Abstract
Purpose
Gefitinib is one of the standard treatments for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with epidermal growth factor receptor mutations. It has been reported that acid suppressants (AS) decrease the anti-tumor effect of gefitinib by reducing its solubility. AS is sometimes necessary in cancer patients; however, previous reports have not shown the most compatible AS with gefitinib administration in cancer patients. This study was conducted to determine if histamine type 2 receptor antagonists (H2RAs) can affect the anti-tumor efficacy of gefitinib.
Methods
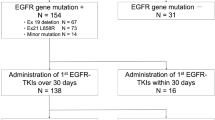
Eighty-seven patients with NSCLC who were administered gefitinib were retrospectively investigated. Patients who were co-administered H2RA were compared with non-AS control patients. H2RA was administered once a day at about 3–5 or 8–12 h after gefitinib intake. The primary endpoint of this study was progression-free survival (PFS), and secondary endpoints were overall survival (OS), overall response rate (ORR), and adverse effects.
Results
Median PFS in H2RA group and control group was 8.0 months and 9.0 months, respectively, with no significant difference (p = 0.82). The incidence of liver dysfunction was significantly less in patients administered H2RA, whereas there were no differences between the two groups with regard to skin toxicity and diarrhea. Multivariate analysis suggested that H2RA co-administration is not a risk factor for worse PFS and OS (hazard ratio of 0.95, 0.86; 95% confidence interval of 0.60–1.48, 0.52–1.43; p = 0.82 and 0.60, respectively).
Conclusion
This study demonstrated that concomitant administration of H2RA with gefitinib does not affect the efficacy of gefitinib.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Sugawara S, Oizumi S, Isobe H, Gemma A, Harada M, Yoshizawa H, Kinoshita I, Fujita Y, Okinaga S, Hirano H, Yoshimori K, Harada T, Ogura T, Ando M, Miyazawa H, Tanaka T, Saijo Y, Hagiwara K, Morita S, Nukiwa T, North-East Japan Study Group (2010) Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med 362:2380–2388. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0909530
Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, Negoro S, Okamoto I, Tsurutani J, Seto T, Satouchi M, Tada H, Hirashima T, Asami K, Katakami N, Takada M, Yoshioka H, Shibata K, Kudoh S, Shimizu E, Saito H, Toyooka S, Nakagawa K, Fukuoka M, West Japan Oncology Group (2010) Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 11:121–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70364-X
Midha A, Dearden S, McCormack R (2015) EGFR mutation incidence in non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology: a systematic review and global map by ethnicity (mutMapII). Am J Cancer Res 5:2892–2911
Shiraishi K, Okada Y, Takahashi A, Kamatani Y, Momozawa Y, Ashikawa K, Kunitoh H, Matsumoto S, Takano A, Shimizu K, Goto A, Tsuta K, Watanabe S, Ohe Y, Watanabe Y, Goto Y, Nokihara H, Furuta K, Yoshida A, Goto K, Hishida T, Tsuboi M, Tsuchihara K, Miyagi Y, Nakayama H, Yokose T, Tanaka K, Nagashima T, Ohtaki Y, Maeda D, Imai K, Minamiya Y, Sakamoto H, Saito A, Shimada Y, Sunami K, Saito M, Inazawa J, Nakamura Y, Yoshida T, Yokota J, Matsuda F, Matsuo K, Daigo Y, Kubo M, Kohno T (2016) Association of variations in HLA class II and other loci with susceptibility to EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinoma. Nat Commun 7:12451. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12451
Kudo K, Hotta K, Ichihara E, Yoshioka H, Kunimasa K, Tsubouchi K, Iwasaku M, Kato Y, Oze I, Takigawa N, Tanimoto M, Kiura K (2015) Impact of body surface area on survival in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with gefitinib monotherapy: observational study of the Okayama Lung Cancer Study Group 0703. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 76:251–256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-015-2789-5
Ichihara E, Hotta K, Takigawa N, Kudo K, Kato Y, Honda Y, Hayakawa H, Minami D, Sato A, Tabata M, Tanimoto M, Kiura K (2013) Impact of physical size on gefitinib efficacy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR mutations. Lung Cancer 81:435–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2013.05.021
Igawa S, Kasajima M, Ishihara M, Kimura M, Hiyoshi Y, Niwa H, Kusuhara S, Harada S, Asakuma M, Otani S, Katono K, Sasaki J, Masuda N (2014) Evaluation of gefitinib efficacy according to body surface area in patients with non-small cell lung cancer harboring an EGFR mutation. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 74:939–946. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2570-1
Imai H, Kuwako T, Kaira K, Masuda T, Miura Y, Seki K, Sakurai R, Utsugi M, Shimizu K, Sunaga N, Tomizawa Y, Ishihara S, Ishizuka T, Mogi A, Hisada T, Minato K, Takise A, Saito R, Yamada M (2017) Evaluation of gefitinib efficacy according to body mass index, body surface area, and body weight in patients with EGFR-mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 79:497–505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-016-3232-2
Smelick GS, Heffron TP, Chu L, Dean B, West DA, Duvall SL, Lum BL, Budha N, Holden SN, Benet LZ, Frymoyer A, Dresser MJ, Ware JA (2013) Prevalence of acid-reducing agents (ARA) in cancer populations and ARA drug-drug interaction potential for molecular targeted agents in clinical development. Mol Pharm 10:4055–4062. https://doi.org/10.1021/mp400403s
Zhang L, Wu F, Lee SC, Zhao H, Zhang L (2014) pH-dependent drug-drug interactions for weak base drugs: potential implications for new drug development. Clin Pharmacol Ther 96:266–277. https://doi.org/10.1038/clpt.2014.87
European Medicines Agency. Iressa: summary of product characteristics [online]. Available from URL: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Information/human/001016/WC500036358.pdf. Accessed 7 Aug 2018
Chu MP, Ghosh S, Chambers CR, Basappa N, Butts CA, Chu Q, Fenton D, Joy AA, Sangha R, Smylie M, Sawyer MB (2015) Gastric acid suppression is associated with decreased erlotinib efficacy in non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer 16:33–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cllc.2014.07.005
Zenke Y, Yoh K, Matsumoto S, Umemura S, Niho S, Ohmatsu H, Goto K, Ohe Y (2016) Clinical impact of gastric acid-suppressing medication use on the efficacy of erlotinib and gefitinib in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harboring EGFR mutations. Clin Lung Cancer 17:412–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cllc.2016.01.006
Kumarakulasinghe NB, Syn N, Soon YY, Asmat A, Zheng H, Loy EY, Pang B, Soo RA (2016) EGFR kinase inhibitors and gastric acid suppressants in EGFR-mutant NSCLC: a retrospective database analysis of potential drug interaction. Oncotarget 7:85542–85550. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.13458
Hilton JF, Tu D, Seymour L, Shepherd FA, Bradbury PA (2013) An evaluation of the possible interaction of gastric acid suppressing medication and the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor erlotinib. Lung Cancer 82:136–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2013.06.008
Lim SG, Sawyerr AM, Hudson M, Sercombe J, Pounder RE (1993) Short report: the absorption of fluconazole and itraconazole under conditions of low intragastric acidity. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 7:317–321
Jaruratanasirikul S, Sriwiriyajan S (1998) Effect of omeprazole on the pharmacokinetics of itraconazole. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 54:159–161
Uno T, Sugimoto K, Sugawara K, Tateishi T (2008) The role of cytochrome P2C19 in R-warfarin pharmacokinetics and its interaction with omeprazole. Ther Drug Monit 30:276–281. https://doi.org/10.1097/FTD.0b013e31816e2d8e
Narumi K, Sato Y, Kobayashi M, Furugen A, Kasashi K, Yamada T, Teshima T, Iseki K (2017) Effects of proton pump inhibitors and famotidine on elimination of plasma methotrexate: evaluation of drug-drug interactions mediated by organic anion transporter 3. Biopharm Drug Dispos 38:501–508. https://doi.org/10.1002/bdd.2091
Budha NR, Frymoyer A, Smelick GS, Jin JY, Yago MR, Dresser MJ, Holden SN, Benet LZ, Ware JA (2012) Drug absorption interactions between oral targeted anticancer agents and PPIs: is pH-dependent solubility the Achilles heel of targeted therapy? Clin Pharmacol Ther 92:203–213. https://doi.org/10.1038/clpt.2012.73
Nakamura Y, Sano K, Soda H, Takatani H, Fukuda M, Nagashima S, Hayashi T, Oka M, Tsukamoto K, Kohno S (2010) Pharmacokinetics of gefitinib predicts antitumor activity for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 5:1404–1409. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181e59a7b
Yokota H, Sato K, Okuda Y, Kobayashi H, Takeda M, Asano M, Ito H, Miura M (2017) Effects of histamine 2-receptor antagonists and proton pump inhibitors on the pharmacokinetics of gefitinib in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer 18:e433–e439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cllc.2017.05.010
Ruiz-Garcia A, Masters JC, Mendes da Costa L, LaBadie RR, Liang Y, Ni G, Ellery CA, Boutros T, Goldberg Z, Bello CL (2016) Effect of food or proton pump inhibitor treatment on the bioavailability of dacomitinib in healthy volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol 56:223–230. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcph.588
Sato T, Ito H, Hirata A, Abe T, Mano N, Yamaguchi H (2018) Interactions of crizotinib and gefitinib with organic anion-transporting polypeptides (OATP)1B1, OATP1B3 and OATP2B1: gefitinib shows contradictory interaction with OATP1B3. Xenobiotica 48:73–78. https://doi.org/10.1080/00498254.2016.1275880
Scheffler M, Di Gion P, Doroshyenko O, Wolf J, Fuhr U (2011) Clinical pharmacokinetics of tyrosine kinase inhibitors: focus on 4-anilinoquinazolines. Clin Pharmacokinet 50:371–403. https://doi.org/10.2165/11587020-000000000-00000
Ozvegy-Laczka C, Hegedus T, Várady G, Ujhelly O, Schuetz JD, Váradi A, Kéri G, Orfi L, Német K, Sarkadi B (2004) High-affinity interaction of tyrosine kinase inhibitors with the ABCG2 multidrug transporter. Mol Pharmacol 65:1485–1495
Hamilton M, Wolf JL, Rusk J, Beard SE, Clark GM, Witt K, Cagnoni PJ (2006) Effects of smoking on the pharmacokinetics of erlotinib. Clin Cancer Res 12:2166–2171
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Designed study: Y.S., Y.T., M.K., N.S., Y.S., I.K., H.D., K.I., and M.S. Performed research: Y.S. Analyzed data: Y.S., Y.T., M.K. Contributed new methods or models: Y.S., Y.T., M.K. Wrote the paper: Y.S. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
YS, MK, YT, NS, YS, IK, KI, and MS have no conflicts of interest.
HD received an honorarium from AstraZeneca for speaking at a symposium.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All the procedures performed in studies involving human participants were carried out in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saito, Y., Takekuma, Y., Kobayashi, M. et al. Impact of histamine type-2 receptor antagonists on the anticancer efficacy of gefitinib in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 77, 381–388 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-020-03013-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-020-03013-9