Abstract
Introduction
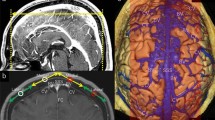
Intracranial venous structures have received increasing attention due to improved neuroimaging techniques and increased awareness of cerebral venous disease. To date, few studies have attempted to investigate the dural entrance of the cerebral bridging vein (BV). The aim of this study was to use the superior sagittal sinus (SSS) as an example to identify anatomical features of the dural entrance of the BVs into the SSS in both human cadavers and digital subtraction angiography (DSA) images.
Methods
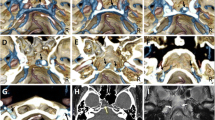
A total of 30 adult and 7 fetal human cadavers and 36 patients were examined with anatomical dissections, vascular casting and DSA. The number, diameter and angle of the BVs entering the SSS were measured and compared between the cadavers and DSA images.
Results
The results demonstrated that (1) the way a BV entered the SSS varied in three dimensions, and thus the BV dural entrance was difficult to precisely localize by DSA, (2) the distribution pattern of the dural entrance of the BVs into the SSS was relatively constant and a nontributary segment of the SSS was centered at the coronal suture and was identifiable by DSA, and (3) nearly all the BVs (97%, 561/581) entered the SSS at an angle opposite to the direction of blood flow.
Conclusion
Unique anatomical features of the dural entrance of a BV into the SSS should be considered in neuroimaging interpretation of the sinus and its associated veins.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stam J (2005) Thrombosis of the cerebral veins and sinuses. N Engl J Med 352:1791–1798
deVeber G, Andrew M, Adams C, et al (2001) Cerebral sinovenous thrombosis in children. N Engl J Med 345:417–423
Ayanzen RH, Bird CR, Keller PJ, et al (2000) Cerebral MR venography: normal anatomy and potential diagnostic pitfalls. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:74–78
Ferro JM, Canhao P, Stam J (2004) Prognosis of cerebral vein and dural sinus thrombosis: results of the international study on cerebral vein and dural sinus thrombosis (ISCVT). Stroke 35:664–670
Wasay M, Bakshi R, Kojan S, et al (2001) A non-randomized comparison of local urokinase thrombolysis versus systemic heparin anticoagulation treatment of superior sagittal sinus thrombosis. Stroke 32:2310–2317
Ozsvath RR, Casey SO, Lustrin ES, et al (1997) Cerebral venography: comparison of CT and MR projection venography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 169:1699–1707
Lafitte F, Boukobza M, Guichard JP, et al (1997) MRI and MRA for diagnosis and follow-up of cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT). Clin Radiol 52:672–679
Majoie CBL, van Straten M, Venema HW, et al (2004) Multisection CT venography of the dural sinuses and cerebral veins by using matched mask bone elimination. AJR Am J Roentgenol 25:787–791
Liang L, Korogi Y, Sugahara T, et al (2001) Evaluation of the intracranial dural sinuses with a 3D contrast-enhanced MP-RAGE sequence: prospective comparison with 2D-TOF MR venography and digital subtraction angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 22:481–492
Liauw L, van Buchem MA, Spilt A, et al (2000) MR angiography of the intracranial venous system. Radiology 214:678–682
Casey SO, Alberico RA, Patel M, et al (1996) Cerebral CT venography. Radiology 198:163–170
Matsumoto M, Kodama N, Sakuma J, et al (2005) 3D-CT arteriography and 3D-CT venography: the separate demonstration of arterial-phase and venous-phase on 3D-CT angiography in a single procedure. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:635–641
Kirchhof K, Welzel T, Jansen O, et al. (2002) More reliable noninvasive visualization of the cerebral veins and dural sinuses: comparison of three MR angiographic techniques. Radiology 224:804–810
Haroum A (2005) Utility of contrast-enhanced 3D turbo-flash MR angiography in evaluating the intracranial venous system. Neuroradiology 47:322–327
Kiliç T, Ozduman K, Çavdar S, et al (2005) The galenic venous system: surgical anatomy and its angiographic and magnetic resonance venographic correlations. Eur J Radiol 56:212–219
Wetzel SG, Kirsch E, Stock KW, et al (1999) Cerebral veins: comparative study of CT venography with intraarterial digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:249–255
Lee J-M, Jung S, Moon K-S, et al (2005) Preoperative evaluation of venous systems with 3-dimensional contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance venography in brain tumors: comparison with time-of-flight magnetic resonance venography and digital subtraction angiography. Surg Neurol 64:128–134
Meder JF, Chiras J, Roland J, et al (1994) Venous territories of the brain. J Neuroradiol 21:118–133
Andeweg J (1996) The anatomy of collateral venous flow from the brain and its value in aetiological interpretation of intracranial pathology. Neuroradiol 38:621–628
Rhoton AL (2002) The cerebral veins. Neurosurgery 51 [4 Suppl]:S159–205
Oka KA, Rhoton AL, Barry M, et al (1985) Microsurgical anatomy of the superficial veins of the cerebrum. Neurosurgery 17:711–748
Bousser M-G (2000) Cerebral venous thrombosis: diagnosis and management. J Neurol 247:252–258
Wasay M, Azeemuddin M (2005) Neuroimaging of cerebral venous thrombosis. J Neuroimaging 15:118–128
Roettger C, Trittmacher S, Gerriets T, et al (2004) Sinus thrombosis after a jump from a small rock and sneezing attack: minor endothelial trauma as a precipitating factor for cerebral venous thrombosis? Headache 44:812–815
Lovblad KO, Schneider J, Bassetti C, et al (2002) Fast contrast-enhanced MR whole-brain venography. Neuroradiology 44:681–688
Acknowledgements
The generosity of the Department of Anatomy and Department of Radiology, Anhui Medical University, for providing access to cadavers, neuroimages and technical assistance is acknowledged. The cadavers were bequeathed for medical education and research purposes and were used with the approval of the Medical Ethic Committee of Anhui Medical University, Hefei, China. The project was funded by the Natural Sciences Foundation of Anhui, China (reference no. 050430602) and a University of Otago Research Grant, New Zealand (reference no. 0020030825).
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, H., Tao, W. & Zhang, M. The dural entrance of cerebral bridging veins into the superior sagittal sinus: an anatomical comparison between cadavers and digital subtraction angiography. Neuroradiology 49, 169–175 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0175-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0175-z