Abstract
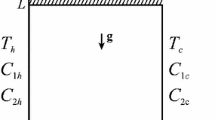
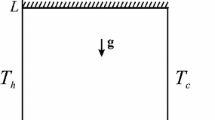
Laminar double-diffusive natural convective flow of a binary fluid mixture in inclined square and rectangular cavities filled with a uniform porous medium in the presence of temperature-difference dependent heat generation (source) or absorption (sink) is considered. Transverse gradients of heat and mass are applied on two opposing walls of the cavity while the other two walls are kept adiabatic and impermeable to mass transfer. The problem is put in terms of the stream function-vorticity formulation. A numerical solution based on the finite-difference methodology is obtained for relatively high Lewis numbers. Representative results illustrating the effects of the inclination angle of the cavity, buoyancy ratio, Darcy number, heat generation or absorption coefficient and the cavity aspect ratio on the contour maps of the streamline, temperature, and concentration as well as the profiles of velocity, temperature and concentration at mid-section of the cavity are reported. In addition, numerical results for the average Nusselt and Sherwood numbers are presented for various parametric conditions and discussed.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
enclosure aspect ratio = H/W
- c :
-
concentration of species
- c h :
-
high species concentration (source)
- c l :
-
low species concentration (sink)
- c p :
-
specific heat of the fluid
- c s :
-
specific heat of porous medium material
- C :
-
dimensionless species concentration = (c − c 1)/(c h − c 1) − 0.5
- D :
-
species diffusivity
- Da :
-
Darcy number = κ/W 2
- g :
-
gravitational acceleration
- H :
-
enclosure height
- Le :
-
Lewis number = α e /D
- N :
-
buoyancy ratio = β c (c h − c 1)/[ β T (T h − T c ) ]
- \(\overline{{{\hbox{Nu}}}}\) :
-
average Nusselt number at heated vertical wall
- p :
-
fluid pressure
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number \( = v \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {v {\alpha_{e}}}} \right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} {\alpha_{e}}\)
- Q 0 :
-
heat generation or absorption coefficient
- Ra :
-
thermal Rayleigh number = gβ T (T h − T c )W3/(α e ν)
- \(\overline{{{\hbox{Sh}}}}\) :
-
average Sherwood number at heated vertical wall
- t :
-
time
- T :
-
temperature
- T h :
-
hot wall temperature (source)
- T c :
-
cold wall temperature (sink)
- u :
-
horizontal velocity component
- U :
-
dimensionless horizontal velocity component = uW/α e
- v :
-
vertical velocity component
- V :
-
dimensionless vertical velocity component = vW/α e
- W :
-
enclosure width
- x :
-
horizontal coordinate
- X :
-
dimensionless horizontal coordinate = x/W
- y :
-
vertical coordinate
- Y :
-
dimensionless vertical coordinate = y/W
- α:
-
inclination angle of the cavity
- αe :
-
effective thermal diffusivity of the porous medium
- βT :
-
thermal expansion coefficient
- βc :
-
compositional expansion coefficient
- ɛ:
-
porosity of the porous medium
- ϕ:
-
dimensionless heat generation or absorption coefficient = Q 0 W 2/(ρ c p α e )
- κ:
-
permeability of the porous medium
- μ:
-
dynamic viscosity
- ν:
-
kinematic viscosity = μ/ρ
- θ:
-
dimensionless temperature = (T − T c )/(T h −T c ) − 0.5
- ρ :
-
Density
- ρ s :
-
Porous medium material density
- σ:
-
specific heats ratio = [ɛ ρ c p + (1 − ɛ)ρ s c s ]/(ρ c p )
- τ :
-
dimensionless time = αe t/W 2
- Ω:
-
vorticity
- ψ:
-
dimensionless stream function = Ψ/α e
- Ψ:
-
stream function
- ζ:
-
dimensionless vorticity = Ω W2/α e
- ∇2 :
-
Laplacian operator
References
Acharya S, Goldstein RJ (1985) Natural convection in an externally heated vertical or inclined square box containing internal energy sources. ASME J Heat Transf 107:855–866
Basak T, Roy S, Paul T, Pop I (2006) Natural convection in a square cavity filled with a porous medium: effects of various thermal boundary conditions. Int J Heat Mass Transf 49:1430–1441
Beghein C, Haghighat F, Allard F (1992) Numerical study of double-diffusive natural convection in a square cavity. Int J Heat Mass Transf 35:833–846
Chamkha AJ (1997) Non-Darcy fully developed mixed convection in a porous medium channel with heat generation/absorption and hydromagnetic effects. Numer Heat Transf 32:653–675
Chen F, Chen C (1993) Double-diffusive fingering convection in a porous medium. J Heat Transf 36:793–897
Churbanov AG, Vabishchevich PN, Chudanov VV, Strizhov VF (1994) A numerical study on natural convection of a heat-generating fluid in rectangular enclosures. Int J Heat Mass Transf 37:2969–2984
Hamady FJ, Lloyd JR, Yang HQ, Yang KT (1989) Study of local natural convection heat transfer in an inclined enclosure. Int J Heat Mass Transf 32:1697–1708
Hart JE (1971) Stability of the flow in a differentially heated inclined box. J Fluid Mech 47:547–576
Hyun JM, Lee JW (1990) Double-diffusive convection in a rectangle with cooperating horizontal gradients of temperature and concentration gradients. Int J Heat Mass Transf 33:1605–1617
Kakac S, Aung W, Viskanta R (1985) Natural convection—fundamentals and applications. Hemisphere, Washington
Lee JW, Hyun JM (1990) Double-diffusive convection in a rectangle with opposing horizontal and concentration gradients. Int J Heat Mass Transf 33:1619–1632
Lin D (1993) Unsteady natural convection heat and mass transfer in a saturated porous enclosure. Warme-und-stoffubertragung 28:49–56
Mamou M, Vasseur P, Bilgen E (1996) Analytical and numerical study of double diffusive convection in a vertical enclosure. Heat Mass Transf 32:115–125
Mamou M, Vasseur P, Bilgen E (1998) A Galerkin finite-element study of the onset of double-diffusive convection in an inclined porous enclosure. Int J Heat Mass Transf 41:1513–1529
Mamou M, Vasseur P, Bilgen E, Gobin D (1995) Double diffusive convection in an inclined slot filled with porous medium. Eur J Mech Fluids 14:629–652
Nishimura T, Wakamatsu M, Morega AM (1998) Oscillatory double-diffusive convection in a rectangular enclosure with combined horizontal temperature and concentration gradients. Int J Heat Mass Transf 4l:1601–1611
Ostrach S (1980) Natural convection with combined driving forces. PhysicoChem Hydrodyn 1:233–247
Ozoe H, Yamamoto K, Sagama H, Churchill SW (1974) Natural convection in an inclined rectangular channel heated on one side and cooled on the opposing side. Int J Heat Mass Transf 17:1209–1217
Raithby GD, K.Hollands GT (1985) Handbook of heat transfer fundamentals. McGraw-Hill, New York
Rasoul J, Prinos P (1997) Natural convection in an inclined enclosure. Int J Numer Methods Heat Fluid Flow 7:438–478
Ravi MR, Henkes RAW, Hoogendoorn CJ (1994) On the high-Rayleigh-number structure of steady laminar natural-convection flow in a square enclosure. J Fluid Mech 262:325–351
Trevisan OV, Bejan A (1986) Mass and heat transfer by natural convection in a vertical slot filled with porous medium. Int J Heat Mass Transf 29:403–415
Vajravelu K, Nayfeh J (1992) Hydromagnetic convection at a cone and a wedge. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 19:701–710
Viskanta R, Bergman TL, Incropera FP (1985) Double-diffusive natural convection. In: Kakac S, Aung W, Viskanta R (eds) Natural convection: fundamentals and applications. Hemisphere, Washington, pp 1075–1099
Yang KT (1988) Transitions and bifurcations in laminar buoyant flows in confined enclosures. J Heat Transf 110:1191–1204
Acknowledgement
The authors acknowledge and appreciate the financial support of this work by the Public Authority for Applied Education & Training under Project No. TS-05-005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chamkha, A.J., Al-Mudhaf, A. Double-diffusive natural convection in inclined porous cavities with various aspect ratios and temperature-dependent heat source or sink. Heat Mass Transfer 44, 679–693 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-007-0299-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-007-0299-7