Abstract
Introduction
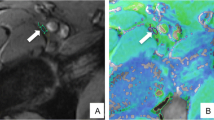
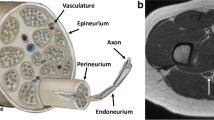
Extracranial MR neurography has so far mainly been used with 2D datasets. We investigated the use of 3D datasets for peripheral neurography of the sciatic nerve.
Methods
A total of 40 thighs (20 healthy volunteers) were examined with a coronally oriented magnetization-prepared rapid acquisition gradient echo sequence with isotropic voxels of 1 × 1 × 1 mm and a field of view of 500 mm. Anatomical landmarks were palpated and marked with MRI markers. After MR scanning, the sciatic nerve was identified by two readers independently in the resulting 3D dataset.
Results
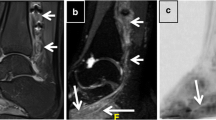
In every volunteer, the sciatic nerve could be identified bilaterally over the whole length of the thigh, even in areas of close contact to isointense muscles. The landmark of the greater trochanter was falsely palpated by 2.2 cm, and the knee joint by 1 cm. The mean distance between the bifurcation of the sciatic nerve and the knee-joint gap was 6 cm (±1.8 cm). The mean results of the two readers differed by 1–6%.
Conclusion
With the described method of MR neurography, the sciatic nerve was depicted reliably and objectively in great anatomical detail over the whole length of the thigh. Important anatomical information can be obtained. The clinical applications of MR neurography for the brachial plexus and lumbosacral plexus/sciatic nerve are discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blair DN, Rapoport S, Sorstman HD, Blair OC (1987) Normal brachial plexus: MR imaging. Radiology 165:763–767
Gupta RK, Mehta VS, Banerji AK, Jain RK (1989) MR evaluation of brachial plexus injuries. Neuroradiology 31:377–381
Howe FA, Filler AG, Bell BA, Griffiths JR (1992) Magnetic resonance neurography. Magn Reson Med 28:328–338
Cudlip SA, Howe FA, Clifton A, Schwartz MS, Bell BA (2002) Magnetic resonance neurography studies of the median nerve before and after carpal tunnel decompression. J Neurosurg 96:1046–1051
Zhou L, Yousem DM, Chaudhry V (2004) Role of magnetic resonance neurography in brachial plexus lesions. Muscle Nerve 30:305–309
Filler AG, Maravilla KR, Tsuruda JS (2004) MR neurography and muscle MR imaging for image diagnosis of disorders affecting the peripheral nerves and musculature. Neurol Clin 22:643–682, vi–vii
Moore KR, Blumenthal DT, Smith AG, Ward JH (2001) Neurolymphomatosis of the lumbar plexus: high-resolution MR neurography findings. Neurology 57:740–742
Schmitz B, Hagen T, Reith W (2003) Three-dimensional true FISP for high-resolution imaging of the whole brain. Eur Radiol 13:1577–1582
Naganawa S, Koshikawa T, Nakamura T, Fukatsu H, Ishigaki T, Aoki I (2003) High-resolution T1-weighted 3D real IR imaging of the temporal bone using triple-dose contrast material. Eur Radiol 13:2650–2658
Kress B, Rasche D, Fiebach J, Tronnier V, Sartor K, Stippich C (2004) MR volumetry of the trigeminal nerve in patients with unilateral facial pain. Rofo 176:719–723
Vloka JD, Hadzic A, April E, Thys DM (2001) The division of the sciatic nerve in the popliteal fossa: anatomical implications for popliteal nerve blockade. Anesth Analg 92:215–217
Floch H, Naux E, Pham Dang C, Dupas B, Pinaud M (2003) Computed tomography scanning of the sciatic nerve posterior to the femur: practical implications for the lateral midfemoral block. Reg Anesth Pain Med 28:445–449
Hadzic A, Vloka JD, Singson R, Santos AC, Thys DM (2002) A comparison of intertendinous and classical approaches to popliteal nerve block using magnetic resonance imaging simulation. Anesth Analg 94:1321–1324
Ericksen ML, Swenson JD, Pace NL (2002) The anatomic relationship of the sciatic nerve to the lesser trochanter: implications for anterior sciatic nerve block. Anesth Analg 95:1071–1074
Neuburger M, Hendrich E, Lang D, Dinse A, Wagner F, Freund W, Brinkmann A, Büttner J (2005) Lateral approach to blockade of the sciatic nerve. Biometric data using magnetic resonance imaging (in German). Anaesthesist 54:877–883
Raphael DT, McIntee D, Tsuruda JS, Colletti P, Tatevossian R (2005) Frontal slab composite magnetic resonance neurography of the brachial plexus: implications for infraclavicular block approaches. Anesthesiology 103:1218–1224
Bendszus M, Stoll G (2005) Technology insight: visualizing peripheral nerve injury using MRI. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 1:45–53
Lewis AM, Layzer R, Engstrom JW, Barbaro NM, Chin CT (2006) Magnetic resonance neurography in extraspinal sciatica. Arch Neurol 63:1469–1472
Filler AG, Haynes J, Jordan SE, Prager J, Villablanca JP, Farahani K, McBride DQ, Tsuruda JS, Morisoli B, Batzdorf U, Johnson JP (2005) Sciatica of nondisc origin and piriformis syndrome: diagnosis by magnetic resonance neurography and interventional magnetic resonance imaging with outcome study of resulting treatment. J Neurosurg Spine 2:99–115
Taboada M, Rodriguez J, Alvarez J, Cortes J, Gude F, Atanassoff PG (2004) Sciatic nerve block via posterior Labat approach is more efficient than lateral popliteal approach using a double-injection technique: a prospective, randomized comparison. Anesthesiology 101:138–142
Sukhani R, Candido KD, Doty R, Yaghmour E, McCarthy RJ (2003) Infragluteal-parabiceps sciatic nerve block: an evaluation of a novel approach using a single-injection technique. Anesth Analg 96:868–873
Maravilla KR, Bowen BC (1998) Imaging of the peripheral nervous system: evaluation of peripheral neuropathy and plexopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1011–1123
Almanza MY, Poon-Chue A, Terk MR (1999) Dual oblique MR method for imaging the sciatic nerve. J Comput Assist Tomogr 23:138–140
Acknowledgements
The help of radiographers B. Köstler, K. Pietsch and J. Heindl is gratefully appreciated.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The experiments were conducted in accordance with German regulations and laws and after a positive decision of our local ethics committee.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Freund, W., Brinkmann, A., Wagner, F. et al. MR neurography with multiplanar reconstruction of 3D MRI datasets: an anatomical study and clinical applications. Neuroradiology 49, 335–341 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0197-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0197-6