Abstract
Introduction
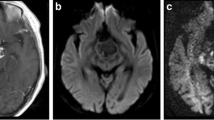
The signal characteristics of an epidermoid on T2-weighted imaging have been attributed to the presence of increased water content within the tumor. In this study, we explore the utility of diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and diffusion tensor metrics (DTM) in knowing the microstructural anatomy of epidermoid cysts.
Materials and methods
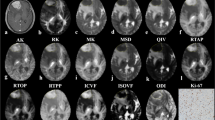
DTI was performed in ten patients with epidermoid cysts. Directionally averaged mean diffusivity (D av), exponential diffusion, and DTM-like fractional anisotropy (FA), diffusion tensor mode (mode), linear (CL), planar (CP), and spherical (CS) anisotropy were measured from the tumor as well as from the normal-looking white matter.
Results
Epidermoid cysts showed high FA. However, D av and exponential diffusion values did not show any restriction of diffusion. Diffusion tensor mode values were near −1, and CP values were high within the tumor. This suggested preferential diffusion of water molecules along a two-dimensional geometry (plane) in epidermoid cysts, which could be attributed to the parallel-layered arrangement of keratin filaments and flakes within these tumors.
Conclusion
Thus, advanced imaging modalities like DTI with DTM can provide information regarding the microstructural anatomy of the epidermoid cysts.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morrison G, Sobel DF, Kelley WM, Norman D (1984) Intraventricular mass lesions. Radiology 153:435–442
Smirniotopoulos JG, Yue NC, Rushing EJ (1993) Cerebellopontine angle masses: radiologic–pathologic correlation. Radiographics 13:1131–1147
Bergui M, Zhong J, Bradac GB, Sales S (2001) Diffusion weighted images of intracranial cyst-like lesions. Neuroradiology 43:824–829. doi:10.1007/s002340100595
Annet L, Duprez T, Grandin C, Dooms G, Collard A, Cosnard G (2002) Apparent diffusion coefficient measurements within intracranial epidermoid cysts in six patients. Neuroradiology 44:326–328
Hakyemeza B, Aksoyb U, Yildizc H, Ergind N (2005) Intracranial epidermoid cysts: diffusion-weighted, FLAIR and conventional MR findings. Eur J Radiol 54:214–220. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2004.06.018
Sundgren PC, Dong Q, Go’mez-Hassan D, Mukherji SK et al (2004) Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain: review of clinical applications. Neuroradiology 46:339–350. doi:10.1007/s00234-003-1114-x
Toh CH, Castillo M, Wong AMC et al (2008) Differentiation between classic and atypical meningiomas with use of diffusion tensor imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A1170
Tropine A, Dellani PD, Glaser M et al (2007) Differentiation of fibroblastic meningiomas from other benign subtypes using diffusion tensor imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 25:703–708. doi:10.1002/jmri.20887
Beppu T, Inoue T, Shibata Y, Yamada N et al (2005) Fractional anisotropy value by diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging as a predictor of cell density and proliferation activity of glioblastomas. Surg Neurol 63:56–61. doi:10.1016/j.surneu.2004.02.034
Goebell E, Fiehler J, Ding XQ et al (2006) Disarrangement of fiber tracts and decline of neuronal density correlate in glioma patients—a combined diffusion tensor imaging and 1 h-MR spectroscopy study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:1426–1431
Hagmann P, Jonasson L, Maeder P et al (2006) Understanding diffusion MR imaging techniques: from scalar diffusion-weighted imaging to diffusion tensor imaging and beyond. Radiographics 26:S205–S223. doi:10.1148/rg.26si065510
Le Bihan D, Mangain JF, Poupon C et al (2001) Diffusion tensor imaging: concepts and applications. J Magn Reson Imaging 46:18–23
Thomas B, Sunaert S (2005) Diffusion tensor imaging: technique, clinical and research applications. Riv Neuroradiol 18:419–435
Chenevert TL, Sundgren PC, Ross BD (2006) Diffusion imaging: insight to cell status and cytoarchitecture. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 16:619–632. doi:10.1016/j.nic.2006.06.005
Bahn MM (1999) Invariant and orthonormal scalar measures derived from magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging. J Magn Reson 141:68–77. doi:10.1006/jmre.1999.1875
Ennis DB, Kindlmann G (2006) Orthogonal tensor invariants and the analysis of diffusion tensor magnetic resonance images. Magn Reson Med 55:136–146. doi:10.1002/mrm.20741
Peled S, Gudbjartsson H, Westin CF, Kikinis R, Jolesz FA (1998) Magnetic resonance imaging shows orientation and asymmetry of white matter fiber tracts. Brain Res 780:27–33. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(97)00635-5
Kumar K, Gupta RK, Nath K et al (2007) Can we differentiate true white matter fibers from pseudofibers inside a brain abscess cavity using geometrical diffusion tensor imaging metrics? NMR Biomed 21(6):581–588. doi:10.1002/nbm.1228
Lantos PL, Louis DN, Rosenblum MK, Kleihues P (2002) Tumors of nervous system. In: Graham DI, Lantos PL (eds) Greenfield’s neuropathology. vol. II. 7th edn. Arnold, London, pp 964–965
Steffy DJ, De Fillip GJ, Spera T, Gabrielson T (1988) MR imaging of primary epidermoid tumors. J Comput Assist Tomogr 12:438–440
Kallmes DF, Provenzale JM, Cioft HJ, McClendon RE (1997) Typical and atypical MR imaging features of intracranial epidermoid tumors. AJR Am J Roentgenol 169:883–887
Ikushima I, Korogi Y, Hirai T, Sugahara T et al (1997) MR of epidermoids with a variety of pulse sequences. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18:1359–1363
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jolapara, M., Kesavadas, C., Radhakrishnan, V.V. et al. Diffusion tensor mode in imaging of intracranial epidermoid cysts: one step ahead of fractional anisotropy. Neuroradiology 51, 123–129 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-008-0464-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-008-0464-9