Abstract
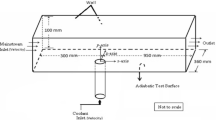
Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) is predominantly present in cooling water which is commonly used as a coolant in many industrial processes. It has inverse solubility characteristics i.e., it is less soluble in warm water, resulting in the deposition of scale on heat transfer surfaces. An experimental study was carried out to determine the effect of tube surface temperature, Reynolds number, tube diameter and salt concentration on the induction time of CaCO3 scaling. It was observed that tube surface temperature, Reynolds number and tube diameter had no effect on the onset time of scaling, whereas salt concentration and tube surface roughness had a profound influence on the induction period. The data collected from the experiments were used to develop dimensionless fouling resistance models for estimation and prediction purposes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received on 22 December 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Budair, M., Khan, M., Zubair, S. et al. CaCO3 scaling in AISI 316 stainless steel tubes – effect of thermal and hydraulic parameters on the induction time and growth rate. Heat and Mass Transfer 34, 163–170 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002310050245
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002310050245