Abstract
Introduction
According to the most recent definition of transient ischemic attack (TIA) and the recommendations of the American Heart Association, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) including diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is considered a mandatory tool in evaluating and treating patients with TIA. This study aims to determine the incidence of TIA-related acute infarction, identify the independent predictors of acute infarction, and investigate the correlation between acute infarction detected by DWI-MRI and stroke risk during hospitalization.
Methods
Over a 36-month period (starting November 2007), all TIA patients (symptom duration of <24 h) who were admitted to hospital within 48 h of symptom onset and who underwent DWI-MRI were included in this population-based prospective study. The incidence of acute infarction, clinical predictors, and association with stroke recurrence during hospitalization were studied.
Results
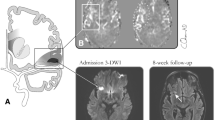
Of 1,910 patients (mean age, 66.7 ± 13 years; 46 % women), 1,862 met the inclusion criteria. A TIA-related acute infarction was detected in 206 patients (11.1 %). Several independent predictors were identified with logistic regression analysis: motor weakness [odds ratio (OR), 1.5], aphasia (OR, 1.6), National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score of ≥10 at admission (OR, 3.2), and hyperlipidemia (OR, 0.6). Of 24 patients (1.3 %) who suffered a stroke during hospitalization (mean, 6 ± 4 days), five had positive DWI. Stroke rate during hospitalization was nonsignificantly higher in patients with positive DWI than those with negative DWI (2.4 vs 1.1 %, respectively; P = 0.12).
Conclusion
The evidence of acute infarction by DWI-MRI in TIA patients was detected in 11.1 % of patients and associated with motor weakness, aphasia, and NIHSS score of ≥10 at admission.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giles MF, Rothwell PM (2007) Risk of stroke early after transient ischaemic attack: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol 6:1063–1072
Johnston SC, Gress DR, Browner WS, Sidney S (2000) Short-term prognosis after emergency department diagnosis of TIA. JAMA 284:2901–2906
Hill MD, Yiannakoulias N, Jeerakathil T, Tu JV, Svenson LW, Schopflocher DP (2004) The high risk of stroke immediately after transient ischemic attack: a population-based study. Neurology 62:2015–2020
Lovett JK, Dennis MS, Sandercock PA, Bamford J, Warlow CP, Rothwell PM (2003) Very early risk of stroke after a first transient ischemic attack. Stroke 34:e138–e140
Chandratheva A, Mehta Z, Geraghty OC, Marquardt L, Rothwell PM (2009) Population-based study of risk and predictors of stroke in the first few hours after a TIA. Neurology 72:1941–1947
Al-Khaled M, Matthis C, Eggers J (2012) Short-term risk and predictors of stroke after transient ischemic attack. J Neurol Sci 312:79–81
Albers GW, Caplan LR, Easton JD, Fayad PB, Mohr JP, Saver JL, Sherman DG (2002) Transient ischemic attack—proposal for a new definition. N Engl J Med 347:1713–1716
Furie KL, Kasner SE, Adams RJ, Albers GW, Bush RL, Fagan SC, Halperin JL, Johnston SC, Katzan I, Kernan WN, Mitchell PH, Ovbiagele B, Palesch YY, Sacco RL, Schwamm LH, Wassertheil-Smoller S, Turan TN, Wentworth D (2011) Guidelines for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke or transient ischemic attack: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 42:227–276
Gladstone DJ, Kapral MK, Fang J, Laupacis A, Tu JV (2004) Management and outcomes of transient ischemic attacks in Ontario. CMAJ 170:1099–1104
Edlow JA, Kim S, Pelletier AJ, Camargo CA Jr (2006) National study on emergency department visits for transient ischemic attack, 1992–2001. Acad Emerg Med 13:666–672
Adeoye O, Heitsch L, Moomaw CJ, Alwell K, Khoury J, Woo D, Flaherty ML, Ferioli S, Khatri P, Broderick JP, Kissela BM, Kleindorfer D (2010) How much would performing diffusion-weighted imaging for all transient ischemic attacks increase MRI utilization? Stroke 41:2218–2222
Ay H, Oliveira-Filho J, Buonanno FS, Schaefer PW, Furie KL, Chang YC, Rordorf G, Schwamm LH, Gonzalez RG, Koroshetz WJ (2002) ‘Footprints’ of transient ischemic attacks: a diffusion-weighted MRI study. Cerebrovasc Dis 14:177–186
Ay H, Koroshetz WJ, Benner T, Vangel MG, Wu O, Schwamm LH, Sorensen AG (2005) Transient ischemic attack with infarction: a unique syndrome? Ann Neurol 57:679–686
Purroy F, Montaner J, Rovira A, Delgado P, Quintana M, Alvarez-Sabin J (2004) Higher risk of further vascular events among transient ischemic attack patients with diffusion-weighted imaging acute ischemic lesions. Stroke 35:2313–2319
Calvet D, Touze E, Oppenheim C, Turc G, Meder JF, Mas JL (2009) DWI lesions and TIA etiology improve the prediction of stroke after TIA. Stroke 40:187–192
Adams HP Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, Marsh EE 3rd (1993) Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke 24:35–41
Culebras A, Kase CS, Masdeu JC, Fox AJ, Bryan RN, Grossman CB, Lee DH, Adams HP, Thies W (1997) Practice guidelines for the use of imaging in transient ischemic attacks and acute stroke. A report of the Stroke Council, American Heart Association. Stroke 28:1480–1497
Easton JD, Saver JL, Albers GW, Alberts MJ, Chaturvedi S, Feldmann E, Hatsukami TS, Higashida RT, Johnston SC, Kidwell CS, Lutsep HL, Miller E, Sacco RL (2009) Definition and evaluation of transient ischemic attack: a scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council; Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention; Council on Cardiovascular Nursing; and the Interdisciplinary Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease. The American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this statement as an educational tool for neurologists. Stroke 40:2276–2293
Schulz UG, Briley D, Meagher T, Molyneux A, Rothwell PM (2004) Diffusion-weighted MRI in 300 patients presenting late with subacute transient ischemic attack or minor stroke. Stroke 35:2459–2465
Crisostomo RA, Garcia MM, Tong DC (2003) Detection of diffusion-weighted MRI abnormalities in patients with transient ischemic attack: correlation with clinical characteristics. Stroke 34:932–937
Redgrave JN, Coutts SB, Schulz UG, Briley D, Rothwell PM (2007) Systematic review of associations between the presence of acute ischemic lesions on diffusion-weighted imaging and clinical predictors of early stroke risk after transient ischemic attack. Stroke 38:1482–1488
Giles MF, Albers GW, Amarenco P, Arsava MM, Asimos A, Ay H, Calvet D, Coutts S, Cucchiara BL, Demchuk AM, Johnston SC, Kelly PJ, Kim AS, Labreuche J, Lavallee PC, Mas JL, Merwick A, Olivot JM, Purroy F, Rosamond WD, Sciolla R, Rothwell PM (2010) Addition of brain infarction to the ABCD2 score (ABCD2I): a collaborative analysis of unpublished data on 4574 patients. Stroke 41:1907–1913
Schwamm LH, Koroshetz WJ, Sorensen AG, Wang B, Copen WA, Budzik R, Rordorf G, Buonanno FS, Schaefer PW, Gonzalez RG (1998) Time course of lesion development in patients with acute stroke: serial diffusion- and hemodynamic-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Stroke 29:2268–2276
Koudstaal PJ, Gerritsma JG, van Gijn J (1989) Clinical disagreement on the diagnosis of transient ischemic attack: is the patient or the doctor to blame? Stroke 20:300–301
Lamy C, Oppenheim C, Calvet D, Domigo V, Naggara O, Meder JL, Mas JL (2006) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in transient ischaemic attacks. Eur Radiol 16:1090–1095
Jimenez-Conde J, Biffi A, Rahman R, Kanakis A, Butler C, Sonni S, Massasa E, Cloonan L, Gilson A, Capozzo K, Cortellini L, Ois A, Cuadrado-Godia E, Rodriguez-Campello A, Furie KL, Roquer J, Rosand J, Rost NS (2010) Hyperlipidemia and reduced white matter hyperintensity volume in patients with ischemic stroke. Stroke 41:437–442
Shook SJ, Gupta R, Vora NA, Tievsky AL, Katzan I, Krieger DW (2006) Statin use is independently associated with smaller infarct volume in nonlacunar MCA territory stroke. J Neuroimaging 16:341–346
Weimar C, Kraywinkel K, Rodl J, Hippe A, Harms L, Kloth A, Diener HC (2002) Etiology, duration, and prognosis of transient ischemic attacks: an analysis from the German Stroke Data Bank. Arch Neurol 59:1584–1588
Rothwell PM, Giles MF, Chandratheva A, Marquardt L, Geraghty O, Redgrave JN, Lovelock CE, Binney LE, Bull LM, Cuthbertson FC, Welch SJ, Bosch S, Alexander FC, Silver LE, Gutnikov SA, Mehta Z (2007) Effect of urgent treatment of transient ischaemic attack and minor stroke on early recurrent stroke (express study): a prospective population-based sequential comparison. Lancet 370:1432–1442
Lavallee PC, Meseguer E, Abboud H, Cabrejo L, Olivot JM, Simon O, Mazighi M, Nifle C, Niclot P, Lapergue B, Klein IF, Brochet E, Steg PG, Leseche G, Labreuche J, Touboul PJ, Amarenco P (2007) A transient ischaemic attack clinic with round-the-clock access (SOS-TIA): feasibility and effects. Lancet Neurol 6:953–960
Dennis M, Bamford J, Sandercock P, Warlow C (1990) Prognosis of transient ischemic attacks in the Oxfordshire Community Stroke Project. Stroke 21:848–853
Giles MF, Albers GW, Amarenco P, Arsava EM, Asimos AW, Ay H, Calvet D, Coutts SB, Cucchiara BL, Demchuk AM, Johnston SC, Kelly PJ, Kim AS, Labreuche J, Lavallee PC, Mas JL, Merwick A, Olivot JM, Purroy F, Rosamond WD, Sciolla R, Rothwell PM (2011) Early stroke risk and ABCD2 score performance in tissue- vs time-defined TIA: a multicenter study. Neurology 77:1222–1228
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Khaled, M., Matthis, C., Münte, T.F. et al. The incidence and clinical predictors of acute infarction in patients with transient ischemic attack using MRI including DWI. Neuroradiology 55, 157–163 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-012-1091-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-012-1091-z