Abstract
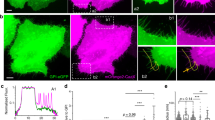
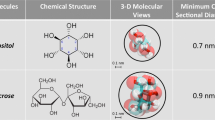
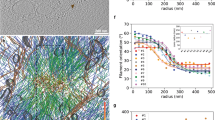
We describe a new phenomenon of anodotropic pseudopod-like blebbing in U937 cells stimulated by nanosecond pulsed electric field (nsPEF). In contrast to “regular,” round-shaped blebs, which are often seen in response to cell damage, pseudopod-like blebs (PLBs) formed as longitudinal membrane protrusions toward anode. PLB length could exceed the cell diameter in 2 min of exposure to 60-ns, 10-kV/cm pulses delivered at 10–20 Hz. Both PLBs and round-shaped nsPEF-induced blebs could be efficiently inhibited by partial isosmotic replacement of bath NaCl for a larger solute (sucrose), thereby pointing to the colloid-osmotic water uptake as the principal driving force for bleb formation. In contrast to round-shaped blebs, PLBs retracted within several minutes after exposure. Cells treated with 1 nM of the actin polymerization blocker cytochalasin D were unable to form PLBs and instead produced stationary, spherical blebs with no elongation or retraction capacity. Live cell fluorescent actin tagging showed that during elongation actin promptly entered the PLB interior, forming bleb cortex and scaffold, which was not seen in stationary blebs. Overall, PLB formation was governed by both passive (physicochemical) effects of membrane permeabilization and active cytoskeleton assembly in the living cell. To a certain extent, PLB mimics the membrane extension in the process of cell migration and can be employed as a nonchemical model for studies of cytomechanics, membrane–cytoskeleton interaction and cell motility.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
André FM, Rassokhin MA, Bowman AM, Pakhomov AG (2010) Gadolinium blocks membrane permeabilization induced by nanosecond electric pulses and reduces cell death. Bioelectrochemistry 79(1):95–100
Barros LF, Kanaseki T, Sabirov R, Morishima S, Castro J, Bittner CX, Maeno E, Ando-Akatsuka Y, Okada Y (2003) Apoptotic and necrotic blebs in epithelial cells display similar neck diameters but different kinase dependency. Cell Death Differ 10(6):687–697
Bereiter-Hahn J (2005) Mechanics of crawling cells. Med Eng Phys 27(9):743–753
Bereiter-Hahn J, Luck M, Miebach T, Stelzer HK, Voth M (1990) Spreading of trypsinized cells: cytoskeletal dynamics and energy requirements. J Cell Sci 96(1):171–188
Blaser H, Reichman-Fried M, Castanon I, Dumstrei K, Marlow FL, Kawakami K, Solnica-Krezel L, Heisenberg CP, Raz E (2006) Migration of zebrafish primordial germ cells: a role for myosin contraction and cytoplasmic flow. Dev Cell 11(5):613–627
Bowman A, Nesin O, Pakhomova O, Pakhomov A (2010) Analysis of plasma membrane integrity by fluorescent detection of Tl+ uptake. J Membr Biol 236(1):15–26
Charras GT (2008) A short history of blebbing. J Microsc 231(3):466–478
Charras G, Paluch E (2008) Blebs lead the way: how to migrate without lamellipodia. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9(9):730–736
Charras GT, Yarrow JC, Horton MA, Mahadevan L, Mitchison TJ (2005) Non-equilibration of hydrostatic pressure in blebbing cells. Nature 435(7040):365–369
Charras GT, Hu C-K, Coughlin M, Mitchison TJ (2006) Reassembly of contractile actin cortex in cell blebs. J Cell Biol 175(3):477–490
Charras GT, Mitchison TJ, Mahadevan L (2009) Animal cell hydraulics. J Cell Sci 122(18):3233–3241
Chhabra ES, Higgs HN (2007) The many faces of actin: matching assembly factors with cellular structures. Nat Cell Biol 9(10):1110–1121
Cunningham CC (1995) Actin polymerization and intracellular solvent flow in cell surface blebbing. J Cell Biol 129(6):1589–1599
Cunningham CC, Gorlin JB, Kwiatkowski DJ, Hartwig JH, Janmey PA, Byers HR, Stossel TP (1992) Actin-binding protein requirement for cortical stability and efficient locomotion. Science 255(5042):325–327
Dai J, Sheetz MP (1999) Membrane tether formation from blebbing cells. Biophys J 77(6):3363–3370
Deng J, Schoenbach KH, Stephen Buescher E, Hair PS, Fox PM, Beebe SJ (2003) The effects of intense submicrosecond electrical pulses on cells. Biophys J 84(4):2709–2714
Derivery E, Fink J, Martin D, Houdusse A, Piel M, Stradal TE, Louvard D, Gautreau A (2008) Free brick1 is a trimeric precursor in the assembly of a functional wave complex. PLoS ONE 3(6):e2462
Fackler OT, Grosse R (2008) Cell motility through plasma membrane blebbing. J Cell Biol 181(6):879–884
Frey W, White JA, Price RO, Blackmore PF, Joshi RP, Nuccitelli R, Beebe SJ, Schoenbach KH, Kolb JF (2006) Plasma membrane voltage changes during nanosecond pulsed electric field exposure. Biophys J 90(10):3608–3615
Gass GV, Chernomordik LV (1990) Reversible large-scale deformations in the membranes of electrically-treated cells: electroinduced bleb formation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1023(1):1–11
Hoffmann EK, Lambert IH, Pedersen SF (2009) Physiology of cell volume regulation in vertebrates. Physiol Rev 89(1):193–277
Hogue MJ (1919) The effect of hypotonic and hypertonic solutions on fibroblasts of the embryonic chick heart in vitro. J Exp Med 30(6):617–648
Holtfreter J (1944) A study of the mechanics of gastrulation. J Exp Zool 95(2):171–212
Keller H, Eggli P (1998) Protrusive activity, cytoplasmic compartmentalization, and restriction rings in locomoting blebbing Walker carcinosarcoma cells are related to detachment of cortical actin from the plasma membrane. Cell Motil Cytoskelet 41(2):181–193
Keller H, Rentsch P, Hagmann J (2002) Differences in cortical actin structure and dynamics document that different types of blebs are formed by distinct mechanisms. Exp Cell Res 277(2):161–172
Kinosita K Jr, Tsong TT (1977) Hemolysis of human erythrocytes by transient electric field. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74(5):1923–1927
Lang TU, Khalbuss WE, Monaco SE, Michelow P, Pantanowitz L (2011) Review of HIV-related cytopathology. Pathol Res Int 2011:256083
Loitto V-M, Forslund T, Sundqvist T, Magnusson K-E, Gustafsson M (2002) Neutrophil leukocyte motility requires directed water influx. J Leukocyte Biol 71(2):212–222
Maugis B, Brugues J, Nassoy P, Guillen N, Sens P, Amblard F (2010) Dynamic instability of the intracellular pressure drives bleb-based motility. J Cell Sci 123(22):3884–3892
Mitchison TJ, Charras GT, Mahadevan L (2008) Implications of a poroelastic cytoplasm for the dynamics of animal cell shape. Semin Cell Dev Biol 19(3):215–223
Nesin OM, Pakhomova ON, Xiao S, Pakhomov AG (2011) Manipulation of cell volume and membrane pore comparison following single cell permeabilization with 60- and 600-ns electric pulses. Biochim Biophys Acta 1808(3):792–801
Norman L, Sengupta K, Aranda-Espinoza H (2011) Blebbing dynamics during endothelial cell spreading. Eur J Cell Biol 90(1):37–48
Pakhomov AG, Pakhomova ON (2010) Nanopores: a distinct transmembrane passageway in electroporated cells. In: Pakhomov AG, Miklavcic D, Markov MS (eds) Advanced electroporation techniques in biology and medicine. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 178–194
Pakhomov AG, Bowman AM, Ibey BL, Andre FM, Pakhomova ON, Schoenbach KH (2009) Lipid nanopores can form a stable, ion channel-like conduction pathway in cell membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 385(2):181–186
Petersen MA, Dailey ME (2004) Diverse microglial motility behaviors during clearance of dead cells in hippocampal slices. Glia 46(2):195–206
Pletjushkina OJ, Rajfur Z, Pomorski P, Oliver TN, Vasiliev JM, Jacobson KA (2001) Induction of cortical oscillations in spreading cells by depolymerization of microtubules. Cell Motil Cytoskelet 48(4):235–244
Pollard TD, Borisy GG (2003) Cellular motility driven by assembly and disassembly of actin filaments. Cell 112(4):453–465
Rassokhin MA, Pakhomov AG (2010) Fast anodotropic expansion of cell membrane under exposure to high-rate nanosecond duration electric pulses (nsEP). In: The American society for cell biology 50th annual meeting, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 11–15 December 2010
Rassokhin MA, Pakhomov AG (2011) Cell reshaping triggered by nanosecond electric pulses (nsEP). In: 8th international bioelectrics symposium, Toulouse, France, 4–6 May 2011
Saulis G (1999) Cell electroporation: estimation of the number of pores and their sizes. Biomed Sci Instrum 35:291–296
Sebbagh M, Renvoize C, Hamelin J, Riche N, Bertoglio J, Breard J (2001) Caspase-3-mediated cleavage of ROCK I induces MLC phosphorylation and apoptotic membrane blebbing. Nat Cell Biol 3(4):346–352
Sheth B, Banks P, Burton DR, Monk PN (1991) The regulation of actin polymerization in differentiating U937 cells correlates with increased membrane levels of the pertussis-toxin-sensitive G-protein Gi2. Biochem J 275(Pt 3):809–811
Tekle E, Wolfe MD, Oubrahim H, Chock PB (2008) Phagocytic clearance of electric field induced “apoptosis-mimetic” cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 376(2):256–260
Tinevez J-Y, Schulze U, Salbreux G, Roensch J, Joanny J-F, Paluch E (2009) Role of cortical tension in bleb growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(44):18581–18586
Torgerson RR, McNiven MA (1998) The actin-myosin cytoskeleton mediates reversible agonist-induced membrane blebbing. J Cell Sci 111(19):2911–2922
Tsong TY (1991) Electroporation of cell membranes. Biophys J 60(2):297–306
White J, Pliquett U, Blackmore P, Joshi R, Schoenbach K, Kolb J (2011) Plasma membrane charging of Jurkat cells by nanosecond pulsed electric fields. Eur Biophys J 40(8):947–957
Yang C, Hoelzle M, Disanza A, Scita G, Svitkina T (2009) Coordination of membrane and actin cytoskeleton dynamics during filopodia protrusion. PLoS ONE 4(5):e5678
Zollinger HU (1948) Cytologic studies with the phase microscope; morphologic changes associated with the death of cells in vitro and in vivo. Am J Pathol 24(5):1039–1053
Acknowledgments
The work was funded by R01CA125482 from the National Cancer Institute and R01GM088303 from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rassokhin, M.A., Pakhomov, A.G. Electric Field Exposure Triggers and Guides Formation of Pseudopod-Like Blebs in U937 Monocytes. J Membrane Biol 245, 521–529 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-012-9433-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-012-9433-7