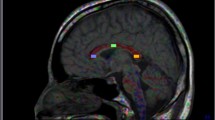
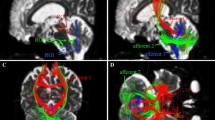
Abstract
Introduction
We performed diffusion tensor imaging to determine if multiple system atrophy (MSA)-cerebellar (C) and MSA-Parkinsonism (P) show similar changes, as shown in pathological studies.
Methods
Nineteen patients with MSA-C, 12 patients with MSA-P, 20 patients with Parkinson disease, and 20 healthy controls were evaluated with the use of voxel-based morphometry analysis of diffusion tensor imaging.
Results
There was an increase in apparent diffusion coefficient values in the middle cerebellar peduncles and cerebellum and a decrease in fractional anisotropy in the pyramidal tract, middle cerebellar peduncles, and white matter of the cerebellum in patients with MSA-C and MSA-P compared to the controls (P < 0.001). In addition, isotropic diffusion-weighted image values were reduced in the cerebellar cortex and deep cerebellar nuclei in patients with MSA-C and increased in the basal ganglia in patients with MSA-P.
Conclusion
These results indicate that despite their disparate clinical manifestations, patients with MSA-C and MSA-P share similar diffusion tensor imaging features in the infratentorial region. Further, the combination of FA, ADC and iDWI images can be used to distinguish between MSA (either form) and Parkinson disease, which has potential therapeutic implications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gilman S, Wenning GK, Low PA, Brooks DJ, Mathias CJ, Trojanowski JQ, Wood NW, Colosimo C, Dürr A, Fowler CJ, Kaufmann H, Klockgether T, Lees A, Poewe W, Quinn N, Revesz T, Robertson D, Sandroni P, Seppi K, Vidailhet M (2008) Second consensus statement on the diagnosis of multiple system atrophy. Neurology 71:670–676
Gilman S, Little R, Johanns J, Heumann M, Kluin KJ, Junck L, Koeppe RA, An H (2000) Evolution of sporadic olivopontocerebellar atrophy into multiple system atrophy. Neurology 55:527–532
Wenning GK, Tison F, Ben Shlomo Y, Daniel SE, Quinn NP (1997) Multiple system atrophy: a review of 203 pathologically proven cases. Mov Disord 12:133–147
Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H (2006) Cellular pathology in multiple system atrophy. Neuropathology 26:338–345
Ozawa T, Paviour D, Quinn NP, Josephs KA, Sangha H, Kilford L, Healy DG, Wood NW, Lees AJ, Holton JL, Revesz T (2004) The spectrum of pathological involvement of the striatonigral and olivopontocerebellar systems in multiple system atrophy: clinicopathological correlations. Brain 127:2657–2671
Bozzali M, Franceschi M, Falini A, Pontesilli S, Cercignani M, Magnani G, Scotti G, Comi G, Filippi M (2001) Quantification of tissue damage in AD using diffusion tensor and magnetization transfer MRI. Neurology 57:1135–1137
Beaulieu C (2002) The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system - a technical review. NMR Biomed 15:435–455
Pierpaoli C, Barnett A, Pajevic S, Chen R, Penix LR, Virta A, Basser P (2001) Water diffusion changes in Wallerian degeneration and their dependence on white matter architecture. Neuroimage 13:1174–1185
Salmond CH, Menon DK, Chatfield DA, Williams GB, Pena A, Sahakian BJ, Pickard JD (2006) Diffusion tensor imaging in chronic head injury survivors: correlations with learning and memory indices. Neuroimage 29:117–124
Basser PJ, Pierpaoli C (1996) Microstructural and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative-diffusion-tensor MRI. J Magn Reson B 111:209–219
Matsuzawa H, Nakayama N, Kwee IL, Nakada T (2005) Isotropic component trace analysis. J Neuroimaging 15:233–239
Kanazawa M, Shimohata T, Terajima K, Onodera O, Tanaka K, Tsuji S, Okamoto K, Nishizawa M (2004) Quantitative evaluation of brainstem involvement in multiple system atrophy by diffusion-weighted MR imaging. J Neurol 251:1121–1124
Schocke MF, Seppi K, Esterhammer R, Kremser C, Mair KJ, Czermak BV, Jaschke W, Poewe W, Wenning GK (2004) Trace of diffusion tensor differentiates the Parkinson variant of multiple system atrophy and Parkinson's disease. Neuroimage 21:1443–1451
Seppi K, Schocke MF, Mair KJ, Esterhammer R, Scherfler C, Geser F, Kremser C, Boesch S, Jaschke W, Poewe W, Wenning GK (2006) Progression of putaminal degeneration in multiple system atrophy: a serial diffusion MR study. Neuroimage 31:240–245
Yoshikawa K, Nakata Y, Yamada K, Nakagawa M (2004) Early pathological changes in the parkinsonian brain demonstrated by diffusion tensor MRI. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:481–484
Bang OY, Huh K, Lee PH, Kim HJ (2003) Clinical and neuroradiological features of patients with spinocerebellar ataxias from Korean kindreds. Arch Neurol 60:1566–1574
Kim SE, Choi JY, Choe YS, Choi Y, Lee WY (2003) Serotonin transporters in the midbrain of Parkinson's disease patients: a study with 123I-β-CIT SPECT. J Nucl Med 44:870–876
Harris AD, Pereira RS, Mitchell JR, Hill MD, Sevick RJ, Frayne R (2004) A comparison of images generated from diffusion-weighted and diffusion-tensor imaging data in hyper-acute stroke. J Magn Reson Imaging 20:193–200
Zhang J, van Zijl PC, Mori S (2002) Three-dimensional diffusion tensor magnetic resonance microimaging of adult mouse brain and hippocampus. Neuroimage 15(892):901
Sotak CH (2002) The role of diffusion tensor imaging in the evaluation of ischemic brain injury - a review. NMR Biomed 15:561–569
Bruno S, Cercignani M, Ron MA (2008) White matter abnormalities in bipolar disorder: a voxel-based diffusion tensor imaging study. Bipolar Disord 10:460–468
Nestor PJ, Graham NL, Fryer TD, Williams GB, Patterson K, Hodges JR (2003) Progressive non-fluent aphasia is associated with hypometabolism centred on the left anterior insula. Brain 126:2406–2418
Wang PS, Liu RS, Yang BH, Soong BW (2007) Topographic brain mapping of the international cooperative ataxia rating scale. A positron emission tomography study. J Neurol 254:722–728
Wang PS, Liu RS, Yang BH, Soong BW (2007) Regional patterns of cerebral glucose metabolism in spinocerebellar ataxia type 2, 3 and 6: a voxel-based FDG-positron emission tomography analysis. J Neurol 254:838–845
Specht K, Minnerop M, Abele M, Reul J, Wüllner U, Klockgether T (2003) In vivo voxel-based morphometry in multiple system atrophy of the cerebellar type. Arch Neurol 60:1431–1435
Brenneis C, Boesch SM, Egger KE, Seppi K, Scherfler C, Schocke M, Wenning GK, Poewe W (2006) Cortical atrophy in the cerebellar variant of multiple system atrophy: a voxel-based morphometry study. Mov Disord 21:159–165
Specht K, Minnerop M, Müller-Hubenthal J, Klockgether T (2005) Voxel-based analysis of multiple-system atrophy of cerebellar type: complementary results by combining voxel-based morphometry and voxel-based relaxometry. Neuroimage 25:287–293
Brenneis C, Seppi K, Schocke MF, Müller J, Luginger E, Bösch S, Löscher WN, Büchel C, Poewe W, Wenning GK (2003) Voxel-based morphometry detects cortical atrophy in the Parkinson variant of multiple system atrophy. Mov Disord 18:1132–1138
Lantos PL, Papp MI (1994) Cellular pathology of multiple system atrophy: a review. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 57:129–133
Minnerop M, Specht K, Ruhlmann J, Schimke N, Abele M, Weyer A, Wullner U, Klockgether T (2007) Voxel-based morphometry and voxel-based relaxometry in multiple system atrophy-a comparison between clinical subtypes and correlations with clinical parameters. Neuroimage 36:1086–1095
Juh R, Pae CU, Lee CU, Yang D, Chung Y, Suh T, Choe B (2005) Voxel based comparison of glucose metabolism in the differential diagnosis of the multiple system atrophy using statistical parametric mapping. Neurosci Res 52:211–219
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Science Council, Taipei, Taiwan, ROC (NSC98-214-B-010-036-MY3 and NSC99-2314-B-010-013-MY3), Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taiwan, ROC (V99-C1-052) and Yen-Tjing-Ling Medical Foundation (CI-98-3).
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, PS., Wu, HM., Lin, CP. et al. Use of diffusion tensor imaging to identify similarities and differences between cerebellar and Parkinsonism forms of multiple system atrophy. Neuroradiology 53, 471–481 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-010-0757-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-010-0757-7