Abstract
Introduction
The aim of this study was to evaluate the role of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in the diagnosis of viral encephalitis and its relationship with the stage of the illness.
Methods
We performed conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) including T1-W, T2-W and fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) sequences and DWI in 18 patients with viral encephalitis diagnosed on the basis of laboratory, clinical and radiologic findings. Based on the qualitative and quantitative comparison of the conventional MRI and DWI, the patients were divided into three groups. Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values of the involved and contralateral normal brain tissues were computed and compared for each group. The degree of correlation between the time (TI) from the onset of neurologic symptoms to the MR examination and ADC values was determined.
Results
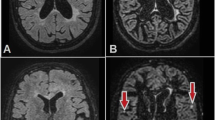
In group I (n=11) DWI was superior to conventional MRI in detecting the encephalitic involved sites and in depicting the borders of the encephalitic lesions. In group II (n=4) DWI was similar to conventional MRI. In group III (n=3) conventional MRI was superior to DWI. Mean ADC values of affected versus contralateral normal brain tissues were 0.458±0.161×10−3 versus 0.86±0.08×10−3 in group I, 0.670±0.142×10−3 versus 0.93±0.07×10−3 in group II, and 1.413±0.211×10−3 versus 1.05±0.06×10−3 in group III. Patients in group I had significantly lower ADC values than those in group II, while patients in group III had the highest ADC values (P<0.05). The ADC values were significantly lower in the affected sites than in the unaffected sites of patients in groups I and II, but were significantly higher in the affected sites than in the unaffected sites of patients in group III (P<0.05). There was an excellent correlation between ADC values and duration of the disease (r=0.874, P=0.01).
Conclusion
DWI is superior to other conventional diagnostic MR sequences in the detection of early viral encephalitic lesions and depiction of the lesion borders and, in combination with other sequences, DWI may contribute to the determination of the disease phase.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Struffert T, Reith W (2000) Herpes simplex virus encephalitis: neuroradiologic differential diagnosis. Radiologe 40:1011–1016
Le Bihan D, Turner R, Douek P, Patronas N (1992) Diffusion MR imaging: clinical applications. AJR Am J Roentgenol 159:591–599
Guo AC, Provenzale JM, Cruz LCH Jr, Petrella JR (2001) Cerebral abscesses: investigation using apparent diffusion coefficient maps. Neuroradiology 43:370–374
Heiner L, Demaerel P (2003) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging findings in a patient with herpes simplex encephalitis. Eur J Radiology 45:195–198
Tsuchiya K, Katase S, Yoshino A, Hachiya J (1999) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of encephalitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 173:1097–1099
Whitley RJ (1990) Viral encephalitis. N Engl J Med 323:242–250
White ML, Edwards-Brown MK (1995) Fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) MRI of herpes encephalitis. J Comput Assist Tomogr 19:501–505
Tsuchiya K, Inaoka S, Mizutani Y, Hachiya J (1997) Fast fluid-attenuated inversion recovery MR of intracranial infections. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18:909–913
Mueller-Mang C, Mang TG, Kalhs P, Thurnher MM (2006) Imaging characteristics of toxoplasmosis encephalitis after bone marrow transplantation: report of two cases and review of the literature. Neuroradiology 48:84–89
Sener RN (2002) Diffusion MRI in Rasmussen’s encephalitis, herpes simplex encephalitis, and bacterial meningoencephalitis. Comput Med Imaging Graph 26:327–332
Prakash M, Kumar S, Gupta RK (2004) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in Japanese encephalitis. J Comput Assist Tomogr 28:756–761
Miyake M (1964) The pathology of Japanese encephalitis. A review. Bull World Health Organ 30:153–160
Küker W, Nagele T, Schmidt F, Heckl S, Herrlinger U (2004) Diffusion-weighted MRI in herpes simplex encephalitis: a report of three cases. Neuroradiology 46:122–125
Jorens PG, Parizel PM, Demey HE, Smets K, Jadoul K, Verbeek MM, Wevers RA, Cras P (2005) Meningoencephalitis caused by Streptococcus pneumonia: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. Diagnosis with diffusion-weighted MRI leading to treatment with corticosteroids. Neuroradiology 47:758–764
Teixeira J, Zimmerman RA, Haselgrove JC, Bilainuk LT, Hunter JV (2001) Diffusion imaging in pediatric central nervous system infections. Neuroradiology 43:1031–1039
Nouranifar RK, Ali M, Nath J (2003) The earliest manifestation of focal encephalitis on diffusion-weighted MRI. Clin Imaging 27:316–320
Provanzale JM, Sorensen AG (1999) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in acute stroke: theoretic consideration and clinical applications. AJR Am J Roentgenol 173:1459–1467
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Grenier P, Cabanis E, Lava-Jeantet M (1986) MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: application of diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders. Radiology 161:401–407
Provenzale JM, Engelters ST, Petrella JR, Smith JS, MacFall JR (1999) Use of MR exponential diffusion-weighted images to eradicate T2 “shine-through” effect. AJR Am J Roentgenol 172:537–539
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiroğlu, Y., Calli, C., Yunten, N. et al. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of viral encephalitis. Neuroradiology 48, 875–880 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0143-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0143-7