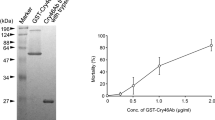
Abstract
Spectrofluorimetric measurements were conducted to quantify, in real-time, membrane permeability changes resulting from the treatment of Sf9 insect cells (Spodoptera frugiperda, Lepidoptera) with different Bacillus thuringiensis Cry insecticidal proteins. Coumarin-derived CD222 and Merocyanin-540 probes were respectively used to monitor extracellular K+ and membrane potential variations upon Sf9 cells incubation with Cry toxins. Our results establish that Cry1C induces, after a delay, the depolarization of the cell membrane and the full depletion of intracellular K+. These changes were not observed upon Sf9 cells treated with Cry1A family toxins. Both the rate of the K+ efflux and the delay before its onset were dependent on toxin concentration. Both parameters were sensitive to temperature but only the delay was affected by pH. Cry1C-induced K+ efflux was inhibited by lanthanum ions in a dose-dependent manner. This study provides the first kinetic and quantitative characterization of the ion fluxes through the channels formed by a Cry toxin in the plasma membrane of a susceptible insect cell line.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 4 October 1999/Revised: 21 December 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guihard, G., Vachon, V., Laprade, R. et al. Kinetic Properties of the Channels Formed by the Bacillus thuringiensis Insecticidal Crystal Protein Cry1C in the Plasma Membrane of Sf9 Cells. J. Membrane Biol. 175, 115–122 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002320001060
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002320001060