Abstract
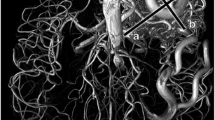
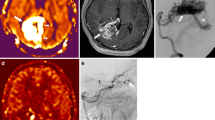
Arteriovenous malformations of the brain are complex vascular lesions that are an important cause of death and long-term disability. Currently, catheter angiography (CA) is the reference standard procedure for the diagnosis and follow-up of treated arteriovenous malformations (AVMs). This is an invasive procedure with potential risks. Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is commonly used in neurovascular imaging as a non-invasive alternative. Various MRA techniques have been used in the diagnosis and follow-up of AVMs but these have suffered from lack of temporal or spatial resolution. In this 60-patient study we describe the combination of two techniques: dynamic magnetic resonance digital subtraction angiography with a high temporal resolution, and a non-dynamic contrast-enhanced time-of-flight sequence with a high spatial resolution technique, in the assessment of AVM. The results showed an excellent correlation between MRA and CA measurement of both maximum linear dimension and AVM nidus volume.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fleetwood IG, Steinberg GK (2002) Arteriovenous malformations. Lancet 359:863–873
Arteriovenous Malformation Study Group (1999) Arteriovenous malformations of the brain in adults. N Engl J Med 340:1812–1818
Brown RD Jr, Wiebers DO, Torner JC, O’Fallon WM (1996) Frequency of intracranial hemorrhage as a presenting symptom and subtype analysis: a population-based study of intracranial vascular malformations in Olmsted Country, Minnesota. J Neurosurg 85:29–32
Willinsky RA, Taylor SM, TerBrugge K, Farb RI, Tomlinson G, Montanera W (2003) Neurologic complications of cerebral angiography: prospective analysis of 2899 procedures and review of the literature. Radiology 227:522–528
Hankey GJ, Warlow CP, Sellar RJ (1990) Cerebral angiographic risk in mild cerebrovascular disease. Stroke 21:209–222
Coley SC, Wild JM, Wilkinson ID, Griffiths PD (2003) Neurovascular MRI with dynamic contrast-enhanced subtraction angiography. Neuroradiology 45:843–850
Griffiths PD, Hoggard N, Warren DJ, Wilkinson ID, Anderson B, Romanowski CA (2000) Brain arteriovenous malformations: assessment with dynamic MR digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1892–1899
Warren DJ, Hoggard N, Walton L, Radatz MW, Kemeny AA, Forster DM, Wilkinson ID, Griffiths PD (2001) Cerebral arteriovenous malformations: comparison of novel magnetic resonance angiographic techniques and conventional catheter angiography. Neurosurgery 48:973–982; discussion 982–983
Aoki S, Yoshikawa T, Hori M, Nanbu A, Kumagai H, Nishiyama Y, Nukui H, Araki T (2000) MR digital subtraction angiography for the assessment of cranial arteriovenous malformations and fistulas. AJR Am J Roentgenol 175:451–453
Spetzler RF, Martin NA (1986) A proposed grading system for arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 65:476–483
Lunsford LD, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Bissonette DJ, Jungreis CA, Maitz AH, Horton JA, Coffey RJ (1991) Stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations of the brain. J Neurosurg 75:512–524
Steiner L, Lindquist C, Adler JR, Torner JC, Alves W, Steiner M (1992) Clinical outcome of radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 77:1–8
Yamamoto Y, Coffey RJ, Nichols DA, Shaw EG (1995) Interim report on the radiosurgical treatment of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. The influence of size, dose, time, and technical factors on obliteration rate. J Neurosurg 83:832–837
Debrun G, Aletich V, Ausman JI, Charbel F, Dujovny M (1997) Embolization of the nidus of brain arteriovenous malformation with n-butyl cyanoacrylate. Neurosurgery 40:112–121
Gobin YP, Laurent A, Merienne L, Schlienger M, Aymard A, Houdart E, Casasco A, Lefkopoulos D, George B, Merland JJ (1996) Treatment of brain arteriovenous malformations by embolization and radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 85:19–28
Oppenheim C, Meder JF, Trystram D, Nataf F, Godon-Hardy S, Blustajn J, Merienne L, Schlienger M, Fredy D (1999) Radiosurgery of cerebral arteriovenous malformations: is an early angiogram needed?. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:475–481
Mani RL, Eisenberg RL (1978) Complications of catheter cerebral arteriography: analysis of 5,000 procedures. III. Assessment of arteries injected, contrast medium used, duration of procedure, and age of patient. AJR Am J Roentgenol 131:871–874
Mani RL, Eisenberg RL (1978) Complications of catheter cerebral arteriography: analysis of 5,000 procedures. II. Relation of complication rates to clinical and arteriographic diagnoses. AJR Am J Roentgenol 131:867–869
Mani RL, Eisenberg RL, McDonald EJ Jr, Pollock JA, Mani JR (1978) Complications of catheter cerebral arteriography: analysis of 5,000 procedures. I. Criteria and incidence. AJR Am J Roentgenol 131:861–865
Kato K, Tomura N, Takahashi S, Sakuma I, Watarai J (2003) Ischemic lesions related to cerebral angiography: evaluation by diffusion weighted MR imaging. Neuroradiology 45:39–43
Bendszus M, Koltzenburg M, Burger R, Warmuth-Metz M, Hofmann E, Solymosi L (1999) Silent embolism in diagnostic cerebral angiography and neurointerventional procedures: a prospective study. Lancet 354:1594–1597
Mori H, Aoki S, Okubo T, Hayashi N, Masumoto T, Yoshikawa T, Tago M, Shin M, Kurita H, Abe O, Ohtomo K (2003) Two-dimensional thick-slice MR digital subtraction angiography in the assessment of small to medium-size intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Neuroradiology 45:27–33
Blatter DD, Parker DL, Ahn SS, Bahr AL, Robison RO, Schwartz RB, Jolesz FA, Boyer RS (1992) Cerebral MR angiography with multiple overlapping thin slab acquisition. Part II. Early clinical experience. Radiology 183:379–389
Blatter DD, Parker DL, Robison RO (1991) Cerebral MR angiography with multiple overlapping thin slab acquisition. Part I. Quantitative analysis of vessel visibility. Radiology 179:805–811
Essig M, Engenhart R, Knopp MV, Bock M, Scharf J, Debus J, Wenz F, Hawighorst H, Schad LR, van Kaick G (1996) Cerebral arteriovenous malformations: improved nidus demarcation by means of dynamic tagging MR-angiography. Magn Reson Imaging 14:227–233
Klisch J, Strecker R, Hennig J, Schumacher M (2000) Time-resolved projection MRA: clinical application in intracranial vascular malformations. Neuroradiology 42:104–107
Parker DL, Tsuruda JS, Goodrich KC, Alexander AL, Buswell HR (1998) Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography of cerebral arteries. A review. Invest Radiol 33:560–572
Tsuchiya K, Katase S, Yoshino A, Hachiya J (2000) MR digital subtraction angiography of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:707–711
Smith HJ, Strother CM, Kikuchi Y, Duff T, Ramirez L, Merless A, Toutant S (1988) MR imaging in the management of supratentorial intracranial AVMs. AJR Am J Roentgenol 150:1143–1153
Pott M, Huber M, Assheuer J, Bewermeyer H (1992) Comparison of MRI, CT and angiography in cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Bildgebung 59:98–102
Liu K, Rutt BK (1998) Sliding interleaved kY (SLINKY) acquisition: a novel 3D MRA technique with suppressed slab boundary artifact. J Magn Reson Imaging 8:903–911
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagaraja, S., Capener, D., Coley, S.C. et al. Brain arteriovenous malformations: measurement of nidal volume using a combination of static and dynamic magnetic resonance angiography techniques. Neuroradiology 47, 387–392 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-005-1349-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-005-1349-9