Abstract
Background
The efficacy and safety of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) in atrial fibrillation (AF) patients with impaired liver function (ILF) have not been sufficiently studied. The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of DOACs for stroke prevention in patients with AF and ILF.
Method
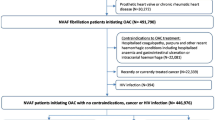
This study was based on data from 15 centers in China, including 4,982 AF patients. The patients were divided into 2 subgroups based on their liver function status: patients with normal liver function (NLF)(n = 4213) and patients with ILF (n = 769). Logistic regression analysis was used to investigate the risk of total bleeding, major bleeding, thromboembolism, and all-cause deaths in AF patients with NLF and ILF after taking dabigatran or rivaroxaban, respectively.
Results
Among AF patients treated with dabigatran or rivaroxaban, patients with ILF were associated with significantly higher major bleeding, compared with NLF patients (aOR: 4.797; 95% CI: 2.224–10.256; P < 0.001). In patients with NLF, dabigatran (n = 2011) had considerably lower risk of total bleeding than rivaroxaban (n = 2202) (aOR: 1.23; 95% CI: 1.002–1.513; P = 0.049). In patients with ILF, dabigatran (n = 321) significantly favored lower risks of major bleeding compared with rivaroxaban(n = 448) (aOR: 5.484; 95% CI: 1.508–35.269; P = 0.026).
Conclusion
After using dabigatran or rivaroxaban, patients with ILF had remarkably increased risk of major bleeding compared with patients with NLF. In AF patients with NLF, dabigatran had the distinct strength of significantly reduced risk of total bleeding compared with rivaroxaban. In patients with AF and ILF, dabigatran use was associated with lower risk for major bleeding compared with rivaroxaban.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Huang ZC, Li CQ, Liu XY et al (2021) Efficacy and safety of direct oral anticoagulants in patients with atrial fibrillation and liver disease: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 35(6):1205–1215
Chugh SS, Havmoeller R, Narayanan K et al (2014) Worldwide epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: a global burden of disease 2010 study. Circulation 129(8):837–847
Vizzardi E, Curnis A, Latini MG et al (2014) Risk factors for atrial fibrillation recurrence: a literature review. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown) 15(3):235–253
Joglar JA, Chung MK, Armbruster AL (2024) 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/HRS guideline for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association joint committee on clinical practice guidelines [published correction appears in Circulation. 2024 Jan 2;149(1):e167] [published correction appears in Circulation. 2024 Feb 27;149(9):e936]. Circulation 149(1):e1–e156
Ferri N, Colombo E, Tenconi M et al (2022) Drug-drug interactions of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs): from pharmacological to clinical practice. Pharmaceutics 14(6):1120 Published 2022 May 24
Gao X, Cai X, Yang Y et al (2021) Diagnostic accuracy of the HAS-BLED bleeding score in VKA- or DOAC-treated patients with atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Cardiovasc Med 8:757087 Published 2021 Nov 22
Qamar A, Vaduganathan M, Greenberger NJ et al (2018) Oral anticoagulation in patients with liver disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 71(19):2162–2175
Granger CB, Alexander JH, McMurray JJ, Lopes RD, Hylek EM, Hanna M, Al-Khalidi HR, Ansell J, Atar D, Avezum A, Bahit MC, Diaz R, Easton JD, Ezekowitz JA, Flaker G, Garcia D, Geraldes M, Gersh BJ, Golitsyn S, Goto S, Hermosillo AG, Hohnloser SH, Horowitz J, Mohan P, Jansky P, Lewis BS, Lopez‐Sendon JL, Pais P, Parkhomenko A, Verheugt FW, Zhu J, Wallentin L (2011) Apixaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 365:981–992
Giugliano RP, Ruff CT, Braunwald E, Murphy SA, Wiviott SD, Halperin JL, Waldo AL, Ezekowitz MD, Weitz JI, Spinar J, Ruzyllo W, Ruda M, Koretsune Y, Betcher J, Shi M, Grip LT, Patel SP, Patel I, Hanyok JJ, Mercuri M, Antman EM (2013) Edoxaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 369:2093–2104
Agnelli G, Buller HR, Cohen A, Curto M, Gallus AS, Johnson M, Masiukiewicz U, Pak R, Thompson J, Raskob GE, Weitz JI (2013) Oral apixaban for the treatment of acute venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med 369:799–808
Buller HR, Decousus H, Grosso MA, Mercuri M, Middeldorp S, Prins MH, Raskob GE, Schellong SM, Schwocho L, Segers A, Shi M, Verhamme P, Wells P (2013) Edoxaban versus warfarin for the treatment of symptomatic venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med 369:1406–1415
Lawal OD, Aronow HD, Shobayo F et al (2023) Comparative effectiveness and safety of direct oral anticoagulants and warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation and chronic liver disease: a nationwide cohort study. Circulation 147(10):782–794
Lau WCY, Torre CO, Man KKC et al (2022) Comparative effectiveness and safety between apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban, and rivaroxaban among patients with atrial fibrillation: a multinational population-based cohort study [published correction appears in Ann Intern Med. 2022;]. Ann Intern Med 175(11):1515–1524
Talmor-Barkan Y, Yacovzada NS, Rossman H et al (2022) Head-to-head efficacy and safety of rivaroxaban, apixaban, and dabigatran in an observational nationwide targeted trial. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother 9(1):26–37
Bai Y, Deng H, Shantsila A, Lip GY (2017) Rivaroxaban versus dabigatran or warfarin in real-world studies of stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation: systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke 48(4):970–976
Wang CL, Wu VC, Kuo CF et al (2018) Efficacy and safety of non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation patients with impaired liver function: a retrospective cohort study. J Am Heart Assoc 7(15):e009263
Tripodi A, Mannucci PM (2011) The coagulopathy of chronic liver disease. N Engl J Med 365(2):147–156. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1011170
Kujovich JL (2015) Coagulopathy in liver disease: a balancing act. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2015:243–249
Lip GY, Nieuwlaat R, Pisters R et al (2010) Refining clinical risk stratification for predicting stroke and thromboembolism in atrial fibrillation using a novel risk factor-based approach: the Euro heart survey on atrial fibrillation. Chest 137(2):263–272
Pisters R, Lane DA, Nieuwlaat R (2010) A novel user-friendly score (HAS-BLED) to assess 1-year risk of major bleeding in patients with atrial fibrillation: the Euro heart survey. Chest 138(5):1093–1100
Schulman S, Kearon C (2005) Subcommittee on control of anticoagulation of the scientific and standardization committee of the international society on thrombosis and haemostasis. Definition of major bleeding in clinical investigations of antihemostatic medicinal products in non-surgical patients. J Thromb Haemost 3(4):692–694
Connolly SJ, Ezekowitz MD, Yusuf S et al (2009) Dabigatran versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation [published correction appears in N Engl J Med. 2010 Nov 4;363(19):1877]. N Engl J Med 361(12):1139–1151
Kirchhof P, Benussi S, Kotecha D, ESC Scientific Document Group et al (2016) 2016 ESC guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Eur Heart J 37(38):2893–2962
Chen S, Pürerfellner H, Meyer C et al (2022) Anticoagulation in atrial fibrillation and liver disease: a pooled-analysis of > 20 000 patients. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother 8(4):336–345
Patel MR, Mahaffey KW, Garg J et al (2011) Rivaroxaban versus warfarin in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 365:883–891
López-López JA, Sterne JAC, Thom HHZ et al (2017) Oral anticoagulants for prevention of stroke in atrial fibrillation: systematic review, network meta-analysis, and cost effectiveness analysis. BMJ 359
Cohen AT, Hamilton M, Mitchell SA et al (2015) Comparison of the novel oral anticoagulants apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban, and rivaroxaban in the initial and long-term treatment and prevention of venous thromboembolism: systematic review and network meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 10(12):e0144856
Rutherford OW, Jonasson C, Ghanima W et al (2020) Comparison of dabigatran, rivaroxaban, and apixaban for effectiveness and safety in atrial fibrillation: a nationwide cohort study. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother 6(2):75–85
Staerk L, Gerds TA, Lip GYH et al (2018) Standard and reduced doses of dabigatran, rivaroxaban and apixaban for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation: a nationwide cohort study. J Intern Med 283(1):45–55
Andersson NW, Svanström H, Lund M et al (2018) Comparative effectiveness and safety of apixaban, dabigatran, and rivaroxaban in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Int J Cardiol 268:113–119
Costache RS, Dragomirică AS, Gheorghe BE et al (2023) Oral anticoagulation in patients with chronic liver disease. Med (Kaunas) 59(2):346
Steffel J, Collins R, Antz M et al (2021) 2021 European Heart Rhythm Association practical guide on the use of non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants in patients with atrial fibrillation. Europace 23(10):1612–1676
Kanuri SH, Kreutz RP (2019) Pharmacogenomics of novel direct oral anticoagulants: newly identified genes and genetic variants. J Pers Med 9(1):7
Gronich N, Stein N, Muszkat M (2021) Association between use of pharmacokinetic-interacting drugs and effectiveness and safety of direct acting oral anticoagulants: nested case-control study. Clin Pharmacol Ther 110(6):1526–1536
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jinhua Zhang initiated the study. Ruijuan Li, Ping Gu, Qiaowei Zheng, Yuxin Liu, Hengfen Dai, Xiangsheng Lin, Yuxin Liu, Xiaoming Du, Jun Su, Wang Zhang, Min Zhang, Zhu Zhu, Xiaohong Huang and Nianxu Huang collected and entered the data. Guilan Wu and Wenlin Xu performed data collation. Xinhai Huang and Jinhua Zhang performed data extraction and analyses. Xinhai Huang drafted the first version of the manuscript. Xinhai Huang, Guilan Wu and Jinhua Zhan critically reviewed the manuscript and revised it. Xinhai Huang and Wenlin Xu worked on data validation. Xinhai Huang and Guilan Wu performed the graphical revisions. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Human ethics and consent to participate
The study complied with the Declaration of Helsinki and was authorized by The Ethics Committee of Fujian Maternal and Child Health Hospital on January 19, 2023 (registration number: ChiCTR2300067734). Due to the retrospective nature of this study, the review board waived the informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, X., Xu, W., Wu, G. et al. Efficacy and safety of dabigatran and rivaroxaban in atrial fibrillation patients with impaired liver function: a multicenter retrospective cohort study. Eur J Clin Pharmacol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-024-03689-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-024-03689-3