Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effect of acidification and alkalinization on the pharmacokinetics of sparfloxacin in healthy subjects.
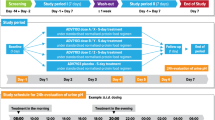
Methods: A single 200-mg oral dose of sparfloxacin was given to nine healthy Japanese volunteers on three separate occasions under different conditions of urinary pH. Acidic and alkaline conditions were achieved by repeated oral doses of ammonium chloride and sodium bicarbonate, respectively. The concentrations of sparfloxacin and its metabolite in plasma and urine were determined by high-performance liquid chromatography assays.
Results: The difference between treatments for Cmax, AUC∞, and CL · f−1 were found to be significant. The relative bioavailability of sparfloxacin was 84.4% and 122.3% after ammonium chloride and sodium bicarbonate treatments, respectively. The amount of unchanged sparfloxacin in urine samples collected 0–48 h after sparfloxacin administration represented 10.1% of the dose in the control, 14.3% of the dose in urine acidification and 8.4% of the dose with alkalinization of urine. Renal clearance was found to depend on urinary pH. However, the plasma elimination and the metabolism of sparfloxacin were not significantly altered by acidification or alkalinization of the urine.
Conclusion: The urinary pH dependence of the renal clearance of sparfloxacin will be of minor clinical importance with regard to the low contribution of renal excretion to the overall elimination of sparfloxacin. On the other hand, the alteration in the environmental pH in the gastrointestinal tract, produced by the concomitant ingestion of ammonium chloride or sodium bicarbonate, influences the absorption and bioavailability of sparfloxacin. This effect is likely to be clinically significant.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 18 March 1998 / Accepted in revised form: 1 July 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamberi, M., Kotegawa, T., Tsutsumi, K. et al. Sparfloxacin pharmacokinetics in healthy volunteers: the influence of acidification and alkalinization. E J Clin Pharmacol 54, 633–637 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002280050526
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002280050526