Abstract
Introduction
We investigated the role of magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) in the early follow-up of patients after stereotactic radiosurgery (STRS) for cerebral arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) and determined the influence of individual morphological factors of AVMs in early response to treatment.
Methods
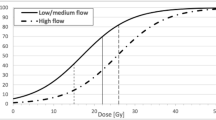
A group of 40 patients (41 AVMs) consented to a dedicated 1.5-T MR protocol 12 months after receiving STRS for a brain AVM. In addition to standard spin echo sequences, 3-D contrast-enhanced sliding interleaved Ky MRA (CE-SLINKY) and dynamic time-resolved subtraction angiography (MR-DSA) were performed. Nidal volumes were calculated using CE-SLINKY data in patients with a persisting arteriovenous shunt. Planning angiographic data was investigated in all 40 patients. The following AVM factors were used in the statistical analysis to determine their role in nidus obliteration: (1) maximum linear dimension, (2) nidal volume, (3) AVM location (4) nidal morphology, (5) venous drainage, (6) “high-flow angiographic change”, (7) prior embolization, and (8) dose reduction.
Results
Complete nidal obliteration was found in 9 patients, 26 showed greater than 50% nidal reduction and 6 had less than 50%. Two AVM factors, venous drainage and AVM location, were found to significantly correlate with rate of obliteration.
Conclusion
We successfully demonstrated the use of MRA to quantitatively assess the response of AVMs to STRS. Two AVM factors, venous drainage and AVM location were found to correlate with rate of obliteration prior to the application of the Bonferroni correction, but if this more rigorous statistical test was applied then none of the factors was found to be significant.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fleetwood IG, Steinberg GK (2002) Arteriovenous malformations. Lancet 359:863–873
Oppenheim C, Meder JF, Trystram D, Nataf F, Godon-Hardy S, Blustajn J, Merienne L, Schlienger M, Fredy D (1999) Radiosurgery of cerebral arteriovenous malformations: is an early angiogram needed? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:475–481
Yamamoto M, Jimbo M, Ide M, Lindquist C, Steiner L (1993) Postradiation volume changes in gamma unit-treated cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Surg Neurol 40:485–490
Kjellberg RN, Hanamura T, Davis KR, Lyons SL, Adams RD (1983) Bragg-peak proton-beam therapy for arteriovenous malformations of the brain. N Engl J Med 309:269–274
Aoki S, Nanbu A, Yoshikawa T, Hori M, Kumagai H, Araki T (1999) 2D in thick-slice MR digital subtraction angiography with one-second temporal resolution: Assessment of cerebrovascular disorders. Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the American Society of Neuroradiology, 1999, Oak Brook, IL. American Society of Neuroradiology, p 122
Griffiths PD, Hoggard N, Warren DJ, Wilkinson ID, Anderson B, Romanowski CA (2000) Brain arteriovenous malformations: assessment with dynamic MR digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1892–1899
Warren DJ, Hoggard N, Walton L, Radatz MW, Kemeny AA, Forster DM, Wilkinson ID, Griffiths PD (2001) Cerebral arteriovenous malformations: comparison of novel magnetic resonance angiographic techniques and conventional catheter angiography. Neurosurgery 48:973–982; discussion 982–983
Nagaraja S, Capener D, Coley SC, Lee KJ, Wilkinson ID, Kemeny AA, Griffiths PD (2005) Brain arteriovenous malformations: measurement of nidal volume using a combination of static and dynamic magnetic resonance angiography techniques. Neuroradiology 47:387–392
Mori H, Aoki S, Okubo T, Hayashi N, Masumoto T, Yoshikawa T, Tago M, Shin M, Kurita H, Abe O, Ohtomo K (2003) Two-dimensional thick-slice MR digital subtraction angiography in the assessment of small to medium-size intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Neuroradiology 45:27–33
Liu K (1999) SLINKY: more understanding, optimisation and application for high resolution MRA. Proceedings of the Seventh Scientific Meeting of the International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, p 1908
Liu K, Lee DH, Rutt BK (1998) Systematic assessment and evaluation of sliding interleaved kY (SLINKY) acquisition for 3D MRA. J Magn Reson Imaging 8:912–923
Liu K, Rutt BK (1998) Sliding interleaved kY (SLINKY) acquisition: a novel 3D MRA technique with suppressed slab boundary artifact. J Magn Reson Imaging 8:903–911
Yamamoto M, Jimbo M, Kobayashi M, Toyoda C, Ide M, Tanaka N, Lindquist C, Steiner L (1992) Long-term results of radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformation: neurodiagnostic imaging and histological studies of angiographically confirmed nidus obliteration. Surg Neurol 37:219–230
Mani RL, Eisenberg RL (1978) Complications of catheter cerebral arteriography: analysis of 5,000 procedures. II. Relation of complication rates to clinical and arteriographic diagnoses. AJR Am J Roentgenol 131:867–869
Mani RL, Eisenberg RL (1978) Complications of catheter cerebral arteriography: analysis of 5,000 procedures. III. Assessment of arteries injected, contrast medium used, duration of procedure, and age of patient. AJR Am J Roentgenol 131:871–874
Mani RL, Eisenberg RL, McDonald EJ Jr, Pollock JA, Mani JR (1978) Complications of catheter cerebral arteriography: analysis of 5,000 procedures. I. Criteria and incidence. AJR Am J Roentgenol 131:861–865
Willinsky RA, Taylor SM, TerBrugge K, Farb RI, Tomlinson G, Montanera W (2003) Neurologic complications of cerebral angiography: prospective analysis of 2,899 procedures and review of the literature. Radiology 227:522–528
Hankey GJ, Warlow CP, Sellar RJ (1990) Cerebral angiographic risk in mild cerebrovascular disease. Stroke 21:209–222
Pasqualin A, Barone G, Cioffi F, Rosta L, Scienza R, Da Pian R (1991) The relevance of anatomic and hemodynamic factors to a classification of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 28:370–379
Colombo F, Pozza F, Chierego G, Casentini L, De Luca G, Francescon P (1994) Linear accelerator radiosurgery of cerebral arteriovenous malformations: an update. Neurosurgery 34:14–20; discussion 20–21
Friedman WA, Bova FJ (1992) Linear accelerator radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 77:832–841
Lunsford LD, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Bissonette DJ, Jungreis CA, Maitz AH, Horton JA, Coffey RJ (1991) Stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations of the brain. J Neurosurg 75:512–524
Steinberg GK, Fabrikant JI, Marks MP, Levy RP, Frankel KA, Phillips MH, Shuer LM, Silverberg GD (1990) Stereotactic heavy-charged-particle Bragg-peak radiation for intracranial arteriovenous malformations. N Engl J Med 323:96–101
Yamamoto Y, Coffey RJ, Nichols DA, Shaw EG (1995) Interim report on the radiosurgical treatment of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. The influence of size, dose, time, and technical factors on obliteration rate. J Neurosurg 83:832–837
Karlsson B, Lax I, Soderman M (1999) Can the probability for obliteration after radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations be accurately predicted? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 43:313–319
Pollock BE, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD, Maitz A, Kondziolka D (1998) Factors associated with successful arteriovenous malformation radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 42:1239–1244; discussion 1244–1247
Petereit D, Mehta M, Turski P, Levin A, Strother C, Mistretta C, Mackie R, Gehring M, Kubsad S, Kinsella T (1993) Treatment of arteriovenous malformations with stereotactic radiosurgery employing both magnetic resonance angiography and standard angiography as a database. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 25:309–313
Meder JF, Oppenheim C, Blustajn J, Nataf F, Merienne L, Lefkoupolos D, Laurent A, Merland JJ, Schlienger M, Fredy D (1997) Cerebral arteriovenous malformations: the value of radiologic parameters in predicting response to radiosurgery. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18:1473–1483
Soderman M, Andersson T, Karlsson B, Wallace MC, Edner G (2003) Management of patients with brain arteriovenous malformations. Eur J Radiol 46:195–205
Engenhart R, Wowra B, Debus J, Kimmig BN, Hover KH, Lorenz W, Wannenmacher M (1994) The role of high-dose, single-fraction irradiation in small and large intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 30:521–529
Colombo F, Benedetti A, Pozza F, Marchetti C, Chierego G (1989) Linear accelerator radiosurgery of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 24:833–840
Duma CM, Lunsford LD, Kondziolka D, Bissonette DJ, Somaza S, Flickinger JC (1993) Radiosurgery for vascular malformations of the brain stem. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 58:92–97
Kemeny AA, Dias PS, Forster DM (1989) Results of stereotactic radiosurgery of arteriovenous malformations: an analysis of 52 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 52:554–558
Chang JH, Chang JW, Park YG, Chung SS (2000) Factors related to complete occlusion of arteriovenous malformations after gamma knife radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 93 [Suppl 3]:96–101
Houdart E, Gobin YP, Casasco A, Aymard A, Herbreteau D, Merland JJ (1993) A proposed angiographic classification of intracranial arteriovenous fistulae and malformations. Neuroradiology 35:381–385
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagaraja, S., Lee, K.J., Coley, S.C. et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain arteriovenous malformations: quantitative MR assessment of nidal response at 1 year and angiographic factors predicting early obliteration. Neuroradiology 48, 821–829 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0131-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0131-y