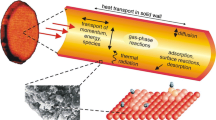
Abstract
In the present work the effect of catalytic surface reaction on non-reactive bulk flow in micro-channel is investigated. The reaction surface is analyzed with assumption of constant wall temperature. To solve this problem, the energy, mole fraction and catalytic reaction equations are solved by trial and error process. The analysis show that most sensitive parameter is fuel conversion and the sensitivity of hydraulic diameter is more than longitude coordinates.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A C :
-
Cross-sectional area of micro-channel (m2)
- C b :
-
Molar density (mole/m3)
- C P :
-
Constant pressure specific heat (J/KgK)
- D :
-
Diffusion coefficient (m2/s)
- d C :
-
Thickness of Pt catalyst (m)
- d h :
-
Hydraulic diameter (m)
- E :
-
Relative sensitivity parameter
- h :
-
Convection heat transfer coefficient (W/m2K)
- h m :
-
Convection mass transfer coefficient (m/s)
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- Q :
-
Catalyst heat transfer (W)
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- S :
-
Normalized sensitivity analysis parameter
- s :
-
Sensitivity analysis parameter
- Sc :
-
Schmidt number
- Sh :
-
Sherwood number
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- U :
-
Velocity (m/s)
- V :
-
Volume (m3)
- W C :
-
Reaction rate
- X :
-
Axial location (m)
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity (w/mK)
- k C :
-
The rate constant of catalytic reaction
- L :
-
The channel length (m)
- M :
-
Molecular weight of species
- \(\dot{m}\) :
-
Mass flow rate (Kg/s)
- Nu :
-
Nusselt number
- P :
-
Static pressure (atm)
- p :
-
Wetted perimeter of micro-channel (m)
- Pe :
-
Peclet number
- Y :
-
Mole fraction of fuel
- Φ :
-
Model response parameter
- μ :
-
Viscosity (Ns/m2)
- ρ :
-
Density (Kg/m3)
- υ :
-
Diffusion volumes of samples
- c :
-
Conversion, catalytic reaction
- i :
-
Input, samples
- m :
-
Mass
- S :
-
Surface
- 0 :
-
Nominal value
References
Kaisare NS, Vlachos DG (2012) A review on micro-combustion: fundamentals, devices and applications. Prog Energy Combust Sci 38:321–359
Swarup YJ, Debi PM (2009) A review of recent patents on micro-combustion and applications. Recent Pat Eng 3:194–209
Qu W, Mudawar I (2002) Analysis of three-dimensional heat transfer in micro-channel heat sinks. Int J Heat Mass Transf 45:3973–3985
Li J, Chou SK, Huang G, Yang WM, Li ZW (2009) Study on premixed combustion in cylindrical micro combustors: transient flame behavior and wall heat flux. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 33:764–773
Li J, Chou SK, Li ZW, Yang WM (2009) Development of 1D model for the analysis of heat transport in cylindrical micro combustors. Appl Therm Eng 29:1854–1863
Veeraragavan A, Dellimore Kiran, Cadou C (2009) Two-dimensional analytical model of heat transfer for flames in channels. J Thermophys Heat Transf 23(3):551–558
Veeraragavan A (2006) Heat transfer analysis for improved in-situ infrared temperature diagnostics in microcombustors. Master of Science thesis, Faculty of the Graduate School of the University of Maryland, College Park, MD
Fanaee A, Esfahani JA (2011) The investigation of semi-three-dimensional heat transfer modeling in microcombustors. J Therm Sci Eng Appl 3:1–8
Bidabadi M, Fanaee A, Rahbari A (2010) Investigation over the recirculation influence on the combustion of micro organic dust particles. Appl Math Mech 31(6):685–696
Bidabadi M, Montazerinejad S, Fanaee A (2010) An analytical study of radiation effect on the ignition of magnesium particles using perturbation theory. Lat Am Appl Res 40:351–357
Kaisare NS, Deshmukh SR, Vlachos DG (2008) Stability and performance of catalytic micro-reactors: simulations of propane catalytic combustion on Pt. Chem Eng Sci 63:1098–1116
Zeng W, Xie Maozhao, Ma Hongan, Xu W (2008) Bifurcation behaviors of catalytic combustion in a micro-channel. J Therm Sci 17(1):84–89
Spadaccini CM (2004) Combustion systems for power-mems applications. Phd thesis, Faculty of the Graduate School of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Qazizade A, Renksizbulut M, Friedman J (2012) Contribution of homogeneous reactions to hydrogen oxidation in catalytic microchannels. Combust Flame 159:784–792
Veeraragavan A, Cadou CP (2011) Flame speed predictions in planar micro/meso scale combustors with conjugate heat transfer. Combust Flame 158:2178–2187
Pizza G, Mantzaras J, Frouzakis CE, Tomboulides AG, Boulouchos K (2009) Suppression of combustion instabilities of premixed hydrogen/air flames in micro-channels using heterogeneous reactions. Proc Combust Inst 32:3051–3058
Karakaya M, Avci AK (2009) Simulation of on-board fuel conversion in catalytic micro-channel reactor-heat exchanger systems. Top Catal 52:2112–2116
Incropera FP, De Witt DP (2005) Fundamentals of heat and mass transfer, 6th edn. Wiley and sons, New York
Hayes RE, Kolaczkowski ST (1997) Introduction to catalysis combustion. Gordan and Breach Science Publishers, Canada
Esfahani JA (2002) Oxygen-sensitive thermal degradation of PMMA: a numerical study. Combust Sci Technol 174(10):183–198
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fanaee, S.A., Esfahani, J.A. The analytical modeling of propane-oxygen mixture at catalytic micro-channel. Heat Mass Transfer 50, 1365–1373 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-014-1344-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-014-1344-y