Abstract
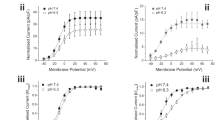
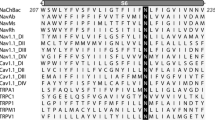
The one-domain voltage-gated sodium channel of Bacillus halodurans (NaChBac) is composed of six transmembrane segments (S1–S6) comprising a pore-forming region flanked by segments S5 and S6 and a voltage-sensing element composed of segment S4. To investigate the role of the S4 segment in NaChBac channel activation, we used the cysteine mutagenesis approach where the positive charges of single and multiple arginine (R) residues of the S4 segment were replaced by the neutrally charged amino acid cysteine (C). To determine whether it was the arginine residue itself or its positive charge that was involved in channel activation, arginine to lysine (R to K) mutations were constructed. Wild-type (WT) and mutant NaChBac channels were expressed in tsA201 cells and Na+ currents were recorded using the whole-cell configuration of the patch-clamp technique. The current/voltage (I-V) and conductance/voltage (G-V) relationships steady-state inactivation (h ∞) and recovery from inactivation were evaluated to determine the effects of the S4 mutations on the biophysical properties of the NaChBac channel. R to C on the S4 segment resulted in a slowing of both activation and inactivation kinetics. Charge neutralization of arginine residues mostly resulted in a shift toward more positive potentials of G-V and h ∞ curves. The G-V curve shifts were associated with a decrease in slope, which may reflect a decrease in the gating charge involved in channel activation. Single neutralization of R114, R117, or R120 by C resulted in a very slow recovery from inactivation. Double neutralization of R111 and R129 confirmed the role of R111 in activation and suggested that R129 is most probably not part of the voltage sensor. Most of the R to K mutants retained WT-like current kinetics but exhibited an intermediate G-V curve, a steady-state inactivation shifted to more hyperpolarized potentials, and intermediate time constants of recovery from inactivation. This indicates that R, at several positions, plays an important role in channel activation. The data are consistent with the notion that the S4 is most probably the voltage sensor of the NaChBac channel and that both positive charges and the nature of the arginine residues are essential for channel activation.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.M. Armstrong B. Hille (1998) ArticleTitleVoltage-gated ion channels and electrical excitability Neuron 20 371–380 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80981-2 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXit1Gmsro%3D Occurrence Handle9539115
W.A. Catterall (1986) ArticleTitleMolecular properties of voltage-sensitive sodium channels Annu. Rev. Biochem. 55 953–985 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004513 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XlsVyhtr4%3D Occurrence Handle2427018
W.A. Catterall (1992) ArticleTitleCellular and molecular biology of voltage-gated sodium channels Physiol. Rev. 72 S15–S48 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXhvVSrsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle1332090
W.A. Catterall (2000) ArticleTitleFrom ionic currents to molecular mechanisms: the structure and function of voltage-gated sodium channels Neuron 26 13–25 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0896-6273(00)81133-2 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjtFSksbY%3D Occurrence Handle10798388
A. Cha F. Bezanilla (1997) ArticleTitleCharacterizing voltage-dependent conformational changes in the Shaker K+ channel with fluorescence Neuron 19 1127–1140 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80403-1 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXnvFeqsrg%3D Occurrence Handle9390525
A. Cha G.E. Snyder P.R. Selvin F. Bezanilla (1999) ArticleTitleAtomic scale movement of the voltage-sensing region in a potassium channel measured via spectroscopy Nature 402 809–813 Occurrence Handle10.1038/45552 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXpt1Gh Occurrence Handle10617201
M. Chahine A.L. George M. Zhou S. Ji W. Sun R.L. Barchi R. Horn (1994) ArticleTitleSodium channel mutations in para myotonia congenita uncouple inactivation from activation Neuron 12 281–294 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0896-6273(94)90271-2 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXis1Ogu74%3D Occurrence Handle8110459
B. Chanda F. Bezanilla (2002) ArticleTitleTracking voltage-dependent conformational changes in skeletal muscle sodium channel during activation J. Gen. Physiol. 120 629–645 Occurrence Handle10.1085/jgp.20028679 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XptVOjs70%3D Occurrence Handle12407076
H.A. Fozzard D.A. Hanck (1996) ArticleTitleStructure and function of voltage-dependent sodium channels: comparison of brain II and cardiac isoforms Physiol. Rev. 76 887–926 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XltVags7o%3D Occurrence Handle8757791
K.S. Glauner L.M. Mannuzzu C.S. Gandhi E.Y. Isacoff (1999) ArticleTitleSpectroscopic mapping of voltage sensor movement in the Shaker potassium channel Nature 402 813–817 Occurrence Handle10.1038/45561 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXpt1Gn Occurrence Handle10617202
A.L. Goldin (2002) ArticleTitleEvolution of voltage-gated Na+ channels J. Exp. Biol. 205 575–584 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XivFejtrs%3D Occurrence Handle11907047
C. Gonzalez E. Rosenman F. Bezanilla O. Alvarez R. Latorre (2001) ArticleTitlePeriodic perturbations in Shaker K+ channel gating kinetics by deletions in the S3-S4 linker Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98 9617–9623 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.171306298 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXmtlCnurg%3D Occurrence Handle11493701
H.R. Guy P. Seetharamulu (1986) ArticleTitleMolecular model of the action potential sodium channel Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83 508–512 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XmsVensg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle2417247
O.P. Hamill A. Marty E. Neher B. Sakmann F.J. Sigworth (1981) ArticleTitleImproved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches Pfluegers Arch. 391 85–100 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00656997 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:Bi2D3sjhvVw%3D
B. Hille (2001) Ionic channels of excitable membranes Sinauer Associates Sunderland, MA
A.L. Hodgkin A.F. Huxley B. Katz (1952) ArticleTitleMeasurement of current-voltage relations in the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo J. Physiol. 116 424–448 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:Cy2D2snot1Y%3D Occurrence Handle14946712
Y. Jiang A. Lee J. Chen V. Ruta M. Cadene B.T. Chait R. MacKinnon (2003a) ArticleTitleX-ray structure of a voltage-dependent K+ channel Nature 423 33–41 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nature01580 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXjtlSrtro%3D
Y. Jiang V. Ruta J. Chen A. Lee R. MacKinnon (2003b) ArticleTitleThe principle of gating charge movement in a voltage-dependent K+ channel Nature 423 42–48 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nature01581 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXjtlSrtrs%3D
M.E. Jurman L.M. Boland Y. Liu G. Yellen (1994) ArticleTitleVisual identification of individual transfected cells for electrophysiology using antibody-coated beads Biotechniques 17 876–881 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXmvFKntbo%3D Occurrence Handle7840967
M. Lainé M.C.A. Lin J.P.A. Bannister W.R. Silverman A.F. Mock B. Roux D.M. Papazian (2003) ArticleTitleAtomic proximity between S4 segment and pore domain in Shaker potassium channels Neuron 39 467–481 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0896-6273(03)00468-9 Occurrence Handle12895421
E.R. Liman P. Hess F. Weaver G. Koren (1991) ArticleTitleVoltage-sensing residues in the S4 region of a mammalian K+ channel Nature 353 752–756 Occurrence Handle10.1038/353752a0 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2D2cbntVY%3D Occurrence Handle1944534
R.F. Margolskee B. McHendry-Rinde R. Horn (1993) ArticleTitlePanning transfected cells for electrophysiological studies Biotechniques 15 906–911 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuD1M3kslQ%3D Occurrence Handle7505602
M. Noda T. Ikeda H. Suzuki H. Takeshima T. Takahashi M. Kuno S. Numa (1986) ArticleTitleExpression of functional sodium channels from cloned cDNA Nature 322 826–828 Occurrence Handle10.1038/322826a0 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28Xls1Kit70%3D Occurrence Handle2427955
D.M. Papazian L.C. Timpe Y.N. Jan L.Y. Jan (1991) ArticleTitleAlteration of voltage-dependence of Shaker potassium channel by mutations in the S4 sequence Nature 349 305–310 Occurrence Handle10.1038/349305a0 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXpslShug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle1846229
D. Ren B. Navarro H. Xu L. Yue Q. Shi D.E. Clapham (2001) ArticleTitleA prokaryotic voltage-gated sodium channel Science 294 2372–2375 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.1065635 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXptFGqsrg%3D Occurrence Handle11743207
D. Ren L. Yue B. Navarro A. Ramos D.E. Clapham (2003) ArticleTitleThe cation selectivity filter of the one-repeat voltage-gated sodium channel, NaChBac Biophys. J. 84 24a
M. Strong K.G. Chandy G.A. Gutman (1993) ArticleTitleMolecular evolution of voltage-sensitive ion channel genes: on the origins of electrical excitability Mol. Biol. Evol. 10 221–242 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXhtF2htrk%3D Occurrence Handle7680747
W. Stühmer F. Conti H. Suzuki X.D. Wang M. Noda N. Yahagi H. Kubo S. Numa (1989) ArticleTitleStructural parts involved in activation and inactivation of the sodium channel Nature 339 597–603 Occurrence Handle10.1038/339597a0 Occurrence Handle2543931
H. Takami K. Nakasone N. Ogasawara C. Hirama Y. Nakamura N. Masui F. Fuji Y. Takaki A. Inoue K. Horikoshi (1999) ArticleTitleSequencing of three lambda clones from the genome of alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. strain C-l25 Extremophiles 3 29–34 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s007920050096 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXht1ems74%3D Occurrence Handle10086842
H. Takami K. Nakasone Y. Takaki G. Maeno R. Sasaki N. Masui F. Fuji C. Hirama Y. Nakamura N. Ogasawara S. Kuhara K. Horikoshi (2000) ArticleTitleComplete genome sequence of the alkaliphilic bacterium Bacillus halodurans and genomic sequence comparison with Bacillus subtilis Nucleic Acids Res. 28 4317–4331 Occurrence Handle10.1093/nar/28.21.4317 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXovFOiu7Y%3D Occurrence Handle11058132
N. Yang A.L. George ParticleJr R. Horn (1996) ArticleTitleMolecular basis of charge movement in voltage-gated sodium channels Neuron 16 113–122 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80028-8 Occurrence Handle8562074
N.B. Yang R. Horn (1995) ArticleTitleEvidence for voltage-dependent S4 movement in sodium channels Neuron 15 213–218 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0896-6273(95)90078-0 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXnt1Squr0%3D Occurrence Handle7619524
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Quebec (HSFQ) and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) MT-13181 and the Japan New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO). Dr. M. Chahine is an Edwards senior investigator (Joseph C. Edwards Foundation). The authors are grateful to Dr. L. Gailis and Dr. R Horn for their comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chahine, M., Pilote, S., Pouliot, V. et al. Role of Arginine Residues on the S4 Segment of the Bacillus halodurans Na+ Channel in Voltage-sensing. J Membrane Biol 201, 9–24 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-004-0701-z
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-004-0701-z