Abstract
Background
Routine laboratory monitoring of rivaroxaban and dose adjustment relating to exposure is currently not recommended. However, in certain clinical situations, assessment of rivaroxaban levels is desirable.
Objectives
To examine inter- and intra-subject plasma rivaroxaban variability in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) and to correlate these results to clinical outcomes.
Patients/methods
We included 60 patients with AF treated with rivaroxaban: half on 20 mg daily (R20) and half on 15 mg daily (R15). Three trough and peak blood samples were collected with an interval of 6–8 weeks apart. Plasma rivaroxaban concentration was measured directly by liquid chromatography-tandem mass-spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and indirectly by anti-Xa for rivaroxaban, prothrombin time (PT), and activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT).
Results
Patients on R15 were older (76 ± 6 vs 71 ± 6 years), had lower creatinine clearance (60 ± 26 vs 99 ± 32 mL/min), higher CHADS2 (2.5 ± 1.2 vs 1.8 ± 1.3), all p < 0.01, but had similar rivaroxaban concentrations in trough samples to patients on R20. There was no significant intra-individual variability for trough or peak rivaroxaban concentration assessed by LC-MS/MS, anti-Xa, or PT. Trough rivaroxaban levels determined by LC-MS/MS (48 ± 30 vs 34 ± 26, p = 0.02) and anti-Xa, but not with PT and APTT, were higher in patients with bleeding than in patients without it.
Conclusions
There is a pronounced inter-, but not intra-individual variability in the rivaroxaban trough levels in patients with AF. Assessment of trough rivaroxaban concentration with LC-MS/MS or anti-Xa, but not with APTT or PT, may help to identify patients at increased risk of bleeding.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kirchhof P, Benussi S, Kotecha D, Ahlsson A, Atar D, Casadei B, Castella M, Diener HC, Heidbuchel H, Hendriks J, Hindricks G, Manolis AS, Oldgren J, Popescu BA, Schotten U, Putte BV, Vardas P (2016) 2016 ESC guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Eur Heart J 37:2893–2962
Connolly SJ, Ezekowitz MD, Yusuf S, Phil D, Eikelboom J, Oldgren J, Parekh A, Pogue J, Reilly PA, Themeles E, Varrone J, Wang S, Alings M, Xavier D, Zhu J, Diaz R, Lewis BS, Darius H, Diener HS, Joyner CD, Wallentin L, the RE-LY steering committee and Investigators (2009) Dabigatran versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 361:1139–1151
Patel MR, Mahaffey KW, Garg J, Pan G, Singer DE, Hacke W, Breihardt G, Hankey GJ, Piccini JP, Becker RC, Nessel CC, Paolini JF, Berkowitz SD, Fox KAA, Califf RM (2011) The ROCKET AF steering committee for the ROCKET AF Investigators. Rivaroxaban versus warfarin in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 365:883–891
Granger CB, Alexander JH, McMurray JJ, Lopes RD, Hylek EM, Hanna M, Al-Khalidi HR, Ansell J, Atar D, Avezum A, Bahit MC, Diaz R, Easton JD, Ezekowitz JA, Flaker G, Garcia D, Geraldes M, Gersh BJ, Golitsyn S, Goto S, Hermosillo AG, Hohnloser SH, Horowitz J, Mohan P, Jansky P, Lewis BS, Lopez-Sendon JL, Pais P, Parkhomenko A, Verheugt FW, Zhu J, Wallentin L, ARISTOTLE Committees and Investigators (2011) Apixaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 365:981–992
Giugliano RP, Ruff CT, Braunwald E, Murphy SA, Wiviott SD, Halperin JL, Waldo AL, Ezekowitz MD, Weitz JI, Špinar J, Ruzyllo W, Ruda M, Koretsune Y, Betcher J, Shi M, Grip LT, Patel SP, Patel I, Hanyok JJ, Mercuri M, Antman EM, ENGAGE AF-TIMI 48 Investigators (2013) Edoxaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 369:2093–2104
Katz DF, Maddox TM, Turakhia M, Gehi A, O'Brien EC, Lubitz SA, Turchin A, Doros G, Lei L, Varosy P, Marzec L, Hsu JC (2017) Contemporary trends in oral anticoagulant prescription in atrial fibrillation patients at low to moderate risk of stroke after guideline-recommended change in use of the CHADS2 to the CHA2DS2-VASc score for thromboembolic risk assessment: analysis from the national cardiovascular data registry’s outpatient practice innovation and clinical excellence atrial fibrillation registry. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 10:e003476
European Medicines Agency. Summary of product characteristics, Xarelto (rivaroxaban). Bayer Pharma AG. http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR-ProductInformation/human/000944/WC500057108.pdf. (2018, March 1)
Al-Aieshy F, Malmström RE, Antovic J, Pohanka A, Rönquist-Nii Y, Berndtsson M, Al-Khalili F, Skeppholm M (2016) Clinical evaluation of laboratory methods to monitor exposure of rivaroxaban at trough and peak in patients with atrial fibrillation. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 72:671–679
Francart SJ, Hawes EM, Deal AM, Adcock DM, Gosselin R, Jeanneret C, Friedman KD, Moll S (2014) Performance of coagulation tests in patients on therapeutic doses of rivaroxaban. A cross-sectional pharmacodynamic study based on peak and trough plasma levels. Thromb Haemost 111:1133–1140
Testa S, Tripodi A, Legnani C, Pengo V, Abbate R, Dellanoce C, Carraro P, Salomone L, Paniccia R, Paoletti O, Poli D, Palareti G, START-Laboratory Register (2016) Plasma levels of direct oral anticoagulants in real life patients with atrial fibrillation: results observed in four anticoagulation clinics. Thromb Res 137:178–183
Girgis IG, Patel MR, Peters GR, Moore KT, Mahaffey KW, Nessel CC, Halperin JL, Califf RM, Fox KA, Becker RC (2014) Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of rivaroxaban in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation: results from ROCKET AF. J Clin Pharmacol 54:917–927
Gulilat M, Tang A, Gryn SE, Leong-Sit P, Skanes AC, Alfonsi JE, Dresser GK, Henderson SL, Rose RV, Lizotte DJ, Teft WA, Schwarz UI, Tirona RG, Kim RB (2017) Interpatient variation in rivaroxaban and apixaban plasma concentrations in routine care. Can J Cardiol 33:1036–1043
Mueck W, Stampfuss J, Kubitza D, Becka M (2014) Clinical pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile of rivaroxaban. Clin Pharmacokinet 53:1–16
Eikelboom JW, Quinlan DJ, Hirsh J, Connolly SJ, Weitz JI (2017) Laboratory monitoring of non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulant use in patients with atrial fibrillation: a review. JAMA Cardiol 2:566–574
FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. Clinical review NDA Type 1 (505(b)(1)), August 2011. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/.../2011/202439Orig1s000MedR.pdf. (2018, March 1)
Fox KAA, Piccini JP, Wojdyla D, Becker RC, Halperin JL, Nessel CC, Paolini JF, Hankey GJ, Mahaffey KW, Patel MR, Singer DE, Califf RM (2011) Prevention of stroke and systemic embolism with rivaroxaban compared with warfarin in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation and moderate renal impairment. Eur Heart J 32:2387–2394
Yao JACC2017, Yao X, Shah ND, Sangaralingham LR, Gersh BJ, Noseworthy PA (2017) Non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulant dosing in patients with atrial fibrillation and renal dysfunction. J Am Coll Cardiol 69:2779–2790
Douxfils J, Ageno W, Samama C-M, Lessire S, ten Cate H, Verhamme P, Dogne JM, Mullier F (2018) Laboratory testing in patients treated with direct oral anticoagulants: a practical guide for clinicians. J Thromb Haemost 16:209–219
Samama MM, Contant G, Spiro TE, Perzborn E, Le Flem L, Guinet C, Gourmelin Y, Rohde G, Martinoli JL (2013) Laboratory assessment of rivaroxaban: a review. Thromb J 11(1):11
Acknowledgments
The excellent technical assistance of M. Jakopanec and M. Behrič is gratefully acknowledged.
Funding
The study was supported by the Slovenian Research Agency (Grant No. P3-0308).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
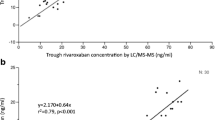
Correlations between rivaroxaban plasma concentrations measured by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and coagulation assays: prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT). Full circles at peak and empty circles at trough. The dotted lines represent the upper reference levels of the assays
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miklič, M., Mavri, A., Vene, N. et al. Intra- and inter- individual rivaroxaban concentrations and potential bleeding risk in patients with atrial fibrillation. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 75, 1069–1075 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-019-02693-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-019-02693-2