Abstract
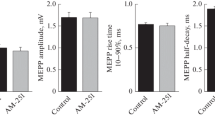
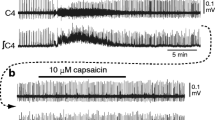
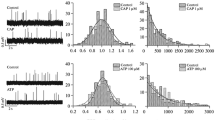
Previous studies have indicated that vanilloid receptor (VR1) mRNA is expressed in muscle fibers. In this study, we evaluated the functional effects of VR1 activation. We measured caffeine-induced contractions in bundles of the extensor digitorum longus muscle of Rana pipiens. Isometric tension measurements showed that two VR1 agonists, capsaicin (CAP) and N-arachidonoyl-dopamine (NADA), reduced muscle peak tension to 57 ± 4 % and 71 ± 3 % of control, respectively. The effect of CAP was partially blocked by a VR1 blocker, capsazepine (CPZ), but the effect of NADA was not changed by CPZ. Because NADA is able to act on cannabinoid receptors, which are also present in muscle fibers, we tested the cannabinoid antagonist AM281. We found that AM281 antagonized both CAP and NADA effects. AM281 alone reduced peak tension to 80 ± 6 % of control. With both antagonists, the CAP effect was completely blocked, and the NADA effect was partially blocked. These results provide pharmacological evidence of the functional presence of the VR1 receptor in fast skeletal muscle fibers of the frog and suggest that capsaicin and NADA reduce tension by activating both cannabinoid and vanilloid receptors.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alworth LC, Harvey SB (2007) IACUC issues associated with amphibian research. ILAR J 48(3):278–289
Bisogno T, Melck D, Bobrov MYu, Gretskaya NM, Bezuglov VV, De Petrocellis L, Di Marzo V (2000) N-acyl-dopamines: novel synthetic CB(1) cannabinoid-receptor ligands and inhibitors of anandamide inactivation with cannabimimetic activity in vitro and in vivo. Biochem J 351(3):817–824
Bleakman D, Brorson JR, Miller RJ (1990) The effect of capsaicin on voltage-gated calcium currents and calcium signals in cultured dorsal root ganglion cells. Br J Pharmacol 101(2):423–431
Cavuoto P, McAinch AJ, Hatzinikolas G, Janovská A, Game P, Wittert GA (2007) The expression of receptors for endocannabinoids in human and rodent skeletal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 364:105–110
Dewey WL (1986) Cannabinoid pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev 38:151–178
Gilly WF, Hui CS (1980) Mechanical activation in slow and twitch skeletal muscle fibers of the frog. J Physiol 301:137–156
Hillard CJ, Manna S, Greenberg MJ, DiCamelli R, Ross RA, Stevenson LA, Murphy V, Pertwee RG, Campbell WB (1999) Synthesis and characterization of potent and selective agonists of the neuronal cannabinoid receptor (CB1). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 289(3):1427–1428
Hopps JJ, Dunn WR, Randall MD (2012) Vasorelaxation to capsaicin and its effects on calcium influx in arteries. Eur J Pharmacol 681(1–3):88–93
Howlett AC, Barth F, Bonner TI, Cabral G, Casellas P, Devane WA, Felder CC, Herkenham M, Mackie K, Martin BR, Mechoulam R, Pertwee RG (2002) International Union of Pharmacology. XXVII. Classification of cannabinoid receptors. Pharmacol Rev 54(2):161–202
Huang SM, Walker JM (2006) Enhancement of spontaneous and heat-evoked activity in spinal nociceptive neurons by the endovanilloid/endocannabinoid N-arachidonoyldopamine (NADA). J Neurophysiol 95(2):1207–1212
Huang SM, Bisogno T, Trevisani M, Al-Hayani A, De Petrocellis L, Fezza F, Tognetto M, Petros TJ, Krey JF, Chu CJ, Miller JD, Davies SN, Geppetti P, Walker JM, Di Marzo V (2002) An endogenous capsaicin-like substance with high potency at recombinant and native vanilloid VR1 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99(12):8400–8405
Huerta M, Muñiz J, Stefani E (1986) Effects of external calcium on potassium contracture in tonic muscle fibers of the frog (Rana pipiens). J Physiol 376:219–230
Huerta M, Ortiz-Mesina M, Trujillo X, Sánchez-Pastor E, Vásquez C, Castro E, Velasco R, Montoya-Pérez R, Onetti C (2009) Effects of cannabinoid on caffeine contractures in slow and fast skeletal muscle fibers of the frog. J Membr Biol 229(2):91–99
Huerta M, Sánchez-Pastor E, Trujillo X, Andrade F (2011) Co-localization of the cannabinoid 1 and acetylcholine receptors in the motor-endplate of the frog. 40th Annual meeting Washington USA C920
Institute for Laboratory Animal Research (1996) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. National Research Council, Commision on life science, pp 1–50
Jordt SE, Julius D (2002) Molecular basis for species-specific sensitivity to “hot” chili peppers. Cell 108(3):421–430
Kuffler SW, Vaughan-Williams EM (1953) Properties of the ‘slow’ skeletal muscles fibers of the frog. J Physiol 21(2):318–340
Lo YC, Wu SN, Wu JR, Chen IJ (1995) Effect of capsaicin on membrane currents in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells of rat aorta. Eur J Pharmacol 292(3–4):321–328
Lotteau S, Ducreux S, Romestaing C, Legrand C, Van Coppenolle F (2013) Characterization of functional TRPV1 channels in the sarcoplasmic reticulum of mouse skeletal muscle. PLoS ONE 8(3):e58673
Marinelli S, Di Marzo V, Florenzano F, Fezza F, Viscomi MT, van der Stelt M, Bernardi G, Molinari M, Maccarrone M, Mercuri NB (2007) N-arachidonoyl-dopamine tunes synaptic transmission onto dopaminergic neurons by activating both cannabinoid and vanilloid receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 32(2):298–308
Olah Z, Szabos T, Karai L, Hough C, Fields RD, Caudle RM, Blumberg PM, Ladarola MJ (2001) Ligand-induced dynamic membrane changes and cell deletion conferred by vanilloid receptor 1. J Biol Chem 276:11021–11030
Sánchez-Pastor E, Trujillo X, Huerta M, Andrade F (2007) Effects of cannabinoids on synaptic transmission in the frog neuromuscular junction. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 321(2):439–445
Sañudo-Peña MC, Romero J, Seale GE, Fernandez-Ruiz JJ, Walker JM (2000) Activational role of cannabinoids on movement. Eur J Pharmacol. 391(3):269–274
Silveira PE, Silveira NA, Morini Vde C, Kushmerick C, Naves LA (2010) Opposing effects of cannabinoids and vanilloids on evoked quantal release at the frog neuromuscular junction. Neurosci Lett 473(2):97–101
Soderstrom K, Leid M, Moore FL, Murray TF (2000) Behavioral, pharmacological, and molecular characterization of an amphibian cannabinoid receptor. J Neurochem 75(1):413–423
Starowicz K, Nigam S, Di Marzo V (2007) Biochemistry and pharmacology of endovanilloids. Pharmacol Ther 114(1):13–33
Starowicz K, Cristino L, Di Marzo V (2008) TRPV1 receptors in the central nervous system: potential for previously unforeseen therapeutic applications. Curr Pharm Des 14(1):42–54
Starowicz K, Makuch W, Osikowicz M, Piscitelli F, Petrosino S, Di Marzo V, Przewlocka B (2012) Spinal anandamide produces analgesia in neuropathic rats: possible CB(1)- and TRPV1-mediated mechanisms. Neuropharmacology 62(4):1746–1755
Szallasi A, Blumberg PM (1999) Vanilloid (Capsaicin) receptors and mechanisms. Pharmacol Rev 51(2):159–212
Thyagarajan B, Krivitskaya N, Potian JG, Hognason K, Garcia CC, McArdle JJ (2009) Capsaicin protects mouse neuromuscular junctions from the neuroparalytic effects of botulinum neurotoxin A. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 331(2):361–371
Tóth A, Boczán J, Kedei N, Lizanecz E, Bagi Z, Papp Z, Edes I, Csiba L, Blumberg PM (2005) Expression and distribution of vanilloid receptor 1 (TRPV1) in the adult rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 135(1–2):162–168
Trujillo X, Sánchez-Pastor E, Andrade F, Huerta M (2014a) Effects of cannabinoids on tension induced by acetylcholine and choline in slow skeletal muscle fibers of the frog. J Membr Biol 247(1):57–62
Trujillo X, Sánchez-Pastor E, Andrade F, Huerta M (2014b) Presence and colocalization of type-1 cannabinoid receptors with acetylcholine receptors in the motor end-plate of twitch skeletal muscle fibers in the frog. J Membr Biol. doi:10.1007/s00232-014-9721-5
Velasco R, Trujillo X, Vásquez C, Huerta M, Trujillo-Hernández B (2003) Effect of dimethyl sulfoxide on excitation-contraction coupling in chicken slow skeletal muscle. J Pharmacol Sci 93(2):149–154
Vriens J, Appendino G, Nilius B (2009) Pharmacology of vanilloid transient receptor potential cation channels. Mol Pharmacol 75(6):1262–1279
Wu ZZ, Chen SR, Pan HL (2005) Transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 activation down-regulates voltage-gated calcium channels through calcium-dependent calcineurin in sensory neurons. J Biol Chem 280(18):18142–18151
Xin H, Tanaka H, Yamaguchi M, Takemori S, Nakamura A, Kohama K (2005) Vanilloid receptor expressed in the sarcoplasmic reticulum of rat skeletal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 332:756–762
Yeon D, Kwon S, Lee Y, Leem J, Nam T, Ahn D (2001) Capsaicin-induced relaxation in rabbit coronary artery. J Vet Med Sci 63(5):499–503
Zajicek J, Fox P, Sanders H, Wright D, Vickery J, Nunn A, Thompson A, UK MS Research Group (2003) Cannabinoids for treatment of spasticity and other symptoms related to multiple sclerosis (CAMS study): multicentre randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 362(9395):1517–1526
Zygmunt PM, Petersson J, Andersson DA, Chuang H, Sorgard M, Di Marzo V, Julius D, Hogestatt ED (1999) Vanilloid receptors on sensory nerves mediate the vasodilator action of anandamide. Nature 400(6743):452–457
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xóchitl Trujillo, Mónica Ortiz-Mesina and Tannia Uribe have equally contributed to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trujillo, X., Ortiz-Mesina, M., Uribe, T. et al. Capsaicin and N-Arachidonoyl-dopamine (NADA) Decrease Tension by Activating Both Cannabinoid and Vanilloid Receptors in Fast Skeletal Muscle Fibers of the Frog. J Membrane Biol 248, 31–38 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-014-9727-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-014-9727-z