Abstract
Introduction
Shared rotating control acquisition can shorten the imaging time of territorial arterial spin labeling (tASL) by 33% compared with the normal control acquisition scheme but potentially results in an inaccurate estimate of vascular territories due to imperfect magnetization transfer compensation. Our purpose was to validate the accuracy of the shared rotating control acquisition method in evaluation of vascular territories.
Methods
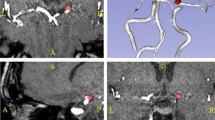
Twenty-four patients underwent tASL at a 3.0-T MRI with the conventional normal control acquisition method. Composite vascular territory maps, in which the blood flows from the right and left internal carotid arteries and the posterior circulation were encoded in red–green–blue, were generated as a normal averaged control-label scheme and as a simulated shared rotating control scheme. Two observers independently reported the most dominant territorial flow in 26 brain regions corresponding to the arterial segments at three post-labeling time points. Inter-reader and inter-method agreements were analyzed using κ statistics.
Results
Overall inter-reader agreements were excellent for both the normal control and the shared rotating control methods (κ = 0.98, respectively). Overall inter-method agreement was also excellent (κ = 0.98), although relatively low agreement was noted in the bilateral posterior cerebral artery territories (κ = 0.79 to 0.93).
Conclusion
Our results suggested that tASL using shared rotating control acquisition can provide information on the vascular territories comparable to that obtained using the normal control acquisition while substantially shortening the imaging time.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hendrikse J, van der Grond J, Lu H, van Zijl PC, Golay X (2004) Flow territory mapping of the cerebral arteries with regional perfusion MRI. Stroke 35:882–887
Werner R, Alfke K, Schaeffer T, Nabavi A, Mehdorn HM, Jansen O (2004) Brain perfusion territory imaging applying oblique-plane arterial spin labeling with a standard send/receiver head coil. Magn Reson Med 52:1443–1447
van Laar PJ (2006) HendrikseJ, Golay X, Lu H, Osch MJP, van der Grond J. In vivo flow territory mapping of major brain feeding arteries Neuroimage 29:136–144
Hendrikse R, van der Zwan A, Ramos LM, van Osch MJ, Golay X, Tulleken CA, van der Grond J (2005) Altered flow territories after extracranial-intracranial bypass surgery. Neurosurgery 57:486–494
van Laar PJ, Hendrikse J, Klijn CJM, Kappelle LJ, van Osch MJP, van der Grond J (2007) Symptomatic carotid artery occlusion: flow territories of major brain-feeding arteries. Radiology 242:526–534
Chng SM, Petersen ET, Zimine I, Sitoh Y-Y, Lim CCT, Golay X (2008) Territorial arterial spin labeling in the assessment of collateral circulation. Stroke 39:3248–3254
Zimine I, Petersen ET, Golay X (2006) Dual vessel arterial spin labelinig scheme for regional perfusion imaging. Magn Reson Med 56:1140–1144
Gunther M (2006) Efficient visualization of vascular territories in the human brain by cycled arterial spin labeling MRI. Magn Reson Med 56:671–675
Zimine I, Yoshiura T, Hiwatashi A, Noguchi T, van Cauteren M (2009) Utility of shared rotating control acquisition for territorial ASL. In: Proceedings of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. pp 3652
Petersen ET, Lim T, Golay X (2006) Model-free arterial spin labeling quantification approach for perfusion MRI. Magn Reson Med 55:219–232
Barber PA, Demchuk AM, Zhang J, Buchan AM (2000) Validity and reliability of a quantitative computed tomography score in predicting outcome of hyperacute stroke before thrombolytic therapy. Aspects study group. Alberta stroke programme early CT score. Lancet 355:1670–1674
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamano, H., Yoshiura, T., Hiwatashi, A. et al. Accelerated territorial arterial spin labeling based on shared rotating control acquisition: an observer study for validation. Neuroradiology 54, 65–71 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-011-0919-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-011-0919-2