosurg 87:374–380
Martin D, Rodesch G, Alvarez H, Lasjaunias P (1996) Preliminary results of embolisation of nonsurgical intracranial aneurysms with GD coils: the 1st year of their use. Neuroradiology 38:S142–S150
Vinuela F, Duckwiler G, Mawad M (1997) Guglielmi detachable coil embolization of acute intracranial aneurysm: perioperative anatomical and clinical outcome in 403 patients. J Neurosurg 86:475–482
Markus HS, King A, Shipley M et al (2010) Asymptomatic embolisation for prediction of stroke in the asymptomatic carotid emboli study (ACES): a prospective observational study. Lancet Neurol 9:663–671
Wolf O, Heider P, Heinz M et al (2004) Microembolic signals detected by transcranial doppler sonography during carotid endarterectomy and correlation with serial diffusion-weighted imaging. Stroke 35:e373–e375
Valton L, Larrue V, le Traon AP, Massabuau P, Geraud G (1998) Microembolic signals and risk of early recurrence in patients with stroke or transient ischemic attack. Stroke 29:2125–2128
Forteza AM, Babikian VL, Hyde C, Winter M, Pochay V (1996) Effect of time and cerebrovascular symptoms of the prevalence of microembolic signals in patients with cervical carotid stenosis. Stroke 27:687–690
Chung SW, Baik SK, Kim Y, Park J (2008) Thromboembolic events after coil embolization of cerebral aneurysms: prospective study with diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging follow-up. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 43:275–280
Soeda A, Sakai N, Sakai H et al (2003) Thromboembolic events associated with guglielmi detachable coil embolization of asymptomatic cerebral aneurysms: evaluation of 66 consecutive cases with use of diffusion-weighted MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:127–132
Koebbe CJ, Horowitz MB, Levy EI et al (2002) Intraarterial thrombolysis for thromboemboli associated with endovascular aneurysm coiling. Report of five cases. Interv Neuroradiol 8:151–158
Markus HS, Droste DW, Kaps M et al (2005) Dual antiplatelet therapy with clopidogrel and aspirin in symptomatic carotid stenosis evaluated using doppler embolic signal detection: the clopidogrel and aspirin for reduction of emboli in symptomatic carotid stenosis (CARESS) trial. Circulation 111:2233–2240
Ringelstein EB, Droste DW, Babikian VL et al (1998) Consensus on microembolus detection by TCD. Int Consens Group Microembolus Detect Stroke 29:725–729
Markus H (1993) Transcranial doppler detection of circulating cerebral emboli. A review. Stroke 24:1246–1250
Ringelstein EB (2004) Clinical relevance of microembolus detection. Klin Neurophysiol. doi:10.1055/s-2004-832140
Acknowledgments
We thank Wade Martin of Medical Research International for editorial revision of this manuscript.
Ethical standards and patient consent
We declare that all human and animal studies have been approved by the Kyungpook National University Hospital Institutional Review Board and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. We declare that all patients gave informed consent prior to inclusion in this study.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, JH., Kang, DH., Kim, YW. et al. Microembolic signal monitoring and the prediction of thromboembolic events following coil embolization of unruptured intracranial aneurysms: diffusion-weighted imaging correlation. Neuroradiology 57, 189–196 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-014-1451-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-014-1451-y