Abstract
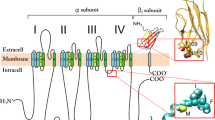
The isoform-specific direct role of cytoplasmic loops in the gating of two voltage-gated sodium channel isoforms, the human cardiac channel (Nav1.5; hH1) and the human adult skeletal muscle channel (Nav1.4; hSkM1), was investigated. Comparison of biophysical characteristics was made among hSkM1, hH1, and several hSkM1/hH1 chimeras in which the putative cytoplasmic loops that join domain I to II (loop A) and domain II to III (loop B) from one isoform replaced one or both of the analogous loops from the other isoform. For all parameters measured, hSkM1 and hH1 behavior were significantly different. Comparison of hSkM1 and hH1 biophysical characteristics with the function of their respective chimeras indicate that only the half-activation voltage (V a) is directly and differently altered by the species of cytoplasmic loop such that a channel consisting of one or both hSkM1 loops activates at smaller depolarizations, while a larger depolarization is required for activation of a channel containing one or both of the analogous hH1 loops. When either cardiac channel loop A or B is attached to hSkM1, a 6–7 mV depolarizing shift in V a is measured, increasing to a nearly 20 mV depolarization when both cardiac-channel loops are attached. The addition of either skeletal muscle-channel loop to hH1 causes a 7 mV hyperpolarization in V a, which increases to about 10 mV for the double loop chimera. There is no significant difference in either steady-state inactivation or in the recovery from inactivation data between hSkM1 and its chimeras and between hH1 and its chimeras. Data indicate that the cytoplasmic loops contribute directly to the magnitude of the window current, suggesting that channels containing skeletal muscle loops have three times the peak persistent channel activity compared to channels containing the cardiac loops. An electrostatic mechanism, in which surface charge differences among these loops might alter differently the voltage sensed by the gating mechanism of the channel, can not account for the observed isoform-specific effects of these loops only on channel activation voltage. In summary, although the DI-DII and DII-DIII loop structures among isoforms are not well conserved, these data indicate that only one gating parameter, V a is affected directly and in an isoform-specific manner by these divergent loop structures, creating loop-specific window currents and percentages of persistently active channels at physiological voltages that will likely impact the excitability of the cell.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Abriel C. Candido X.H.T. Wehrens I. Rivolta H.K. Motoike M. Memmi C. Napolitano S.G. Prior R.S. Kass (2001) ArticleTitleNovel arrhythmogenic mechanism revealed by a Long-QT syndrome mutation in the cardiac Na+ channel. Circ. Res. 88 740–745 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXjtlWrt74%3D Occurrence Handle11304498
A.K. Alekov W. Peter N. Mitrovic F. Lehmann-Horn H. Lerche (2001) ArticleTitleTwo mutations in the IV/S4-S5 segment of the human skeletal muscle Na+ channel disrupt fast and enhance slow inactivation. Neurosci. Lett. 306 173–176 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-3940(01)01895-X Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXkt12gsrw%3D Occurrence Handle11406323
D. Attwell I. Cohen D. Eisner M. Ohba C. Ojeda (1979) ArticleTitleThe steady state TTX-sensitive (“window”) sodium current in cardiac purkinje fibres. Pfluegers Arch. 379 137–142 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1MXhvVWhsbs%3D
S. Bendahhou T.R. Cummins J.F. Potts J. Tong W.S. Agnew (1995) ArticleTitleSerine-1321-independent regulation of the mu 1 adult skeletal muscle Na+ channel by protein kinase C. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92 12003–12007 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XhtlyrtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle8618832
E. Bennett M.S. Urcan S.S. Tinkle A.G. Koszowski S.R. Levinson (1997) ArticleTitleContribution of sialic acid to the voltage dependence of sodium channel gating. A possible electrostatic mechanism. J. Gen. Physiol. 109 327–343 Occurrence Handle10.1085/jgp.109.3.327 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXhvFCltLg%3D Occurrence Handle9089440
E.S. Bennett (1999) ArticleTitleEffects of channel cytoplasmic regions on the activation mechanisms of cardiac versus skeletal muscle Na+ channels. Biophys. J. 77 2999–3009 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXotVGhsLo%3D Occurrence Handle10585922
E.S. Bennett (2001) ArticleTitleChannel cytoplasmic loops alter voltage-dependent sodium channel activation in an isoform-specific manner. J. Physiol. 535 371–381 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXmvFGisrY%3D Occurrence Handle11533130
E.S. Bennett (2002) ArticleTitleIsoform-specific effects of sialic acid on voltage-dependent Na+ channel gating: Functional sialic acids are localized to the S5-S6 loop of domain I. J. Physiol. 538 675–690 Occurrence Handle10.1113/jphysiol.2001.013285 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XislGnsrs%3D Occurrence Handle11826157
P.B. Bennett K. Yazawa N. Makita A.L., Jr. George (1995) ArticleTitleMolecular mechanism for an inherited cardiac arrhythmia. Nature 376 683–685 Occurrence Handle10.1038/376683a0 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXnslagtb0%3D Occurrence Handle7651517
S.C. Cannon R.H., Jr. Brown D.P. Corey (1991) ArticleTitleA sodium channel defect in hyperkalemic periodic paralysis: potassium-induced failure of inactivation. Neuron 6 619–626 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By6C1Mjlt1Y%3D Occurrence Handle1849724
W.A. Catterall (1997) ArticleTitleModulation of sodium and calcium channels by protein phosphorylation and G proteins. Adv. Sec. Mess. Phosphoprot. Res. 31 159–181 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c%2Fgt12gtw%3D%3D
L.D. Chabala B.W. Urban L.B. Weiss W.N. Green O.S. Andersen (1991) ArticleTitleSteady-state gating of batrachotoxin-modified sodium channels. Variability and electrolyte-dependent modulation. J. Gen. Physiol. 98 197–224 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2D2cvktFA%3D Occurrence Handle1658190
M. Chahine A.L., Jr. George M. Zhou S. Ji W. Sun R.L. Barchi R. Horn (1994) ArticleTitleSodium channel mutations in paramyotonia congenita uncouple inactivation from activation. Neuron 12 281–294 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXis1Ogu74%3D Occurrence Handle8110459
M. Chahine A.L., Jr. George (1997) ArticleTitleMyotonic dystrophy kinase modulates skeletal muscle but not cardiac voltage-gated sodium channels. FEBS Lett. 412 621–624 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0014-5793(97)00869-7 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXltVGjt7k%3D Occurrence Handle9276478
S. Cukierman (1991) ArticleTitleAsymmetric electrostatic effects on the gating of rat brain sodium channels in planar lipid membranes. Biophys. J. 60 845–855 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38Xhslaktg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle1660316
S. Cukierman B.K. Krueger (1991) ArticleTitleEffects of internal divalent cations on the gating of rat brain Na+ channels reconstituted in planar lipid bilayers. Pfluegers Arch. 419 559–565 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XnvVyqsg%3D%3D
S. Cukierman W.C. Zinkand RJ. French B.K. Krueger (1988) ArticleTitleEffects of membrane surface charge and calcium on the gating of rat brain sodium channels in planar bilayers. J. Gen. Physiol. 92 431–447 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiaD1c%2FlsVQ%3D Occurrence Handle2849628
T.R. Cummins J. Zhou F.J. Sigworth C. Ukomadu M. Stephan L.J. Ptacek W.S. Agnew (1993) ArticleTitleFunctional consequences of a Na+ channel mutation causing hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Neuron 10 667–678 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXltFCru74%3D Occurrence Handle8386527
J.F. Desaphy A. De Luca D.C. Camerino (1998) ArticleTitleBlockade by cAMP of native sodium channels of adult rat skeletal muscle fibers. Am. J. Physiol. 275 C1465–C1472 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXhsFGjug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9843707
I. Deschenes N. Neyroud D. DiSilvestre E. Marban D.T. Yue G.F. Tomaselli (2002) ArticleTitleIsoform-specific modulation of voltage-gated Na+ channels by calmodulin. Circ. Res. 90 E49–E57 Occurrence Handle10.1161/01.RES.0000012502.92751.E6 Occurrence Handle11884381
R. Dumaine Q. Wang M.T. Keating H.A. Hartmann P.J. Schwartz A.M. Brown G.E. Kirsch (1996) ArticleTitleMultiple mechanisms of Na+ channel-linked long-QT syndrome. Circ. Res. 78 916–924 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28Xis1Shur4%3D Occurrence Handle8620612
Z. Fan A.L., Jr. George J.W. Kyle J.C. Makielski (1996) ArticleTitleTwo human paramyotonia congenita mutations have opposite effects on lidocaine block of Na+ channels expressed in a mammalian cell line. J. Physiol. 496 275–286 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28Xmt1Wlsbw%3D Occurrence Handle8910215
B. Frankenhaeuser A.L. Hodgkin (1957) ArticleTitleThe action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axon. J. Physiol. 137 2l8–244
B. Frohnwieser L.Q. Chen W. Schreibmayer R.G. Kallen (1997) ArticleTitleModulation of the human cardiac sodium channel alpha-subunit by cAMP-dependent protein kinase and the responsible sequence domain. J. Physiol. 498 309–318 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXhtFCls78%3D Occurrence Handle9032680
R. Hahin D.T. Campbell (1983) ArticleTitleSimple shifts in the voltage dependence of sodium channel gating caused by divalent cations. J. Gen. Physiol. 82 785–802 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiuC3MzkslQ%3D Occurrence Handle6319538
L.J. Hayward R.H., Jr. Brown S.C. Cannon (1996) ArticleTitleInactivation defects caused by myotonia-associated mutations in the sodium channel III-IV linker. J. Gen. Physiol. 107 559–576 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28Xjtlegs78%3D Occurrence Handle8740371
S. Ji A.L., Jr. George R. Horn R.L. Barchi (1996) ArticleTitleParamyotonia congenita mutations reveal different roles for segments S3 and S4 of domain D4 in hSkM1 sodium channel gating. J. Gen. Physiol. 107 183–194 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28Xit12gtr8%3D Occurrence Handle8833340
J.H. Lawrence D.W. Orias J.R. Balser H.B. Nuss G.F. Tomaselli B. O’Rourke E. Marban (1996) ArticleTitleSingle-channel analysis of inactivation-defective rat skeletal muscle sodium channels containing the F1304Q mutation. Biophys. J. 71 1285–1294 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XlsVGnt74%3D Occurrence Handle8874003
H. Lerche N. Mitrovic V. Dubowitz F. Lehmann-Horn (1996) ArticleTitleParamyotonia congenita: the R1448P Na+ channel mutation in adult human skeletal muscle. Ann. Neurol. 39 599–608 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymB3c3lslY%3D Occurrence Handle8619545
C. Lossin D.W. Wang T.H. Rhodes C.G. Vanoye A.L., Jr. George (2002) ArticleTitleMolecular basis of an inherited epilepsy. Neuron 34 877–884
T. Lu H.C. Lee J.A. Kabat E.F. Shibata (1999) ArticleTitleModulation of rat cardiac sodium channel by the stimulatory G protein alpha subunit. J. Physiol. 518 371–384 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXmtVWgtr0%3D Occurrence Handle10381586
N. Makita P.B., Jr. Bennett A.L., Jr. George (1996) ArticleTitleMultiple domains contribute to the distinct inactivation properties of human heart and skeletal muscle Na+ channels. Circ. Res. 78 244–252 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XnsFyhtA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle8575068
V.A. Maltsev A.I. Undrovinas (1997) ArticleTitleCytoskeleton modulates coupling between availability and activation of cardiac sodium channel. Am. J. Physiol. 273 H1832–H1840 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXnt1Wiurc%3D Occurrence Handle9362250
J.J. Matsuda H. Lee E.F. Shibata (1992) ArticleTitleEnhancement of rabbit cardiac sodium channels by beta-adrenergic stimulation. Circ. Res. 70 199–@207 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXltVSgur0%3D Occurrence Handle1309315
O. Moran P. Tammaro M. Nizzari F. Conti (2000) ArticleTitleFunctional properties of sodium channels do not depend on the cytoskeleton integrity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 276 204–209 Occurrence Handle10.1006/bbrc.2000.3463 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXmslKnur4%3D Occurrence Handle11006107
T. Nagatomo Z. Fan B. Ye G.S. Tonkovich C.T. January J.W. Kyle J.C. Makielski (1998) ArticleTitleTemperature dependence of early and late currents in human cardiac wild-type and long Q-T DeltaKPQ Na+ channels. Am. J. Physiol. 275 H2016–H2024 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXht1OlsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9843800
M.K. Patel D. Mistry J.E., III. John J.P. Mounsey (2000) ArticleTitleSodium channel isoform-specific effects of halothane: protein kinase C co-expression and slow inactivation gating. Br. J. Pharmacol. 130 1785–1792 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXmtFenurc%3D Occurrence Handle10952666
L.J. Ptacek A.L., Jr. George R.C. Griggs R. Tawil R.G. Kallen R.L. Barchi M. Robertson M.F. Leppert (1991) ArticleTitleIdentification of a mutation in the gene causing hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Cell 67 1021–1027 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXjslSrtg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle1659948
L.J. Ptacek A.L., Jr. George R.L. Barchi R.C. Griggs J.E. Riggs M. Robertson M.F. Leppert (1992) ArticleTitleMutations in an S4 segment of the adult skeletal muscle sodium channel cause paramyotonia congenita. Neuron 8 891–897 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38Xks1Oqtrg%3D Occurrence Handle1316765
C.F. Ratcliffe Y. Qu K.A. McCormick V.C. Tibbs J.E. Dixon T. Scheuer W.A. Catterall (2000) ArticleTitleA sodium channel signaling complex: modulation by associated receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase beta. Nat. Neurosci. 3 437–444 Occurrence Handle10.1038/74805 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXivFyjtLw%3D Occurrence Handle10769382
S. Rossie (1999) ArticleTitleRegulation of voltage-sensitive sodium and calcium channels by phosphorylation. Adv. Sec. Mess. Phosphoprot. Res. 33 23–48 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3jsVOgtA%3D%3D
F. Rugiero M. Mistry D. Sage J.A. Black S.G. Waxman M. Crest N. Clerc P. Delmas M. Gola (2003) ArticleTitleSelective expression of a persistent tetrodotoxin-resistant Na+ current and Nav1.9 subunit in myenteric sensory neurons. J. Neurosci. 23 2715–2725 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXjtFCnt70%3D Occurrence Handle12684457
W. Schreibmayer (1999) ArticleTitleIsoform diversity and modulation of sodium channels by protein kinases. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 9 187–200 Occurrence Handle10.1159/000016316 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXnvVCnsLo%3D Occurrence Handle10575197
P.J. Schwartz S.G. Prior R. Dumaine C. Napoliano C. Antzelevitch M. Stramba-Badiale T.A. Richard M.R. Berti R. Bloise (2000) ArticleTitleA molecular link between the sudden infant death syndrome and the Long-QT syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 343 262–267 Occurrence Handle10.1056/NEJM200007273430405 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXlvVSmtLk%3D Occurrence Handle10911008
R.D. Smith A.L. Goldin (2000) ArticleTitlePotentiation of rat brain sodium channel currents by PKA in Xenopus oocytes involves the I-II linker. Am. J. Physiol. 278 C638–C645 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXis12itrw%3D
L.A. Sorbera M. Morad (1991) ArticleTitleModulation of cardiac sodium channels by cAMP receptors on the myocyte surface. Science 253 1286–1289 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXmtVChs74%3D Occurrence Handle1653970
J. Spampanato A. Escayg M.H. Meisler A.L. Goldin (2003) ArticleTitleGeneralized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus type 2 mutation W1240R alters voltage-dependent gating of Nav1.1 sodium channels. Neurosci. 116 37–46 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0306-4522(02)00698-X Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXlt1ygtw%3D%3D
I. Splawski K.W. Timoth M. Tateyama C.E. Clancy A. Malhotra A.H. Beggs F.P. Cappuccio G.A. Sagnella R.S. Kass M.T. Keating (2002) ArticleTitleVariant of SCN5A sodium channel implicated in risk of cardiac arrhythmia. Science 297 1333–1336 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.1073569 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xms1ejtbw%3D Occurrence Handle12193783
L. Tyrrell M. Renganathan S.D. Dib-Hajj S.G. Waxman (2001) ArticleTitleGlycosylation alters steady-state inactivation of sodium channel Nav1.9/NaN in dorsal root ganglion neurons and is developmentally regulated. J. Neurosci. 21 9629–9637 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XivV2r Occurrence Handle11739573
A.I. Undrovinas G.S. Shander J.C. Makielski (1995) ArticleTitleCytoskeleton modulates gating of voltage-dependent sodium channel in heart. Am. J. Physiol. 269 H203–H214 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXnt1Gkt7c%3D Occurrence Handle7631850
X. Wan S. Chen A. Sadeghpour Q. Wang G.E. Kirsch (2001) ArticleTitleAccelerated inactivation in a mutant Na+ channel associated with idiopathic ventricular fibrillation. Am. J. Physiol. 280 H354–H360 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXjtVyltbk%3D
D.W. Wang K. Yazawa A.L., Jr. George P.B. Bennett (1996) ArticleTitleCharacterization of human cardiac Na+ channel mutations in the congenital long QT syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93 13200–13205 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.93.23.13200 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XmvV2qtL8%3D Occurrence Handle8917568
J. Wei D.W. Wang M. Alings F. Fish M. Wathen D.M. Roden A.L., Jr. George (1999) ArticleTitleCongential Long-QT syndrome caused by a novel mutation in a conserved acidic domain of the cardiac Na+ channel. Circulation 99 3165–3171 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXktlSisbk%3D Occurrence Handle10377081
S J. Wieland Q. Gong H. Poblete J.E. Fletcher L.Q. Chen R.G. Kallen (1996) ArticleTitleModulation of human muscle sodium channels by intracellular fatty acids in dependent on the channel isoform. J. Biol Chem. 271 19037–19041 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.271.32.19037 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XkvFyns7w%3D Occurrence Handle8702574
Y. Zhang H.A. Hartmann J. Satin (1999) ArticleTitleGlycosylation influences voltage-dependent gating of cardiac and skeletal muscle sodium channels. J. Membrane Biol. 171 195–207 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002329900571 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXmsFCntrg%3D
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants from the American Heart Association, Florida Affiliate, and from the National Institute for Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bennett, E. Channel Activation Voltage Alone Is Directly Altered in an Isoform-specific Manner by Nav1.4 and Nav1.5 Cytoplasmic Linkers . J. Membrane Biol. 197, 155–168 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-004-0650-6
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-004-0650-6