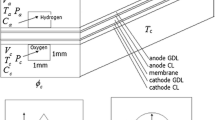
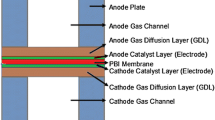
Abstract
Humidity and humidification in a proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEM) can significantly affect the performance of these energy generating devices. Since protons (H+) needs to be accompanied by water molecules to pass from the anode side to the cathode side, the PEM fuel cell membrane should be sufficiently wet. Low or high amount of water in the membrane can interrupt the flow of protons and thus reduce the efficiency of the fuel cell. In this context, several experimental studies and modeling have been carried out on PEM fuel cell and interesting results have been achieved. In this paper, the humidity and flow rate of gas in the anode and cathode are modified to examine its effect on fuel cell performance. The results show that the effect of humidity changing in the anode side is greater than that of the cathode so that at zero humidity of anode and 70 % humidity of the cathode, a maximum current flow of 0.512 A/cm2 for 0.12 V was obtained. However, at 70 % anode humidity and zero cathode humidity, a maximum flow of 0.86 A/cm2 for 0.13 V was obtained.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhou B, Huang W, Zong Y, Sobiesiak A (2006) Water and pressure effects on a single PEM fuel cell. J Power Sources 155:190–202
Jung SH, Kim SL, Kim MS, Park Y, Lim TW (2007) Experimental study of gas humidification with injectors for automotive PEM fuel cell systems. J Power Sources 170:324–333
Yan Q, Toghiani H, Wu J (2006) Investigation of water transport through membrane in a PEM fuel cell by water balance experiments. J Power Sources 158:316–325
Dai W, Wang H, Yuan X-Z, Martin JJ, Yang D, Qiao J, Ma J (2009) A review on water balance in the membrane electrode assembly of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Int J Hydrogen Energy 34:9461–9478
Jeon DH, Kim KN, Baek SM, Nam JH (2011) The effect of relative humidity of the cathode on the performance and the uniformity of PEM fuel cells. Int J Hydrogen Energy 36:12499–12511
Zhang J, Tang Y, Song C, Xia Z, Li H, Wang H, Zhang J (2008) PEM fuel cell relative humidity (RH) and its effect on performance at high temperatures. Electrochim Acta 53:5315–5321
Ahmadi N, Rezazadeh S, Yekani M, Fakouri A, Mirzaee I, Chen S-Y, Anderson M, Gholipour J, Bridier F, Nsom B (2013) Numerical investigation of the effect of inlet gases humidity on polymer exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) performance. Trans Can Soc Mech Eng 37:1
Hassan NSM, Daud WRW, Sopian K, Sahari J (2009) Water management in a single cell proton exchange membrane fuel cells with a serpentine flow field. J Power Sources 193:249–257
Matamoros L, Brüggemann D (2006) Simulation of the water and heat management in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J Power Sources 161:203–213
Kraytsberg A, Ein-Eli Y (2006) PEM FC with improved water management. J Power Sources 160:194–201
Zong Y, Zhou B, Sobiesiak A (2006) Water and thermal management in a single PEM fuel cell with non-uniform stack temperature. J Power Sources 161:143–159
Owejan JP, Gagliardo JJ, Sergi JM, Kandlikar SG, Trabold TA (2009) Water management studies in PEM fuel cells, Part I: fuel cell design and in situ water distributions. Int J Hydrogen Energy 34:3436–3444
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gholizadeh, M., Ghazikhani, M. & Khazaee, I. Experimental study of humidity changes on the performance of an elliptical single four-channel PEM fuel cell. Heat Mass Transfer 53, 233–239 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-016-1819-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-016-1819-0