Abstract
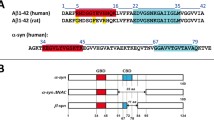
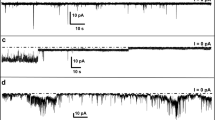
We have proposed that the cytotoxic action of Alzheimer’s amyloid beta protein might be initiated by the interaction with the neuronal cell membrane, and subsequent formation of toxic ion channels. Consequently, AβP toxicity can be explained on the basis of harmful ion fluxes across AβP channels. The conformation of AβP in membranes is not known. However, several models suggests that a transmembrane annular polymeric structure is responsible for the ion channel properties of the membrane-bound AβP. To identify that portion of the AβP molecule making up the conducting pore we have hypothesized that the region of the AβP sequence in the vicinity of the hypothetical pore might interact with complementary regions in the adjacent AβP subunits. We have further hypothesized that an interaction by a peptide segment would block AβP conductance. To test this hypothesis we synthesized peptides that encompass the histidine dyad (H-H) previously hypothesized to line the pore. We report here that peptides designed to most closely match the proposed pore are, in fact, the most effective at blocking ion currents through the membrane-incorporated AβP channel. As previously shown for Zn2+ blockade, peptide blockade is also asymmetric. The results also provide additional evidence for the asymmetric insertion of the AβP molecules into lipid membranes, and give support to the concept that rings of histidines line the entry to one side of the AβP pore.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Arispe (2001) ArticleTitleControl of the interaction of the Alzheimer’s AβPs and homologous analogues, with lipid membranes. Biophys. J. 80 135a
N.J. Arispe M. Doh (2003) ArticleTitlePeptides that block Alzheimer’s AβP ion channels protect cells from AβP toxicity. Biophysical J. 84 53a
N. Arispe M. Doh A. De Maio (2002) ArticleTitleLipid interactions differentiates the constitutive and stress-induced heat shock proteins Hsc70 and Hsp70. Cell Stress and Chaperones 7 330–338 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXksVyluw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle12653477
N. Arispe H.B. Pollard E. Rojas (1994) ArticleTitleβ-amyloid Ca2+-channel hypothesis for neuronal death in Alzheimer disease. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 140 19–125
N. Arispe H.B. Pollard E. Rojas (1996a) ArticleTitleZn2+ interaction with Alzheimer amyloid β protein calcium channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93 1710–1715 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28Xht1entLg%3D
N. Arispe E. Rojas B.R. Gene L.N.Y. Wu R. Wuthier (1996b) ArticleTitleSimilarity in calcium channel activity of annexin V and matrix vesicles in planar lipid bilayers. Biophys. J. 71 1764–1775 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XmtVOktr4%3D
N. Arispe E. Rojas H.B. Pollard (1993a) ArticleTitleAlzheimer disease amyloid β-protein forms calcium channels in bilayer membranes: blockade by tromethamine and aluminium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90 567–571 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXpvFKitQ%3D%3D
N. Arispe E. Rojas H.B. Pollard (1993b) ArticleTitleGiant multilevel cation channels formed by Alzheimer disease amyloid β-protein [AβP-(1–40)] in bilayer membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90 10573–10577 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXnsVOisQ%3D%3D
N.A. Avdulov S.V. Cochina U. Igbavboa C.S. Warden A.V. Vassiliev W.G. Wood (1997) ArticleTitleLipid binding to amyloid-β-peptide aggregates. Preferential binding of cholesterol as compared with phosphatidylcholine and fatty acids. J. Neurochem. 69 1746–1752 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXmsVCktrc%3D Occurrence Handle9326304
C.J. Barrow A. Yasuda P.T.M. Kenny M.G. Zagorski (1992) ArticleTitleSolution conformations and aggregational properties of synthetic amyloid β-peptides of Alzheimer’s disease. Analysis of circular dichroism spectra. J. Mol. Biol. 225 1075–1093 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XltV2gs7g%3D Occurrence Handle1613791
R. Bathia H. Lin R. Lal (2000) ArticleTitleFresh and globular amyloid-β- protein induces rapid cellular degeneration. A possible implication for calcium-uptake via AβP-channel. FASEB J. 14 1233–1243 Occurrence Handle10834945
R.A. Blackwood J.D. Ernst (1990) ArticleTitleCharacterization of Ca2+-dependent phospholipid binding, vesicle aggregation and membrane fusion by annexins. Biochem. J. 266 195–200 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXhtFCntLo%3D Occurrence Handle2138016
D. Burdick B. Soreghan M. Kwon J. Kosmoski M. Knauer A. Henschen J. Yates C. Cotman C. Glabe (1992) ArticleTitleAssembly and aggregation properties of synthetic Alzheimer’s A4/beta amyloid peptide analogs. J. Biol. Chem. 267 546–554 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XjvFSmtA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle1730616
M. de la Fuente A.V. Parra (1995) ArticleTitleVesicle aggregation by annexin I: role of a secondary membrane binding site. Biochemistry. 34 10393–10399 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXnt1KmtLc%3D Occurrence Handle7654693
S.R. Durrell H.R. Guy N. Arispe E. Rojas H.B. Pollard (1994) ArticleTitleTheoretical models of the ion channel structure of amyloid-β-protein. Biophys. J. 67 2137–2145 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXisVajtL0%3D Occurrence Handle7535109
S.P. Frazer Y.-H. Suh M.B.A. Djamgoz (1997) ArticleTitleIonic effects of the Alzheimer’s disease β-amyloid precursor protein and its metabolic fragments. Trends Neurosci. 20 67–72 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0166-2236(96)10079-5 Occurrence Handle9023874
K. Furukawa Y. Abe N. Akaike (1994) ArticleTitleAmyloid β protein-induced irreversible current in rat cortical neurones. NeuroReport. 5 2016–2018 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXitlKis78%3D Occurrence Handle7532452
Z. Galdzicki R. Fukuyama K. Wadhwani S. Rapoport G. Ehrenstein (1994) ArticleTitleβ-amyloid increases choline conductance of PC12 cells: possible mechanism of toxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 646 332–336 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0006-8993(94)90101-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXksFGis7Y%3D Occurrence Handle8069685
J. Ghanta C.-L. Shen L.L. Kiessling R.M. Murphy (1996) ArticleTitleA strategy for designing inhibitors of β-amyloid toxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 271 29525–29528 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.271.47.29525 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XntFKmsrw%3D Occurrence Handle8939877
G.G. Glenner C.W. Wong (1984) ArticleTitleAlzheimer’s Disease: Initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 120 885–890 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2cXitVOntLw%3D Occurrence Handle6375662
C. Haass M. Schlossmacher A.Y. Hung et al. (1992) ArticleTitleAmyloid β-peptide is produced by cultured cells during normal metabolism. Nature 359 322–325 Occurrence Handle10.1038/359322a0 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XmtV2msro%3D Occurrence Handle1383826
C. Haass D.J. Selkoe (1993) ArticleTitleCellular processing of β-amyloid precursor protein and the genesis of amyloid-β-peptide. Cell 75 1039–1042 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXnsVeksQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle8261505
J.A. Hardy G.A. Higgins (1992) ArticleTitleAlzheimer’s disease: the amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science 256 780–783 Occurrence Handle1589757
Y. Hirakura M.C. Lin B.L. Kagan (1999) ArticleTitleAlzheimer amyloid beta peptide 1-42 channels: effect of solvent, pH, and congo red. J. Neurosci. Res. 57 458–460 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1097-4547(19990815)57:4<458::AID-JNR5>3.3.CO;2-W Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXltFWmtbk%3D Occurrence Handle10440895
Y. Hirakura W.W. Yiu A. Yamamoto B.L. Kagan (2000) ArticleTitleAmyloid peptide channels: blockade by zinc and inhibition by Congo red. Amyloid 7 194–199 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXnsFCqtrg%3D Occurrence Handle11019860
M. Kawahara N. Arispe Y. Kuroda E. Rojas (1997) ArticleTitleAlzheimer’s disease amyloid β-protein forms Zn2+-sensitive cation-selective channels across excited membrane patches from hypothalamic neurons. Biophysical J. 73 67–75 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXktlaksLo%3D
N.C. Kowall A.C. McKee B.A. Yankner M.F. Beal (1992) ArticleTitleIn vivo neurotoxicity of beta amyloid [β(1–40)] and thte β(25–35) fragment. Neurobiol. of Aging 13 531–542 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0197-4580(92)90083-A
K.Y.C. Lee (2001) ArticleTitleInteractions of Alzheimer’s amyloid-beta-peptides with lipid membranes. Biophys. J. 80 23a
G. Lee H.B. Pollard (1997) ArticleTitleHighly sensitive and stable phosphatidylserine liposome aggregation assay for annexins. Analyt. Biochem. 252 160–164 Occurrence Handle10.1006/abio.1997.2311 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXmsVWrs7Y%3D Occurrence Handle9324954
H. Lin R. Bhatia R. Lal (2001) ArticleTitleAmyloid protein forms ion channels: implications for Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology. FASEB J. 15 2433–2444 Occurrence Handle10.1096/fj.01-0377com Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXoslSisrs%3D Occurrence Handle11689468
H. Lin Y.J. Zhu R. Lal (1999) ArticleTitleAmyloid β-protein (1–40) forms calcium-permeable Zn2+ sensitive channels in reconstituted lipid vesicles. Biochemistry 38 11189–11196 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXkvVCrsro%3D Occurrence Handle10460176
M.C. Lin B. Kagan (2002) ArticleTitleElectrophysiologic properties of channels induced by Aβ25–35 in planar lipid bilayers. Peptides 23 1215–1228 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0196-9781(02)00057-8 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XlsVOqt7c%3D Occurrence Handle12128079
A.T. Maloof (1992) ArticleTitleEffect of beta amyloid peptides on neurons in hippocampal slice cultures. Neurobiol. of Aging 13 543–551 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0197-4580(92)90054-2
R.P. Mason J.D. Estermyer J.F. Kelly P.E. Mason (1996) ArticleTitleAlzheimer’s disease amyloid β peptide 25–35 is localized in the membrane hydrocarbon core: X-ray diffration analysis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 222 78–82 Occurrence Handle10.1006/bbrc.1996.0699 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XivVOitro%3D Occurrence Handle8630078
C.L. Masters G. Simms N.A. Weinman G. Multhaup B.L. McDonald K. Beyreuther (1985) ArticleTitleAmyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer’s disease and Down syndrome. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 82 4245–4249 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXktlGltr0%3D Occurrence Handle3159021
M.P. Mattson (1997) ArticleTitleCellular actions of beta-amyloid precursor protein and its soluble and fibrillogenic derivatives. Physiol Rev. 77 1081–1132 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXnt1yhu7g%3D Occurrence Handle9354812
M.P. Mattson B. Cheng D. Davis K. Bryant I. Liberberg R.E. Rydel (1992) ArticleTitleβ-Amyloid peptides destabilize calcium homeostasis and render human cortical neurons vulnerable to excitoxicity. J. Neurosci. 12 376–389 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XhvFajs74%3D Occurrence Handle1346802
T. Mirzabekov M.C. Lin W.L. Yuan P.J. Marshall M. Carman K. Tomaselli I. Lieberburg B.L. Kagan (1994) ArticleTitleChannel formation in planar lipid bilayers by a neurotoxic fragment of the beta-amyloid peptide. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 202 1142–1148 Occurrence Handle10.1006/bbrc.1994.2047 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXmt1ekurY%3D Occurrence Handle7519420
W.E. Muller S. Koch A. Eckert H. Hartmann K. Scheuer (1995) ArticleTitleβ-amyloid peptide decreases membrane fluidity. Brain Res. 674 133–136 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0006-8993(94)01463-R Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqB1M7ps1c%3D Occurrence Handle7773681
R.L. Neve L.R. Dawes B.A. Yankner L.L. Benewitz W. Rodriguez G.A. Higgins (1990) ArticleTitleGenetics and biology of the Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor. Prog. Brain. Res. 86 257–267 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXltFWltrw%3D Occurrence Handle2150887
C.J. Pike M.J. Overman C.W. Cotman (1995) ArticleTitleAmino-terminal deletions enhance aggregation of amyloid peptides in vitro. J. Biol Chem. 270 23895–23898 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.270.41.23895 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXovVSgsL4%3D Occurrence Handle7592576
C.J. Pike A.J. Walencewicz C.G. Glabe C.W. Cottman (1991) ArticleTitleIn vitro aging of β-amyloid protein causes peptide aggregation and neurotoxicity. Brain Res. 563 311–314 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0006-8993(91)91553-D Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38Xks1al Occurrence Handle1786545
J.F. Poduslo G.L. Curran A. Kumar B. Frangione C. Soto (1999) ArticleTitleBeta-sheet breaker peptide inhibitor of Alzheimer’s amyloidogenesis with increased blood-brain barrier permeability and resistance to proteolytic degradation in plasma. J. Neurobiol. 39 371–382 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1097-4695(19990605)39:3<371::AID-NEU4>3.3.CO;2-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXjvVCmsr4%3D Occurrence Handle10363910
S.K. Rhee A.P. Quist R. Lal (1998) ArticleTitleAmyloid β-protein (1–42) forms calcium-permeable Zn2+-sensitive channels. J. Biol. Chem 273 13379–13382 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.273.22.13379 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXjvVejsLY%3D Occurrence Handle9593665
D. Scheuner C. Eckman M. Jensen X. Song M. Citron N. Suzuki T.D. Bird J. Hardy M. Hutton W. Kukull E. Larson E. Levy-Lahad M. Vitanen E. Peskind P. Poorkaj G. Schellenberg R. Tanzi W. Wasco L. Lannfelt D. Selkoe S. Younkin (1996) ArticleTitleSecreted amyloid β-protein similar to that in the senile plaques of Alzheimer’s disease is increased in vivo by the presenilin 1 and 2 and APP mutations linked to familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2 864–870 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XkslGiu7g%3D Occurrence Handle8705854
D.E. Schmechel A.M. Saunders W.S. Strittmatter B.J. Grain C.M. Hulette S.H. Joo et al. (1993) ArticleTitleIncreased amyloid beta-peptide deposition in cerebral cortex as a consequence of apoliprotein E genotype in late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90 9646–9653
D.L. Selkoe (1991) ArticleTitleThe molecular pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 6 487–498 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXltlartrk%3D Occurrence Handle1673054
D.L. Selkoe (1994) ArticleTitleAlzheimer’s disease: a central role for amyloid. J. Neuropath. Exp. Neurol. 53 438–447 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXmsFamsbk%3D Occurrence Handle8083687
M.A. Simmons C.R. Schneider (1993) ArticleTitleAmyloid β peptides act directly on single neurons. Neurosci. Letts. 150 133–136 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0304-3940(93)90519-Q Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXks12mtLc%3D
C. Soto M.S. Kindy M. Baumann B. Frangione (1996) ArticleTitleInhibition of Alzheimer’s amyloidosis by peptides that prevent β-sheet conformation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 226 672–680 Occurrence Handle10.1006/bbrc.1996.1413 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XlvFagsbg%3D Occurrence Handle8831674
C. Soto E.M. Sigurdsson L. Morelli R.A. Kumar E.M. Castano B. Frangione (1998) ArticleTitleBeta-sheet breaker peptides inhibit fibrillogenesis in a rat brain model of amyloidosis: implications for Alzheimer’s therapy. Nat. Med. 4 822–826 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXktlKnsrg%3D Occurrence Handle9662374
C. Soto G.P. Saborio B. Permanne (2000) ArticleTitleInhibiting the conversion of soluble amyloid-beta peptide into abnormally folded amyloidogenic intermediates: relevance for Alzheimer’s disease therapy. Acta Neurol. Scand. Suppl. 176 90–95 Occurrence Handle10.1034/j.1600-0404.2000.00313.x Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M7lvFWisQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11261811
C. Soto (1999a) ArticleTitlePlaque busters: strategies to inhibit amyloid formation in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Med Today. 5 343–350 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXlslehurY%3D
C. Soto (1999b) ArticleTitleAlzheimer’s and prion disease as disorders of protein conformation: implications for the design of novel therapeutic approaches. J. Mol. Med. 77 412–418 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXkvV2rt7w%3D
C. Soto (2001) ArticleTitleProtein misfolding and disease; protein refolding and therapy. FEBS Lett. 498 204–207 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0014-5793(01)02486-3 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXksVGksr4%3D Occurrence Handle11412858
E. Terzi G. Holzemann J. Seelig (1995) ArticleTitleSelf-association of beta-amyloid peptide (1–40) in solution and binding to lipid membranes. J. Mol Biol. 252 633–642 Occurrence Handle10.1006/jmbi.1995.0525 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXos1OhtL0%3D Occurrence Handle7563079
L.O. Tjernberg J. Näslund F. Lindqvist J. Johansson A.R. Karlström J. Thyberg L. Terenius C. Nordstedt (1996) ArticleTitleArrest of β-amyloid fibril formation by a pentapeptide ligand. J. Biol. Chem. 271 8545–8548 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.271.15.8545 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28Xitlegu7k%3D Occurrence Handle8621479
J. Vargas J.M. Alarcon E. Rojas (2000) ArticleTitleDisplacement currents associated with the insertion of Alzheimer disease amyloid β-peptide into planar bilayer membranes. Biophys J. 79 934–944 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXlsFOgurk%3D Occurrence Handle10920024
S.J. Wood L. MacKenzie B. Maleeff M.R. Hurle R. Wetzel (1996) ArticleTitleSelective inhibition of Abeta fibril formation. J. Biol Chem. 271 4086–4092 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.271.48.30392 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XhtlSmsL0%3D Occurrence Handle8626745
S.J. Wood R. Wetzel J.D. Martin M.R. Hurle (1995) ArticleTitleProlines and amyloidogenicity in fragments of the Alzheimer’s peptide beta/A4. Biochemistry. 34 724–730 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXjtVyrtbw%3D Occurrence Handle7827029
B.L. Yankner L.K. Duffy D.A. Kirschner (1990a) ArticleTitleNeurotropic and neurotoxic effects of amyloid beta protein: reversal by tachykinin neuropeptides. Science 250 279–282 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXlslansg%3D%3D
Y.J. Zhu H. Lin R. Lal (2000) ArticleTitleFresh and nonfibrillar amyloid β protein(l–40) induces rapid cellular degeneration in aged human fibroblasts evidence for AβP-channel-mediated cellular toxicity. FASEB J. 14 1244–1254 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjvFyjtL4%3D Occurrence Handle10834946
Acknowledgements
The author thanks Dr. H.B. Pollard and Dr. D. Mears for invaluable comments and discussion, and Mr. M. Doh for technical assistance. This work was supported by a grant from The Alzheimer’s Association of America.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arispe, N. Architecture of the Alzheimer’s AβP Ion Channel Pore . J. Membrane Biol. 197, 33–48 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-003-0638-7
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-003-0638-7