Abstract
Introduction
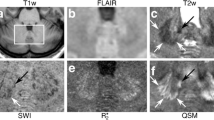
Adult-onset ADLD with autonomic symptoms is a rare disease with a clinical course somewhat similar to chronic progressive MS but with different imaging findings consisting of extensive white matter changes in the cerebrum and cerebellar peduncles. Patients usually present in the fourth to sixth decade with autonomic symptoms, manifesting later symptoms from the pyramidal tracts and ataxia. Here, we present magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) findings in this disease.
Methods
Fourteen subjects, from two non-related families, with genetic linkage to the disease were studied with magnetic resonance imaging and single-voxel MRS. Clinically, they ranged from asymptomatic to wheelchair-using. Their results were compared to those of age- and sex-matched healthy controls.
Results
One MRS was excluded due to suboptimal quality. The remaining 13 subjects manifested characteristic evidence of pathology on MRI, 11 of them exhibited extensive changes. The metabolite concentrations of total Cr, total Cho, and total NAA measured in millimolars, using internal water as a reference, were significantly lower in these 11 subjects compared to controls, and we found linear correlations between all these metabolite levels. When total Cr was used as a reference, we found no difference between subjects and controls. No lactate was detected.
Conclusion
The decreased metabolite concentrations measured using internal water as a reference are most likely due to increased water content in the tissues, diluting all metabolites to a similar degree. This is also in agreement with the high signal intensity exhibited in the white matter on T2-weighted MR images and with the reported histopathological findings of vacuolated myelin.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man, OMIM (TM) (2011) McKusick-Nathans Institute of Genetic Medicine, Johns Hopkins University and National Center for Biotechnology Information, National Library of Medicine. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/
Melberg A, Hallberg L, Kalimo H, Raininko R (2006) MR characteristics and neuropathology in adult-onset autosomal dominant leukodystrophy with autonomic symptoms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:904–911
Eldridge R, Anayiotos CP, Schlesinger S, Cowen D, Bever C, Patronas N, McFarland H (1984) Hereditary adult-onset leukodystrophy simulating chronic progressive multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 311:948–953
Padiath QS, Saigoh K, Schiffmann R, Asahara H, Yamada T, Koeppen A, Hogan K, Ptácek LJ, Fu Y-H (2006) Lamin B1 duplications cause autosomal dominant leukodystrophy. Nat Genet 38:1114–1123
Brussino A, Vaula G, Cagnoli C, Mauro A, Pradotto L, Daniele D, Di Gregorio E, Barberis M, Arduino C et al (2009) A novel family with Lamin B1 duplication associated with adult-onset leucoencephalopathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 80:237–240
Dos Santos MM, Grond-Ginsbach C, Aksay SS, Chen B, Tchatchou S, Wolf NI, van der Knaap MS, Grau AJ (2011) Adult-onset autosomal dominant leukodystrophy due to LMNB1 gene duplication. J Neurol 259:579–581
Fogel BL, Lee JY, Lane J, Wahnich A, Chan S, Huang A, Osborn GE, Klein E, Mamah C et al (2012) Mutations in rare ataxia genes are uncommon causes of sporadic cerebellar ataxia. Mov Disord 27:442–446
Meijer IA, Simoes-Lopes AA, Laurent S, Katz T, St-Onge J, Verlaan DJ, Dupré N, Thibault M, Mathurin J, Bouchard JP, Rouleau GA (2008) A novel duplication confirms the involvement of 5q23.2 in autosomal dominant leukodystrophy. Arch Neurol 65:1496–1501
Schuster J, Sundblom J, Thuresson A-C, Hassin-Baer S, Klopstock T, Dichgans M, Cohen OS, Raininko R, Melberg A, Dahl N (2011) Genomic duplications mediate overexpression of lamin B1 in adult-onset autosomal dominant leukodystrophy (ADLD) with autonomic symptoms. Neurogenetics 12:65–72
Lin S-T, Fu Y-H (2009) miR-23 regulation of lamin B1 is crucial for oligodendrocyte development and myelination. Dis Model Mech 2:178–188
Sundblom J, Melberg A, Kalimo H, Smits A, Raininko R (2009) MR imaging characteristics and neuropathology of the spinal cord in adult-onset autosomal dominant leukodystrophy with autonomic symptoms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:328–335
Coffeen CM, McKenna CE, Koeppen AH, Plaster NM, Maragakis N, Mihalopoulos J, Schwankhaus JD, Flanigan KM, Gregg RG, Ptácek LJ, Fu YH (2000) Genetic localization of an autosomal dominant leukodystrophy mimicking chronic progressive multiple sclerosis to chromosome 5q31. Hum Mol Genet 9:787–793
Schwankhaus JD, Katz DA, Eldridge R, Schlesinger S, McFarland H (1994) Clinical and pathological features of an autosomal dominant, adult-onset leukodystrophy simulating chronic progressive multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 51:757–766
Padiath QS, Fu Y-H (2010) Autosomal dominant leukodystrophy caused by lamin B1 duplications a clinical and molecular case study of altered nuclear function and disease. Methods Cell Biol 98:337–357
van der Voorn JP, Pouwels PJW, Hart AAM, Serrarens J, Willemsen MAAP, Kremer HPH, Barkhof F, van der Knaap MS (2006) Childhood white matter disorders: quantitative MR imaging and spectroscopy. Radiology 241:510–517
Bizzi A, Castelli G, Bugiani M, Barker PB, Herskovits EH, Danesi U, Erbetta A, Moroni I, Farina L, Uziel G (2008) Classification of childhood white matter disorders using proton MR spectroscopic imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:1270–1275
Marklund L, Melin M, Melberg A, Giedraitis V, Dahl N (2006) Adult-onset autosomal dominant leukodystrophy with autonomic symptoms restricted to 1.5 Mbp on chromosome 5q23. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 141B:608–614
R Development Core Team (2010) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org/
Brockmann K, Dechent P, Wilken B, Rusch O, Frahm J, Hanefeld F (2003) Proton MRS profile of cerebral metabolic abnormalities in Krabbe disease. Neurology 60:819–825
Wang C, Melberg A, Weis J, Månsson J-E, Raininko R (2007) The earliest MR imaging and proton MR spectroscopy abnormalities in adult-onset Krabbe disease. Acta Neurol Scand 116:268–272
Farina L, Bizzi A, Finocchiaro G, Pareyson D, Sghirlanzoni A, Bertagnolio B, Savoiardo M, Naidu S, Singhal BS, Wenger DA (2000) MR imaging and proton MR spectroscopy in adult Krabbe disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1478–1482
Brockmann K, Dechent P, Meins M, Haupt M, Sperner J, Stephani U, Frahm J, Hanefeld F (2003) Cerebral proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in infantile Alexander disease. J Neurol 250:300–306
Janson CG, McPhee SWJ, Francis J, Shera D, Assadi M, Freese A, Hurh P, Haselgrove J, Wang DJ, Bilaniuk L, Leone P (2006) Natural history of Canavan disease revealed by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) and diffusion-weighted MRI. Neuropediatrics 37:209–221
Sohn S-Y, Ko Y-J, Hong JM, Kim S-H, Kim H-S, Kim J-H, Chi J-G, Moon SY (2010) A case of pigmentary orthochromatic leukodystrophy with findings of proton MR spectroscopy and serial brain MRIs. J Neurol Sci 295:23–26
Marshall I, Wardlaw J, Cannon J, Slattery J, Sellar RJ (1996) Reproducibility of metabolite peak areas in 1H MRS of brain. J Magn Reson Imaging 14:281–292
Simmons A, Smail M, Moore E, Williams SC (1998) Serial precision of metabolite peak area ratios and water referenced metabolite peak areas in proton MR spectroscopy of the human brain. J Magn Reson Imaging 16:319–330
Chard DT, McLean MA, Parker GJM, MacManus DG, Miller DH (2002) Reproducibility of in vivo metabolite quantification with proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 15:219–225
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the Ländell Foundation, Selander Foundation, Hedberg Foundation for Medical Research and the Swedish Medical Research Council Grant 73X-13158.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Finnsson, J., Melberg, A. & Raininko, R. 1H-MR spectroscopy of adult-onset autosomal dominant leukodystrophy with autonomic symptoms. Neuroradiology 55, 933–939 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-013-1174-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-013-1174-5