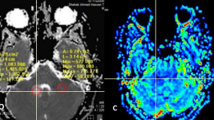
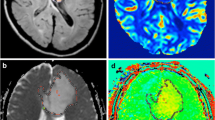
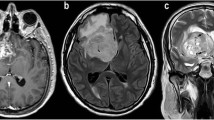
Abstract
Introduction
Contrast-enhanced MR imaging is the method of choice for routine assessment of brain tumors, but it has limited sensitivity and specificity. We verified if the addition of metabolic, diffusion and hemodynamic information improved the definition of glioma extent and grade.
Methods
Thirty-one patients with cerebral gliomas (21 high- and 10 low-grade) underwent conventional MR imaging, proton MR spectroscopic imaging (1H-MRSI), diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) and perfusion weighted imaging (PWI) at 3 Tesla, before undergoing surgery and histological confirmation. Normalized metabolite signals, including choline (Cho), N-acetylaspartate (NAA), creatine and lactate/lipids, were obtained by 1H-MRSI; apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) by DWI; and relative cerebral blood volume (rCBV) by PWI.
Results
Perienhancing areas with abnormal MR signal showed 3 multiparametric patterns: “tumor”, with abnormal Cho/NAA ratio, lower ADC and higher rCBV; “edema”, with normal Cho/NAA ratio, higher ADC and lower rCBV; and “tumor/edema”, with abnormal Cho/NAA ratio and intermediate ADC and rCBV. Perienhancing areas with normal MR signal showed 2 multiparametric patterns: “infiltrated”, with high Cho and/or abnormal Cho/NAA ratio; and “normal”, with normal spectra. Stepwise discriminant analysis showed that the better classification accuracy of perienhancing areas was achieved when regarding all MR variables, while 1H-MRSI variables and rCBV better differentiated high- from low-grade gliomas.
Conclusion
Multiparametric MR assessment of gliomas, based on 1H-MRSI, PWI and DWI, discriminates infiltrating tumor from surrounding vasogenic edema or normal tissues, and high- from low-grade gliomas. This approach may provide useful information for guiding stereotactic biopsies, surgical resection and radiation treatment.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behin A, Hoang-Xuan K, Carpentier AF, Delattre J-Y (2003) Primary brain tumours in adults. Lancet 361:323–331
Grant R (2004) Overview: brain tumour diagnosis and management/Royal College of Physicians guidelines. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75 [Suppl 2]:II18–II23
Schneider JP, Trantakis C, Rubach M, et al (2005) Intraoperative MRI to guide the resection of primary supratentorial glioblastoma multiforme – a quantitative radiological analysis. Neuroradiology 47:489–500
Law M, Yang S, Wang H, et al (2003) Glioma grading: sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values of perfusion MR imaging and proton MR spectroscopic imaging compared with conventional MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1989–1998
Croteau D, Scarpace L, Hearshen D, et al (2001) Correlation between magnetic resonance spectroscopy imaging and image-guided biopsies: semiquantitative and qualitative histopathological analyses of patients with untreated glioma. Neurosurgery 49:823–829
Li X, Lu Y, Pirzkall A, McKnight T, Nelson SJ (2002) Analysis of the spatial characteristics of metabolic abnormalities in newly diagnosed glioma patients. J Magn Reson Imaging 16:229–237
Preul MC, Caramanos Z, Leblanc R, Villemure JG, Arnold DL (1998) Using pattern analysis of in vivo proton MRSI data to improve the diagnosis and surgical management of patients with brain tumors. NMR Biomed 11:192–200
Burtscher IM, Skagerberg G, Geijer B, Englund E, Ståhlberg F, Holtås S (2000) Proton MR spectroscopy and preoperative diagnostic accuracy: an evaluation of intracranial mass lesions characterized by stereotactic biopsy findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:84–93
Dowling C, Bollen AW, Noworolski SM, et al (2001) Preoperative proton MR spectroscopic imaging of brain tumors: correlation with histopathologic analysis of resection specimens. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:604–612
Pirzkall A, Mcknight TR, Graves EE, et al (2001) MR-spectroscopy guided target delineation for high-grade gliomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 50:915–928
Rees J (2003) Advances in magnetic resonance imaging of brain tumours. Curr Opin Neurol 16:643–650
Sugahara T, Korogi Y, Kochi M, et al (1999) Usefulness of diffusion-weighted MRI with echo-planar technique in the evaluation of cellularity in gliomas. J Magn Reson Imaging 9:53–60
Tien RD, Felsberg GJ, Friedman H, Brown M, MacFall J (1994) MR imaging of high-grade cerebral gliomas: value of diffusion-weighted echoplanar pulse sequences. AJR Am J Roentgenol 162:671–677
Brunberg JA, Chenevert TL, McKeever PE, et al (1995) In vivo MR determination of water diffusion coefficients and diffusion anisotropy: correlation with structural alteration in gliomas of the cerebral hemispheres. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 16:361–371
Krabbe K, Gideon P, Wagn P, Hansen U, Thomsen C, Madsen F (1997) MR diffusion imaging of human intracranial tumours. Neuroradiology 39:483–489
Yamasaki F, Kurisu K, Satoh K, et al (2005) Apparent diffusion coefficient of human brain tumors at MR imaging. Radiology 235:985–991
Lam WWM, Poon WS, Metreweli C (2002) Diffusion MR imaging in glioma: does it have any role in the pre-operation determination of grading of glioma? Clin Radiol 57:219–225
Cha S, Knopp EA, Johnson G, Wetzel SG, Litt AW, Zagzag D (2002) Intracranial mass lesions: dynamic contrast-enhanced susceptibility-weighted echo-planar perfusion MR imaging. Radiology 223:11–29
Lam WWM, Chan KW, Wong WL, Poon WS, Metreweli C (2001) Pre-operative grading of intracranial glioma. Acta Radiol 42:548–554
Jackson A, Kassner A, Annesley-Williams D, Reid H, Zhu X-P, Li K-L (2002) Abnormalities in the recirculation phase of contrast agent bolus passage in cerebral gliomas: comparison with relative blood volume and tumor grade. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:7–14
Preul C, Kühn B, Lang EW, Mehdorn M, Heller M, Link J (2003) Differentiation of cerebral tumors using multi-section echo planar MR perfusion imaging. Eur J Radiol 48:244–251
Law M, Yang S, Babb JS, et al (2004) Comparison of cerebral blood volume and vascular permeability from dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced perfusion MR imaging with glioma grade. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:746–755
Muti M, Aprile I, Principi M, et al (2002) Study on the variations of the apparent diffusion coefficient in areas of solid tumor in high grade gliomas. Magn Reson Imaging 20:635–641
Law M, Cha S, Knopp EA, Johnson G, Arnett J, Litt AW (2002) High-grade gliomas and solitary metastases: differentiation by using perfusion and proton spectroscopic MR imaging. Radiology 222:715–721
Tzika AA, Astrakas LG, Zarifi MK, et al (2003) Multiparametric MR assessment of pediatric brain tumors. Neuroradiology 45:1–10
Yang D, Korogi Y, Sugahara T, et al (2002) Cerebral gliomas: prospective comparison of multivoxel 2D chemical-shift imaging proton MR spectroscopy, echoplanar perfusion and diffusion-weighted MRI. Neuroradiology 44:656–666
Chiang IC, Kuo Y-T, Lu C-Y, et al (2004) Distinction between high-grade gliomas and solitary metastases using peritumoral 3-T magnetic resonance spectroscopy, diffusion, and perfusion imagings. Neuroradiology 46:619–627
Bulakbasi N, Kocaoglu M, Örs F, Tayfun C, Üçöz T (2003) Combination of single-voxel proton MR spectroscopy and apparent diffusion coefficient calculation in the evaluation of common brain tumors. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:225–233
Frayne R, Goodyear BG, Dickhoff P, Lauzon ML, Sevick RJ (2003) Magnetic resonance imaging at 3.0 Tesla: challenges and advantages in clinical neurological imaging. Invest Radiol 38:385–402
Manka C, Träber F, Gieseke J, Schild HH, Kuhl CK (2005) Three-dimensional dynamic susceptibility-weighted perfusion MR imaging at 3.0 T: feasibility and contrast agent dose. Radiology 234:869–877
Gupta RK, Sinha U, Cloughesy TF, Alger JR (1999) Inverse correlation between choline magnetic resonance spectroscopy signal intensity and the apparent diffusion coefficient in human glioma. Magn Reson Med 41:2–7
Strugar JG, Criscuolo GR, Rothbart D, Harrington WN (1995) Vascular endothelial growth/permeability factor expression in human glioma specimens: correlation with vasogenic brain edema and tumor-associated cysts. J Neurosurg 83:682–689
Möller-Hartmann W, Herminghaus S, Krings T, et al (2002) Clinical application of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the diagnosis of intracranial mass lesions. Neuroradiology 44:371–381
Cha S, Johnson G, Wadghiri YZ, et al (2003) Dynamic, contrast-enhanced perfusion MRI in mouse gliomas: correlation with histopathology. Magn Reson Med 49:848–855
Strugar J, Rothbart D, Harrington W, Criscuolo GR (1994) Vascular permeability factor in brain metastases: correlation with vasogenic brain edema and tumor angiogenesis. J Neurosurg 81:560–566
Eis M, Els T, Hoehn-Berlage M (1995) High resolution quantitative relaxation and diffusion MRI of three different experimental brain tumors in rat. Magn Reson Med 34:835–844
Watanabe M, Tanaka R, Takeda N (1992) Magnetic resonance imaging and histopathology of cerebral gliomas. Neuroradiology 34:463–469
Li X, Vigneron DB, Cha S, et al (2005) Relationship of MR-derived lactate, mobile lipids, and relative blood volume for gliomas in vivo. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:760–769
Schlemmer H-P, Bachert P, Herfarth KK, Zuna I, Debus J, van Kaick G (2001) Proton MR spectroscopic evaluation of suspicious brain lesions after stereotactic radiotherapy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1316–1324
Acknowledgement
The authors are grateful to Piero Ghedin for expert technical assistance.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di Costanzo, A., Scarabino, T., Trojsi, F. et al. Multiparametric 3T MR approach to the assessment of cerebral gliomas: tumor extent and malignancy. Neuroradiology 48, 622–631 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0102-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0102-3