Abstract
Introduction
Our purpose was to clarify the magnetic resonance (MR) imaging characteristics of the brachial and lumbar plexuses in patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP) using various kinds of sequences, including diffusion-weighted images (DWI).
Methods
We evaluated the MR imaging findings for lumbar and/or brachial nerve plexuses in 13 CIDP patients and 11 normal volunteers. The nerve swelling was evaluated in comparison with normal controls by coronal short tau inversion recovery (STIR), and signal abnormalities were evaluated by coronal STIR, T1-weighted images, and DWIs. The degrees of contrast enhancement and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values of the plexus were also assessed.
Results
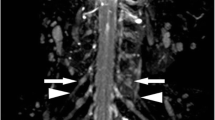
In the patient group, diffuse enlargement and abnormally high signals were detected in 16 out of 24 plexuses (66.7%) on STIR, a slightly high signal was detected in 12 of 24 plexuses (50%) on T1-weighted images, and a high-intensity signal was detected in 10 of 18 plexuses (55.6%) on DWIs with high ADC values. Contrast enhancement of the plexuses was revealed in 6 of 19 plexuses (31.6%) and was mild in all cases. There were statistically significant differences between the ADC values of patients with either swelling or abnormal signals and those of both normal volunteers and patients without neither swelling nor abnormal signals. There were no relationships between MR imaging and any clinical findings.
Conclusion
STIR is sufficient to assist clinicians in diagnosing CIDP. T1-weighted images and DWIs seemed useful for speculating about the pathological changes in swollen plexuses in CIDP patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hahn A, Hartung H, Dick P (2005) Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. In: Dick P (ed) Peripheral neuropathy, vol 2, 4th ed. Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 2221–2253
Joint Task Force of the EFNS and the PNS (2005) European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on management of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: report of a joint task force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society. J Peripher Nerv Syst 10:220–228
Latov N (2002) Diagnosis of CIDP. Neurology 59(Suppl 6):S2–S6
Koller H, Kieseier BC, Jander S, Hartung HP (2005) Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. N Engl J Med 352:1343–1356
Eurelings M, Notermans NC, Franssen H, Van Es H, Ramos H, Wokke J, Van Den Berg H (2001) MRI of the brachial plexus in polyneuropathy associated with monoclonal gammopathy. Muscle Nerve 24:1312–1318
Bradley L, Wilhelm T, King RH, Ginsberg L, Orrell RW (2006) Brachial plexus hypertrophy in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Neuromuscul Disord 16:126–131
Midroni G, Tilly TN, Gray B, Vajsar J (1999) MRI of the cauda equine in CIDP: clinical correlations. J Neurol Sci 170:36–44
Duggins A, McLeod J, Pollard J, Davies L, Yang F, Thompson EO, Soper JR (1999) Spinal root and plexus hypertrophy in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Brain 122:1383–1390
Kuwabara S, Nakajima M, Matsuda S, Hattori T (1997) Magnetic resonance imaging at the demyelinative foci in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Neurology 48:874–877
Tsuchiya K, Imai M, Tateishi H, Nitatori T, Fujikawa A, Takemoto S (2007) Neurography of the spinal nerve roots by diffusion tensor scanning applying motion-probing gradients in six directions. Magn Reson Med Sci 6:1–5
Tsuchiya K, Honya K, Yoshida M, Nitatori T (2008) Demonstration of spinal cord and nerve root abnormalities by diffusion neurography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 32:286–290
Takahara T, Hendrikse J, Yamashita T, Mali W, Kwee T, Imai Y, Luijten P (2008) Diffusion-weighted MR neurography of the brachial plexus: feasibility study. Radiology 249(2):653–660
Bendszus M, Stoll G (2005) Technology insight: visualizing peripheral nerve injury using MRI. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 1:45–53
Kababci N, Gurses B, Firat Z. Bayram A, Ulug A, Kovanlikaya A (2007) Diffusion tensor imaging and tractography of median nerve: Normative diffusion values. AJR 189:923–927
Crino B, Grossman I, Rostami A (1993) Magnetic resonance imaging of the cauda equine in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Ann Neurol 33:311–313
Graham I, Lantos L (2002) Greenfield’s neuropathology, 7th edition, Vol. 2. New York Oxford University Press, pp 617–620
Naba I, Yoshikawa H, Sakoda S, Itabe H, Suzuki H, Kodama T, Yanagihara T (2000) Onion-bulb formation after a single compression injury in the macrophage scavenger receptor knockout mice. Exp Neurol 166:83–89
Sureka J, Charian RA, Alexander M, Thomas BP (2009) MRI of brachial plexopathies. Clin Radiol 64:208–218
Van Es H, Van den Berg L, Franssen H et al (1997) Magnetic resonance imaging of the brachial plexus in patients with multifocal motor neuropathy. Neurology 48(5):1218–1224
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adachi, Y., Sato, N., Okamoto, T. et al. Brachial and lumbar plexuses in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: MRI assessment including apparent diffusion coefficient. Neuroradiology 53, 3–11 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-010-0684-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-010-0684-7