Abstract
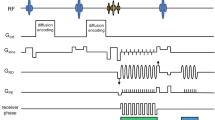
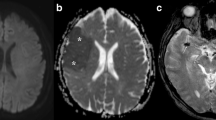
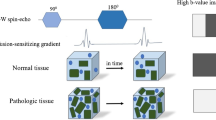
Stroke imaging was revolutionised with the introduction of diffusion-weighted MRI (DWI). The commonly used echoplanar DWI suffers from geometrical distortion near the skull base and the frontal regions and from reduced spatial resolution and fat suppression. To allow a voxel-by-voxel comparison between high-resolution spin-echo images, we implemented spin-echo-based DWI. Motion artefacts were eliminated by phase correction in hybrid frequency-Fourier domain using navigator echoes. In a novel approach, distorted navigator echoes which did not eliminate motion artefacts were replaced with interpolated navigator echoes, leading to restored image information. Navigated DWI yielded high-resolution images in 21 of 24 patients with brain ischaemia, allowing diagnosis of even small or diffuse zones of ischaemia. We determined the spatial distribution and mean of T2- and DWI signal intensity and apparent diffusion coefficients (ADC), using a multidimensional histogram-based analysis. Mean ADC were decreased in ischaemic areas less than 9 days old. The technique may also be useful for high-resolution DWI of tissue other than the brain.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moseley ME, Cohen Y, Mintorovitch J, et al (1990) Early detection of regional cerebral ischemia in cats: comparison of diffusion-weighted and T2-weighted MRI and spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med 14: 330–346
de Crespigny AJ, Marks MP, Enzmann DR, Moseley ME (1995) Navigated diffusion imaging of normal and ischemic human brain. Magn Reson Med 33: 720–728
Lutsep HL, Albers GW, DeCrespigny A, Kamat GN, Marks MP, Moseley ME (1997) Clinical utility of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of ischemic stroke. Ann Neurol 41: 574–580
Geijer B, Brockstedt S, Lindgren A, Ståhlberg F, Norrving B, Holtås S (1999) Radiological diagnosis of acute stroke. Comparison of conventional MR imaging, echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging, and spin-echo diffusion-weighted imaging. Acta Radiol 40: 255–262
Bernarding J, Braun J, Hohmann J, et al (2000) Histogram-based characterization of healthy and ischemic brain tissue using multiparametric MR imaging including ADC maps and relaxometry. Magn Reson Med 43: 53–62
Dietrich O, Heiland S, Benner T, Sartor K (2000) Reducing motion artefacts in diffusion-weighted MRI of the brain: efficacy of navigator echo correction and pulse triggering. Neuroradiology 42: 85–91
Bammer R, Augustin M, Prokesch RW, Stollberger R, Fazekas F (2002) Diffusion-weighted imaging of the spinal cord: interleaved echo-planar imaging is superior to fast spin-echo. J Magn Reson Imaging 15: 364–373
Moseley ME, Butts K, Yenari MA, Marks M, de Crespigny A (1995) Clinical aspects of DWI. NMR Biomed 8: 387–396
Stejskal EO, Tanner JE (1965) Spin diffusion measurements: spin echoes in the presence of a time-dependent field gradient. J Chem Physics 42: 228–292
Anderson W, Gore JC (1994) Analysis and correction of motion artifacts in diffusion weighted imaging. Magn Reson Med 32: 379–387
Warach S, Gaa J, Siewert B, Wielopolski P, Edelman RR (1995) Acute human stroke studied by whole brain echo planar diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 37: 231–241
Pereira RS, Harris AD, Sevick RJ, Frayne R (2002) Effect of b value on contrast during diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging assessment of acute ischemic stroke. J Magn Reson Imaging 15: 591–596
Geijer B, Sundgren PC, Lindgren A, Brockstedt S, Ståhlberg F, Holtås S (2001) The value of b required to avoid T2 shine-through from old lacunar infarcts in diffusion-weighted imaging. Neuroradiology 43: 511–517
Burdette JH, Elster AD (2002). Diffusion-weighted imaging of cerebral infarctions: are higher b values better? J Comput Assist Tomogr 26: 622–627
Chong J, Lu D, Aragao F, et al (1998) Diffusion-weighted MR of acute cerebral infarction: comparison of data processing methods. AJNR 19: 1733–1739
Castillo M, Mukherji SK, Isaacs D, Smith JK (2000) Cerebral infarctions: evaluation with single-axis versus trace diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Am J Roentgenol 174: 853–857
Fletcher LM, Barsotti JB, Hornak JP (1993) A multispectral analysis of brain tissues. Magn Reson Med 29: 623–630
Welch KMA, Windham J, Knight RA, et al (1995) A model to predict the histopathology of human stroke Using diffusion and T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Stroke 26: 1983–1989
Hoehn-Berlage M, Eis M, Back T, Kohno K, Yamashita K (1995) Changes of relaxation times (T1, T2) and apparent diffusion coefficient after permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat: temporal evolution, regional extent, and comparison with histology. Magn Reson Med 34: 824–834
Hossmann KA, Hoehn-Berlage M (1995) Diffusion and perfusion MR imaging of cerebral ischemia. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev 7: 187–217
Warach S, Dashe JF, Edelman RR (1996) Clinical outcome in ischemic stroke predicted by early diffusion-weighted and perfusion magnetic resonance imaging: a preliminary analysis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16: 53–59
Grzesik A, Bernarding J, Braun J, Koennecke HC, Wolf KJ, Tolxdorff T (2000) Characterization of stroke lesions using a histogram-based data analysis including diffusion- and perfusion-weighted imaging. In: Chin-Tu C, Clough AV (eds), Medical imaging: physiology and function from multidimensional images. SPIE 3978 San Diego, pp 23–31
Acknowledgements
This project was partially funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. We would like to thank Jean Pietrowicz for proof reading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bernarding, J., Gedat, E., Koennecke, H.C. et al. Navigated diffusion-weighted imaging with interpolated phase-correction for high-resolution imaging of stroke. Neuroradiology 45, 767–772 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-003-1063-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-003-1063-4