Abstract
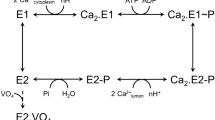
The human α1/His10-β1 isoform of Na,K-ATPase has been reconstituted as a complex with and without FXYD1 into proteoliposomes of various lipid compositions in order to study the effect of the regulatory subunit on the half-saturating Na+ concentration (K 1/2) of Na+ ions for activation of the ion pump. It has been shown that the fraction of negatively charged lipid in the bilayer crucially affects the regulatory properties. At low concentrations of the negatively charged lipid DOPS (<10 %), FXYD1 increases K 1/2 of Na+ ions for activation of the ion pump. Phosphorylation of FXYD1 by protein kinase A at Ser68 abrogates this effect. Conversely, for proteoliposomes made with high concentrations of DOPS (>10 %), little or no effect of FXYD1 on the K 1/2 of Na+ ions is observed. Depending on ionic strength and lipid composition of the proteoliposomes, FXYD1 can alter the K 1/2 of Na+ ions by up to twofold. We propose possible molecular mechanisms to explain the regulatory effects of FXYD1 and the influence of charged lipid and protein phosphorylation. In particular, the positively charged C-terminal helix of FXYD1 appears to be highly mobile and may interact with the cytoplasmic N domain of the α-subunit, the interaction being strongly affected by phosphorylation at Ser68 and the surface charge of the membrane.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson RG (1998) The caveolae membrane system. Annu Rev Biochem 67:199–225
Apell H-J, Bersch B (1987) Oxonol VI as an optical indicator for membrane potentials in lipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta 903:480–494
Apell H-J, Marcus MM, Anner BM, Oetliker H, Läuger P (1985) Optical study of active ion transport in lipid vesicles containing reconstituted Na,K-ATPase. J Membr Biol 85:49–63
Apell H-J, Häring V, Roudna M (1990) Na,K-ATPase in artificial lipid vesicles: comparison of Na, K and Na- only pumping mode. Biochim Biophys Acta 1023:81–90
Bibert S, Roy S, Schaer D, Horisberger JD, Geering K (2008) Phosphorylation of phospholemman (FXYD1) by protein kinases A and C modulates distinct Na,K-ATPase isozymes. J Biol Chem 283:476–486
Bossuyt J, Despa S, Han F, Hou Z, Robia SL, Lingrel JB, Bers DM (2009) Isoform specificity of the Na/K-ATPase association and regulation by phospholemman. J Biol Chem 284:26749–26757
Brown DA, Rose JK (1992) Sorting of GPI-anchored proteins to glycolipid-enriched membrane subdomains during transport to the apical cell surface. Cell 68:533–544
Cirri E, Katz A, Mishra NK, Belogus T, Lifshitz Y, Garty H, Karlish SJ, Apell HJ (2011) Phospholemman (FXYD1) raises the affinity of the human α1β1 isoform of Na,K-ATPase for Na ions. Biochemistry 50:3736–3748
Cohen E, Goldshleger R, Shainskaya A, Tal DM, Ebel C, leMaire M, Karlish SJ (2005) Purification of Na+, K+-ATPase expressed in Pichia pastoris reveals an essential role of phospholipid–protein interactions. J Biol Chem 280:16610–16618
Cornelius F, Mahmmoud YA (2003) Functional modulation of the sodium pump: the regulatory proteins “Fixit”. News Physiol Sci 18:119–124
Crambert G, Geering K (2003) FXYD proteins: new tissue-specific regulators of the ubiquitous Na,K-ATPase. Sci STKE 2003:RE1
Crambert G, Beguin P, Pestov NB, Modyanov NN, Geering K (2002a) βm, a structural member of the X, K-ATPase β subunit family, resides in the ER and does not associate with any known X, K-ATPase α subunit. Biochemistry 41:6723–6733
Crambert G, Fuzesi M, Garty H, Karlish S, Geering K (2002b) Phospholemman (FXYD1) associates with Na, K-ATPase and regulates its transport properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:11476–11481
de Pont JJHHM, van Prooijen-van Eeden A, Bonting SL (1978) Role of negatively charged phospholipids in highly purified (Na++K+)-ATPase from rabbit kidney outer medulla. Biochim Biophys Acta 508:464–477
Despa S, Bossuyt J, Han F, Ginsburg KS, Jia LG, Kutchai H, Tucker AL, Bers DM (2005) Phospholemman-phosphorylation mediates the beta-adrenergic effects on Na/K pump function in cardiac myocytes. Circ Res 97:252–259
Feschenko MS, Donnet C, Wetzel RK, Asinovski NK, Jones LR, Sweadner KJ (2003) Phospholemman, a single-span membrane protein, is an accessory protein of Na,K-ATPase in cerebellum and choroid plexus. J Neurosci 23:2161–2169
Floyd RV, Wray S, Martin-Vasallo P, Mobasheri A (2010) Differential cellular expression of FXYD1 (phospholemman) and FXYD2 (gamma subunit of Na,K-ATPase) in normal human tissues: a study using high density human tissue microarrays. Ann Anat 192:7–16
Franzin CM, Gong XM, Teriete P, Marassi FM (2007) Structures of the FXYD regulatory proteins in lipid micelles and membranes. J Bioenerg Biomembr 39:379–383
Fuller W, Eaton P, Bell JR, Shattock MJ (2004) Ischemia-induced phosphorylation of phospholemman directly activates rat cardiac Na/K-ATPase. FASEB J 18:197–199
Fuller W, Howie J, McLatchie LM, Weber RJ, Hastie CJ, Burness K, Pavlovic D, Shattock MJ (2009) FXYD1 phosphorylation in vitro and in adult rat cardiac myocytes: threonine 69 is a novel substrate for protein kinase C. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 296:C1346–C1355
Garty H, Karlish SJ (2006) Role of FXYD proteins in ion transport. Annu Rev Physiol 68:431–459
Geering K (2005) Function of FXYD proteins, regulators of Na,K-ATPase. J Bioenerg Biomembr 37:387–392
Geering K (2006) FXYD proteins: new regulators of Na-K-ATPase. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290:F241–F250
Geering K (2008) Functional roles of Na,K-ATPase subunits. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 17:526–532
Geering K, Beguin P, Garty H, Karlish S, Fuzesi M, Horisberger JD, Crambert G (2003) FXYD proteins: new tissue- and isoform-specific regulators of Na,K-ATPase. Ann N Y Acad Sci 986:388–394
Gloster J, Harris P (1969) The lipid composition of mitochondrial and microsomal fractions of human myocardial homogenates. Cardiovasc Res 3:45–51
Habeck M, Cirri E, Katz A, Karlish SJ, Apell HJ (2009) Investigation of electrogenic partial reactions in detergent-solubilized Na,K-ATPase. Biochemistry 48:9147–9155
Han F, Tucker AL, Lingrel JB, Despa S, Bers DM (2009) Extracellular potassium dependence of the Na+-K+-ATPase in cardiac myocytes: isoform specificity and effect of phospholemman. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 297:C699–C705
Han F, Bossuyt J, Martin JL, Despa S, Bers DM (2010) Role of phospholemman phosphorylation sites in mediating kinase-dependent regulation of the Na+-K+-ATPase. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 299:C1363–C1369
Haviv H, Cohen E, Lifshitz Y, Tal DM, Goldshleger R, Karlish SJ (2007) Stabilization of Na+, K+-ATPase purified from Pichia pastoris membranes by specific interactions with lipids. Biochemistry 46:12855–12867
Hughes E, Whittaker CA, Barsukov IL, Esmann M, Middleton DA (2011) A study of the membrane association and regulatory effect of the phospholemman cytoplasmic domain. Biochim Biophys Acta 1808:1021–1031
Jørgensen PL (1974) Isolation of (Na++K+)-ATPase. Methods Enzymol 32:277–290
Katz A, Lifshitz Y, Bab-Dinitz E, Kapri-Pardes E, Goldshleger R, Tal DM, Karlish SJ (2010) Selectivity of digitalis glycosides for isoforms of human Na,K-ATPase. J Biol Chem 285:19582–19592
Lambert O, Levy D, Ranck JL, Leblanc G, Rigaud JL (1998) A new “gel-like” phase in dodecyl maltoside–lipid mixtures: implications in solubilization and reconstitution studies. Biophys J 74:918–930
Lifshitz Y, Lindzen M, Garty H, Karlish SJ (2006) Functional interactions of phospholemman (PLM) (FXYD1) with Na+, K+-ATPase: purification of α1/β1/PLM complexes expressed in Pichia pastoris. J Biol Chem 281:15790–15799
Lifshitz Y, Petrovich E, Haviv H, Goldshleger R, Tal DM, Garty H, Karlish SJ (2007) Purification of the human α2 isoform of Na,K-ATPase expressed in Pichia pastoris: stabilization by lipids and FXYD1. Biochemistry 46:14937–14950
Liu L, Askari A (2006) Beta-subunit of cardiac Na+-K+-ATPase dictates the concentration of the functional enzyme in caveolae. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 291:C569–C578
Liu L, Mohammadi K, Aynafshar B, Wang H, Li D, Liu J, Ivanov AV, Xie Z, Askari A (2003) Role of caveolae in signal-transducing function of cardiac Na+/K+-ATPase. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 284:C1550–C1560
McLaughlin S (1977) Electrostatic potentials at membrane–solution interfaces. Current topics in membranes and transport, vol 9. Academic Press, New York, pp 71–144
Mishra NK, Peleg Y, Cirri E, Belogus T, Lifshitz Y, Voelker DR, Apell HJ, Garty H, Karlish SJ (2011) FXYD proteins stabilize Na,K-ATPase: amplification of specific phosphatidylserine–protein interactions. J Biol Chem 286:9699–9712
Morth JP, Pedersen BP, Toustrup-Jensen MS, Sorensen TL, Petersen J, Andersen JP, Vilsen B, Nissen P (2007) Crystal structure of the sodium–potassium pump. Nature 450:1043–1049
Palmer CJ, Scott BT, Jones LR (1991) Purification and complete sequence determination of the major plasma membrane substrate for cAMP-dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C in myocardium. J Biol Chem 266:11126–11130
Pavlovic D, Fuller W, Shattock MJ (2007) The intracellular region of FXYD1 is sufficient to regulate cardiac Na/K ATPase. FASEB J 21:1539–1546
Post LL, Schuel R, Schuel H (1988) Evidence that hatching enzyme of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus is a chymotrypsin-like protease. Biochem Cell Biol 66:1200–1209
Presti CF, Jones LR, Lindemann JP (1985a) Isoproterenol-induced phosphorylation of a 15-kilodalton sarcolemmal protein in intact myocardium. J Biol Chem 260:3860–3867
Presti CF, Scott BT, Jones LR (1985b) Identification of an endogenous protein kinase C activity and its intrinsic 15-kilodalton substrate in purified canine cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles. J Biol Chem 260:13879–13889
Schneeberger A, Apell H-J (1999) Ion selectivity of the cytoplasmic binding sites of the Na,K-ATPase: I. Sodium binding is associated with a conformational rearrangement. J Membr Biol 168:221–228
Schwartz AK, Nagano M, Nakao M, Lindenmayer GE, Allen JC (1971) The sodium- and potassium-activated adenosinetriphosphatase system. Methods Pharmacol 1:361–388
Shinoda T, Ogawa H, Cornelius F, Toyoshima C (2009) Crystal structure of the sodium–potassium pump at 2.4 a resolution. Nature 459:446–450
Silverman BZ, Fuller W, Eaton P, Deng J, Moorman JR, Cheung JY, James AF, Shattock MJ (2005) Serine 68 phosphorylation of phospholemman: acute isoform-specific activation of cardiac Na/K-ATPase. Cardiovasc Res 65:93–103
Smart EJ, Graf GA, McNiven MA, Sessa WC, Engelman JA, Scherer PE, Okamoto T, Lisanti MP (1999) Caveolins, liquid-ordered domains, and signal transduction. Mol Cell Biol 19:7289–7304
Sweadner KJ, Rael E (2000) The FXYD gene family of small ion transport regulators or channels: cDNA sequence, protein signature sequence, and expression. Genomics 68:41–56
Teriete P, Franzin CM, Choi J, Marassi FM (2007) Structure of the Na,K-ATPase regulatory protein FXYD1 in micelles. Biochemistry 46:6774–6783
Walaas SI, Czernik AJ, Olstad OK, Sletten K, Walaas O (1994) Protein kinase C and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylate phospholemman, an insulin and adrenaline-regulated membrane phosphoprotein, at specific sites in the carboxy terminal domain. Biochem J 304(Pt 2):635–640
Acknowledgments
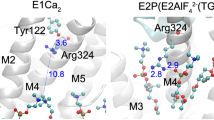
We thank Dr. Kay Diederichs for his help in creating the figures with the molecular structures. The work was financially supported by the German Israeli Foundation (Grant 922-165.9 to H.-J. A. and S. J. K.)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cirri, E., Kirchner, C., Becker, S. et al. Surface Charges of the Membrane Crucially Affect Regulation of Na,K-ATPase by Phospholemman (FXYD1). J Membrane Biol 246, 967–979 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-013-9600-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-013-9600-5