Abstract.
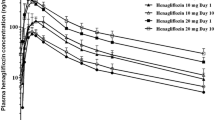
The effects and kinetics of oral glibenclamide (Gb) and glipizide (Gz) were studied in Caucasian and Chinese patients (ten in each group) with type-2 diabetes. In randomised order, 2.5 mg Gb, 2.5 mg Gz or placebo was given orally before the administration of 75 g oral glucose. Concentrations of insulin and proinsulin were determined using radioimmunoassay (RIA) without cross-reactivities, and sulphonylurea concentrations were determined using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). There were no significant interethnic differences in Gb or Gz effects whether on glucose, insulin or proinsulin/insulin ratio at any time point. Following Gz, however, Chinese patients had greater increments of serum proinsulin at 10–30 min compared with Caucasians. Apart from the maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) and area under the plasma concentration–time curve (AUC) of Gz being higher among the Chinese, no significant interethnic differences in pharmacokinetics were found. It appears that the same dosage principles could be used for Caucasian and Chinese patients with type-2 diabetes when Gb or Gz are prescribed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jönsson, A., Chan, J., Rydberg, T. et al. Effects and pharmacokinetics of oral glibenclamide and glipizide in Caucasian and Chinese patients with type-2 diabetes. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 56, 711–714 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002280000214
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002280000214