Abstract
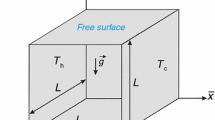
The impact of copper nanoparticles on Marangoni-Benard convection in water-based nanofluids was investigated numerically by examining the effect of variations in the Rayleigh and Marangoni numbers for different values of the Biot number. The aspect ratio of the cavity, and the interaction of the buoyant forces and forces due to surface tension inhomogeneity were also investigated. The relationship between these parameters and the heat transfer behavior was then determined by examining the average Nusselt number. This allowed the development of a methodology by which the critical values of the Rayleigh number and the Marangoni number could be identified. The results indicated that the average Nusselt number increased with increases in the Biot number. In addition, the presence of the copper nanoparticles enhanced the heat transfer rate significantly, with the positive enhancement increasing with increased Biot number.

























Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C :
-
Gladstone-Dale constant
- c p :
-
Specific heat
- g :
-
Gravitational acceleration
- H :
-
Height
- h :
-
Surface heat transfer coefficient
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity
- L :
-
Width
- L b :
-
Length of the model in the beam direction
- n :
-
Refractive index
- P :
-
Non-dimensional pressure
- p :
-
Pressure
- q :
-
Heat flux
- S :
-
Fringe number
- T :
-
Temperature
- T r :
-
Reference temperature
- u, v :
-
Velocity components in x and y direction
- U, V :
-
Non-Dimensional velocity components in X and Y direction
- x, y :
-
Cartesian coordinates
- X, Y :
-
Non-dimensional Cartesian coordinates
- α :
-
Thermal diffusivity
- β :
-
Coefficient of thermal expansion
- λ :
-
Wavelength
- ϕ :
-
Concentration of nanoparticles
- ρ :
-
Density
- σ :
-
Surface tension
- θ :
-
Non-dimensional temperature
- μ :
-
Viscosity
- ν :
-
Kinematic viscosity
- AR:
-
Aspect Ratio L/H
- Bi :
-
Biot number
- Ma :
-
Marangoni Number
- Nu :
-
Nusselt number
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- Ra :
-
Rayleigh number
- C :
-
Free stream
- f :
-
Property of base fluid
- h :
-
Hot
- nf :
-
Property of nanofluid
- r :
-
Reference Section
- s :
-
Property of nanoparticle added
- t :
-
Test section
- w :
-
Wall
References
Lappa M (2009) Thermal convection: patterns, evolution and stability. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester
Benard H (1900) Les tourbillons cellulaires dans une nappe liquide. Rev Gen Sci Pure Appl 11:1261–1271
Rayleigh (1916) On convective currents in a horizontal layer of fluid when the higher temperature is on the under side. Phil Mag 32:529–546
Block MJ (1956) Surface tension as the cause of Benard cells and surface deformation of a liquid film. Nature 178:650–651
Pearson JRA (1958) On convection cells induced by surface tension. J Fluid Mech 4:489–500
Marangoni CGM (1871) Ueber die Ausbreitung der Tropfen einer Flüssigkeit auf der Oberfläche eineranderen. Ann Phys Chem (Poggendorf) 143:337–354
Nield DA (1964) Surface tension and buoyancy effects in cellular convection. J Fluid Mech 19:341–352
Berg HJ, Palmer JC (1971) Convective instabilities in liquid pools heated from below. J Fluid Mech 47:779–787
Cliffe KA, Tavenery SJ (1998) Marangoni Benard convection with a deformable free surface. J Comput Phys 145:193–227
Cliffe KA, Tavener SJ (2002) Two-fluid Marangoni–Be’nard convection. J Comput Phys 182:277–300
Merkt D, Bestehorn M (2003) Bénard–Marangoni convection in a strongly evaporating fluid. Physica-D 185:196–208
Boeck T (2005) Benard–Marangoni convection at large Marangoni numbers: results of numerical simulations. Adv Space Res 36:4–10
Sun ZF, Yu KT (2006) Rayleigh–Benard–Marangoni cellular convection expressions for heat and mass transfer rates. Chem Eng Res Des 84(A3):185–191
Rahal S, Cerisier P, Azuma H (2007) Benard–Marangoni convection in a small circular container: influence of the biot and Prandtl numbers on pattern dynamics and free surface deformation. Exp Fluids 43:547–554
Touazi O, Chénier E, Doumenc F, Guerrier B (2010) Simulation of transient Rayleigh–Bénard–Marangoni convection induced by evaporation. Int J Heat Mass Transf 53:656–664
Choi S (1995) Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticle. ASME FED 231,
Zoubida H, Abu-Nada E, Oztop H, Mataoui A (2012) A review on natural convective heat transfer of nanofluids. Renew Sust Energ Rev 16:5363–5378
Arifin N, Nazar R, Pop I (2011) Non-isobaric Marangoni boundary layer flow for cu, Al2O3 and TiO2 nanoparticles in a water based fluid. Meccanica 46:833–843
Mat NAA, Arifin NM, Nazar R, Ismail F (2012) Radiation effect on Marangoni convection boundary layer flow of a nanofluid. Math Sci 6:21
Lin Y, Zheng L, Zhang X (2014) Radiation effects on Marangoni convection flow and heat transfer in pseudo-plastic non-Newtonian nanofluids with variable thermal conductivity. Int J Heat Mass Transf 77:708–716
Aminfar H, Mohammadpourfard M, Mohseni F (2012) Numerical investigation of thermocapillary and buoyancy driven convection of nanofluids in a floating zone. Int J Mech Sci 65:147–156
Saleh H, Hashim I (2015) Buoyant Marangoni convection of nanofluids in square cavity. Appl Math Mech -Engl Ed 36(9):1169–1184
Namburu PK, Kulkarni DP, Misra D, Das DK (2007) Viscosity of copper oxide nanoparticles dispersed in ethylene glycol and water mixture. Exp Thermal Fluid Sci 32(2):397–402
Khaleduzzaman S, Mahbubul I, Shahrul I, Saidur R (2013) Effect of particle concentration, temperature and surfactant on surface tension of nanofluids. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 49:110–114
Bhuiyan MHU, Saidur R, Mostafizur RM, Mahbubul IM, Amalina MA (2015) Experimental investigation on surface tension of metal oxide–water nanofluids. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 65:82–88
Nasrin R, Alim MA, Chamkha AJ (2012) Buoyancy-driven heat transfer of water–Al2O3 nanofluid in a closed chamber: effects of solid volume fraction, Prandtl number and aspect ratio. Int J Heat Mass Transf 55:7355–7365
Brinkman HC (1952) The viscosity of concentrated suspensions and solutions. J Chem Phys 20:571–581
Maxwell J (1904) Garnett, Colours in metal glasses and in metallic films. Philos Trans Roy Soc A 203:385–420
Saleh H, Roslan R, Hashim I (2011) Natural convection heat transfer in a nanofluid-filled trapezoidal enclosure. Int J Heat Mass Transf 54:194–201
Wohlfarth C (2008) Surface tension of water. Surface tension of pure liquids and binary liquid mixtures, springer, New York, 16–21
Majumdar S (1988) Role of under relaxation in momentum interpolation for calculation of flow with non-staggered grids. Num Heat Transf 13:125–132
Eckert ERG, Goldstein RJ (1976) Measurements in heat transfer. McGraw-Hill, New York
Sajith V, Sobhan CB (2008) Digital interferometric measurement of forced convection heat transfer in a miniature rectangular channel. J Exp Heat Transf 21(04):314–333
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vyas, D.R., Sobhan, C.B. & Peterson, G.P. An investigation of Marangoni-Benard convection in water based nanofluids. Heat Mass Transfer 55, 791–809 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-018-2452-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-018-2452-x