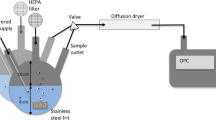
Abstract
Paradichlorobenzene cylinders were cast, then suspended vertically and allowed to sublimate in air. Data on mass versus time were measured, and a sublimation rate was calculated. Three cylinders of different diameters were used: 1 inch (2.54 cm), 1.5 inch (3.81 cm), and 2 inch (5.08 cm). The length of all three cylinders was 10 in. (25.4 cm). Calculations indicate that the Schmidt number was constant. The Sherwood number ranged from 23 to 26, and Rayleigh numbers varied from 11 × 103 to 88 × 103. The objective of this study was to develop a correlation for determining the mass transfer coefficient of vertically suspended paradichlorobenzene cylinders in a natural convection environment. An equation relating Sherwood and Rayleigh numbers was derived.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Surface area
- C :
-
Concentration of paradichlorobenzene
- D :
-
Characteristic dimension (diameter)
- D AB :
-
Binary diffusion coefficient
- g :
-
Acceleration of gravity
- Gr:
-
Grashof number = ρ air gD 3(ρ v,s − ρ v,∞ )/μ2
- h m :
-
Overall mass transfer coefficient
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity
- M p :
-
Molecular mass of paradichlorobenzene
- M a :
-
Molecular mass of air
- \( \dot{m} \) :
-
Sublimation rate
- N A :
-
Molar flux
- p v :
-
Partial pressure of paradichlorobenzene
- Ra:
-
Rayleigh number = Gr · Sc
- Re :
-
Reynolds number = VD/ν
- Sc:
-
Schmidt number = v/D AB
- Sh:
-
Sherwood number = h m D/D AB
- T :
-
Temperature
- T m :
-
Mean or average temperature
- T w :
-
Temperature of cylinder surface
- V :
-
Velocity
- β :
-
Volumetric thermal expansion coefficient
- μ :
-
Viscosity of air
- ν :
-
Kinematic viscosity
- ρ :
-
Density of paradichlorobenzene vapor or of air
References
Bandrowski J, Rybski W (1976) Free convection mass transfer from horizontal plates. Int J Heat Mass Transf 19:827–838
Fite LW (1989) Mass transfer from a sublimating naphthalene cylinder to a crossflow of air. Masters thesis, Memphis State University
Goldstein RJ, Sparrow EM, Jones DC (1973) Natural convection mass transfer adjacent to horizontal plates. Int J Heat Mass Transf 16:1025–1035
Janna WS, Bruce DW (1989) Mass transfer from a sublimating paradichlorobenzene cylinder immersed in a crossflow of air. Memphis State University, Memphis
Moffat RJ (1988) Describing the uncertainties in experimental results. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 1:3–17
Nassif NJ (1992) The determination of average mass transfer coefficients for flow over a flat plate using the naphthalene sublimation technique. Ph.D. dissertation, Memphis State University
Schmidt R (2001) Use of naphthalene sublimation technique for obtaining accurate heat transfer coefficients in electronic cooling applications. Electron Cool 7
Sogin HH (1958) Sublimation from disks to air streams flowing normal to their surfaces. Trans ASME 80:61–69
Sparrow EM, Niethammer JE (1979) Natural convection in a ternary gas mixture-application to the naphthalene sublimation technique. Trans ASME 101:404–410
Internet references
General reference
Janna WS (2000) Engineering heat transfer, 2nd edn. PWS Publishers, Boston
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Mr. Edward Dean for his assistance in debugging the computer code used in the data collection process.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Snapp, W.B., Janna, W. Sublimation of vertically oriented paradichlorobenzene cylinders in a natural convection environment. Heat Mass Transfer 48, 1005–1010 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-011-0952-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-011-0952-z