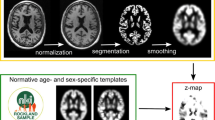
Abstract
Introduction
When characterizing regional cerebral gray matter differences in structural magnetic resonance images (sMRI) by voxel-based morphometry (VBM), one faces a known drawback of VBM, namely that histogram unequalization in the intensity images introduces false-positive results.
Methods
To overcome this limitation, we propose to improve VBM by a new approach (called eVBM for enhanced VBM) that takes the histogram distribution of the sMRI into account by adding a histogram equalization step within the VBM procedure. Combining this technique with two most widely used VBM software packages (FSL and SPM), we studied GM variability in a group of 62 patients with Alzheimer’s disease compared to 73 age-matched elderly controls.
Results
The results show that eVBM can reduce the number of false-positive differences in gray matter concentration.
Conclusion
Because it takes advantage of the properties of VBM while improving sMRI histogram distribution at the same time, the proposed method is a powerful approach for analyzing gray matter differences in sMRI and may be of value in the investigation of sMRI gray and white matter abnormalities in a variety of brain diseases.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wright IC, McGuire PK, Poline JB, Travere JM, Murray RM, Frith CD, Frackowiak RS, Friston KJ (1995) A voxel-based method for the statistical analysis of gray and white matter density applied to schizophrenia. Neuroimage 2:244–252
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2000) Voxel-based morphometry—the methods. Neuroimage 11:805–821
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2001) Why voxel-based morphometry should be used. Neuroimage 14:1238–1243
Bookstein FL (2001) “Voxel-based morphometry” should not be used with imperfectly registered images. Neuroimage 14:1454–1462
Good CD, Johnsrude IS, Ashburner J, Henson RN, Friston KJ, Frackowiak RS (2001) A voxel-based morphometric study of ageing in 465 normal adult human brains. Neuroimage 14:21–36
Mechelli A, Price CJ, Friston KJ, Ashburner J (2005) Voxel-based morphometry of the human brain: methods and applications. Current Medical Imag Reviews 1:1–9
Celone K, Calhoun V, Dickerson B, Atri A, Chua EF, Miller SL, DePeau K, Rentz DM, Selkoe DJ, Blacker D, Albert MS, Sperling RA (2006) Alterations in memory networks in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: an independent component analysis. J Neurosci 26:10222–10231
Baron JC, Chetelat G, Desgranges B, Perchey G, Landeau B, de la Sayette V, Eustache F (2001) In vivo mapping of gray matter loss with voxel-based morphometry in mild Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 14:298–309
Karas GB, Burton EJ, Rombouts SARB, Schijndel RAV, O'Brien JT, Scheltens PH, McKeith IG, Williams D, Ballard C, Barkhof F (2003) A comprehensive study of grey matter loss in patients with Alzheimer’s disease using optimized voxel-based morphometry. Neuroimage 18:895–907
Smith SM, Nichols TE (2009) Threshold-free cluster enhancement: addressing problems of smoothing, threshold dependence and localisation in cluster inference. Neuroimage 44(1):83–98
Tardif CL, Collins DL, Pike GB (2009) Sensitivity of voxel-based morphometry analysis to choice of imaging protocol at 3 T. Neuroimage 44:827–838
Scahill R, Schott J, Stevens J, Rossor M, Fox N (2002) Mapping the evolution of regional atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease: unbiased analysis of fluid-registered serial MRI. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:4703–4709
Ramani A, Jensen J, Helpern J (2006) Quantitative MR imaging in Alzheimer disease. Radiology 241:26–44
Chetelat G, Degranges B, Sayette VDL, Viader F, Eustache BJC (2002) Mapping grey matter loss with voxel-based morphometry in mild cognitive impairment. NeuroReport 13:1939–1943
Frisoni GB, Testa C, Zorzan A, Sabattoli F, Beltramello A, Soininen H, Laakso MP (2002) Detection of grey matter loss in mild Alzheimer’s disease with voxel based morphometry. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 73:657–664
Thompson P, Hayashi K, Zubicaray GD, Janke AL, Rose SE, Semple J, Herman D, Hong MS, Dittmer SS, Doddrell DM, Toga AW (2003) Dynamics of grey matter loss in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 23:994–1005
Hirata Y, Matsuda H, Nemoto K, Ohnishi T, Hirao K, Yamashita F, Asada T, Iwabuchi S, Samejima H (2005) Voxel-based morphometry to discriminate early Alzheimer’s disease from controls. Neurosci Lett 382:269–274
Paola MD, Macaluso E, Carlesimo GA, Tomaiuolo F, Worsley KJ, Fadda L, Caltagirone C (2007) Episodic memory impairment in patients with Alzheimer’s disease is correlated with entorhinal cortex atrophy: a voxel based morphometry study. J Neurol 254:774–781
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Woolrich MW, Beckmann CF, Behrens TEJ, Johansen-Berg H, Bannister PR, De Luca M, Drobnjak I, Flitney DE, Niazy R, Saunders J, Vickers J, Zhang Y, De Stefano N, Brady JM, Matthews PM (2004) Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. Neuroimage 23(S1):208–219
Gonzales RC, Woods RE (1993) Digital image processing. Addison-Wesley, USA, pp 173–182
Marcus DS, Wang TH, Parker J, Csernansky JG, Morris JC, Buckner RL (2007) Open Access Series of Imaging Studies (OASIS): cross-sectional MRI data in young, middle aged, nondemented, and demented older adults. J Cogn Neurosci 19:1498–1507
Morris JC (1993) The clinical dementia rating (CDR): current version and scoring rules. Neurology 43:2412b–2414b
Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Landeau B, Papathanassiou D, Crivello F, Etard O, Delcroix N, Mazoyer B, Joliot M (2002) Automated anatomical labelling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage 15:273–289
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2005) Unified segmentation. Neuroimage 26:839–851
Smith SM (2002) Fast robust automated brain extraction. Hum Brain Mapp 17:143–155
Zhang Y, Brady M, Smith SM (2001) Segmentation of brain MR images through a hidden Markov random field model and the expectation maximization algorithm. IEEE Trans Med Imag 20:45–57
Jenkinson M, Smith SM (2001) A global optimisation method for robust affine registration of brain images. Med Image Anal 5:143–156
Jenkinson M, Bannister PR, Brady JM, Smith SM (2002) Improved optimisation for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. Neuroimage 17:825–841
Andersson JLR, Jenkinson M, Smith SM (2007) Non-linear optimisation. FMRIB technical report TR07JA1 from www.fmrib.ox.ac.uk/analysis/techrep.
Andersson JLR, Jenkinson M, Smith SM (2007) Non-linear registration, aka spatial normalisation. FMRIB technical report TR07JA2 from www.fmrib.ox.ac.uk/analysis/techrep.
Rueckert D, Sonoda LI, Hayes C, Hill DLG, Leach MO, Hawkes DJ (1999) Non-rigid registration using free-form deformations: application to breast MR images. IEEE Trans Med Imag 18:712–721
Nichols TE, Holmes AP (2002) Nonparametric permutation tests for functional neuroimaging: a primer with examples. Hum Brain Mapp 15:1–25
Nichols TE, Hayasak S (2003) Controlling the familywise error rate in functional neuroimaging: a comparative review. Stat Methods Med Res 12:419–446
Dickerson BC, Goncharova I, Sullivan MP, Forchetti C, Wilson RS, Bennett DA, Beckettl A, DetoleDO ML (2001) MRI-derived entorhinal and hippocampus atrophy in incipient and every mild Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 22:747–754
Cardenas VA, Du AT, Hardin D, Ezekiel F, Weber P, Jagust WJ, Chui HC, Schuff N, Weiner MW (2003) Comparison of methods for measuring longitudinal brain change in cognitive impairment and dementia. Neurobiol Aging 24:537–544
Delbeuck X, Linden VD, Collette F (2003) Alzheimer’s disease as a disconnection syndrome? Neuropsychol Rev 13:79–92
Rémya F, Mirrasheda F, Campbellb B, Richter W (2005) Verbal episodic memory impairment in Alzheimer’s disease: a combined structural and functional MRI study. Neuroimage 25:256–266
Hämäläinen A, Tervo S, Grau-Olivares M, Niskanen E, Pennanen C, Huuskonen J, Kivipelto M, Hànninen T, Tapiola M, Vanhanen M, Hallikainen M, Helkala EL, Nissinen A, Vanninen R, Soininen H (2007) Voxel-based morphometry to detect brain atrophy in progressive mild cognitive impairment. Neuroimage 37:1122–1131
Acosta-Cabronero J, Williams GB, Pereira JMS, Pengas G, Nestor PJ (2008) The impact of skull-stripping and radio-frequency bias correction on grey-matter segmentation for voxel-based morphometry. Neuroimage 39:1654–1665
Acknowledgments
X. Li is funded by a “poste vert” from Inserm. This work was supported by the International Laboratory on Neuroimaging and Modeling (Inserm—UPMC Univ Paris 06—Université de Montréal). The authors thank Pr. S. Lehéricy and Dr. V. Perlbarg for their helpful comments.
The authors thank Dr. Randy Buckner and his colleagues for making their OASIS data available to us.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 6493 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Messé, A., Marrelec, G. et al. An enhanced voxel-based morphometry method to investigate structural changes: application to Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroradiology 52, 203–213 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-009-0600-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-009-0600-1