Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to establish a non-linear mixed effects model to quantitatively analyze the placebo responses of neuropsychiatric symptoms (NPS) in Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
Methods
A comprehensive literature search was conducted in public databases. Placebo-controlled randomized AD clinical trials using the neuropsychiatric inventory (NPI) score as the primary or secondary outcome were included. Non-linear mixed effects model was used to describe the time course of the placebo responses of NPS in AD clinical trials. Potential affecting factors were tested as covariates.
Results
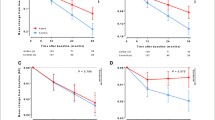
A total of 32 clinical studies (involving 3942 subjects) were included in model-based analysis. We found that the maximal placebo responses of NPS were reached at week 4 approximately, after which rebound effects appeared. The baseline NPI score had a significant impact on the placebo responses. Higher baseline NPI score tended to cause greater reductions in NPI score at week 8 and a smaller degree of rebound. For AD patients whose normalized baseline NPI score was 10 points and 30 points, the reduction in normalized NPI score at week 8 was estimated to be 0.83 and 7.43 points, respectively; and the rebound rate after week 8 was estimated to be 0.1 points/week and 0.08 points/week, respectively.
Conclusions
The duration of 4 weeks is sufficient to determine the drug efficacy for assessing NPS in AD clinical trials. The baseline NPI score was a key factor associated with placebo responses of NPS, which should be considered when designing future clinical trials and conducting comparisons across trials.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allegri RF, Sarasola D, Serrano CM, Taragano FE, Arizaga RL, Butman J, Loñ L (2006) Neuropsychiatric symptoms as a predictor of caregiver burden in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 2:105–110
Borisovskaya A, Pascualy M, Borson S (2014) Cognitive and neuropsychiatric impairments in Alzheimer’s disease: current treatment strategies. Curr Psychiatry Rep 16:1–9
Cummings JL, Mackell J, Kaufer D (2008) Behavioral effects of current Alzheimer’s disease treatments: a descriptive review. Alzheimers Dement 4:49–60
Hort J, O'Brien JT, Gainotti G, Pirttila T, Popescu BO, Rektorova I, Sorbi S, Scheltens P, Dementia ESPo (2010) EFNS guidelines for the diagnosis and management of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Neurol 17:1236–1248
Hyde AJ, May BH, Xue CC, Zhang AL (2017) Variation in placebo effect sizes in clinical trials of oral interventions for management of the behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 25:994–1008
Ito K, Ahadieh S, Corrigan B, French J, Fullerton T, Tensfeldt T, Alzheimer’s Disease Working G (2010) Disease progression meta-analysis model in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 6:39–53
Rogers JA, Polhamus D, Gillespie WR, Ito K, Romero K, Qiu R, Stephenson D, Gastonguay MR, Corrigan B (2012) Combining patient-level and summary-level data for Alzheimer’s disease modeling and simulation: a beta regression meta-analysis. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 39:479–498
Ito K, Corrigan B, Romero K, Anziano R, Neville J, Stephenson D, Lalonde R (2013) Understanding placebo responses in Alzheimer’s disease clinical trials from the literature meta-data and CAMD database. J Alzheimers Dis 37:173–183
Wood S, Cummings JL, Hsu MA, Barclay T, Wheatley MV, Yarema KT, Schnelle JF (2000) The use of the neuropsychiatric inventory in nursing home residents. Characterization and measurement. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 8:75–83
Cummings JL, Mega M, Gray K, Rosenberg-Thompson S, Carusi DA, Gornbein J (1994) The Neuropsychiatric Inventory: comprehensive assessment of psychopathology in dementia. Neurology 44:2308–2314
Cummings JL (1997) The Neuropsychiatric Inventory: assessing psychopathology in dementia patients. Neurology 48:S10–16S
Undurraga J, Baldessarini RJ (2012) Randomized, placebo-controlled trials of antidepressants for acute major depression: thirty-year meta-analytic review. Neuropsychopharmacology 37:851–864
Holford NH, Peace KE (1992) Methodologic aspects of a population pharmacodynamic model for cognitive effects in Alzheimer patients treated with tacrine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:11466–11470
Wählby U, Jonsson EN, Karlsson MO (2001) Assessment of actual significance levels for covariate effects in NONMEM. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 28:231–252
Street JS, Clark WS, Gannon KS, Cummings JL, Bymaster FP, Tamura RN, Mitan SJ, Kadam DL, Sanger TM, Feldman PD, Tollefson GD, Breier A (2000) Olanzapine treatment of psychotic and behavioral symptoms in patients with Alzheimer disease in nursing care facilities: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. The HGEU Study Group. Arch Gen Psychiatry 57:968–976
Tariot PN, Solomon PR, Morris JC, Kershaw P, Lilienfeld S, Ding C (2000) A 5-month, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of galantamine in AD. The Galantamine USA-10 Study Group. Neurology 54:2269–2276
Cummings JL, Nadel A, Masterman D, Cyrus PA (2001) Efficacy of metrifonate in improving the psychiatric and behavioral disturbances of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol 14:101–108
Feldman H, Gauthier S, Hecker J, Vellas B, Subbiah P, Whalen E (2001) A 24-week, randomized, double-blind study of donepezil in moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 57:613–620
Rockwood K, Mintzer J, Truyen L, Wessel T, Wilkinson D (2001) Effects of a flexible galantamine dose in Alzheimer’s disease: a randomised, controlled trial. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 71:589–595
Tariot PN, Cummings JL, Katz IR, Mintzer J, Perdomo CA, Schwam EM, Whalen E (2001) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the efficacy and safety of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer’s disease in the nursing home setting. J Am Geriatr Soc 49:1590–1599
Aisen PS, Schafer KA, Grundman M, Pfeiffer E, Sano M, Davis KL, Farlow MR, Jin S, Thomas RG, Thal LJ (2003) Effects of rofecoxib or naproxen vs placebo on Alzheimer disease progression: a randomized controlled trial. Jama 289:2819–2826
Reisberg B, Doody R, Stöffler A, Schmitt F, Ferris S, Möbius HJ (2003) Memantine in moderate-to-severe Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 348:1333–1341
Ballard CG, Thomas A, Fossey J, Lee L, Jacoby R, Lana MM, Bannister C, McShane R, Swann A, Juszczak E, O'Brien JT (2004) A 3-month, randomized, placebo-controlled, neuroleptic discontinuation study in 100 people with dementia: the neuropsychiatric inventory median cutoff is a predictor of clinical outcome. J Clin Psychiatry 65:114–119
De Deyn PP, Carrasco MM, Deberdt W, Jeandel C, Hay DP, Feldman PD, Young CA, Lehman DL, Breier A (2004) Olanzapine versus placebo in the treatment of psychosis with or without associated behavioral disturbances in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 19:115–126
Brodaty H, Corey-Bloom J, Potocnik FCV, Truyen L, Gold M, Damaraju CRV (2005) Galantamine prolonged-release formulation in the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 20:120–132
De Deyn P, Jeste DV, Swanink R, Kostic D, Breder C, Carson WH, Iwamoto T (2005) Aripiprazole for the treatment of psychosis in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Psychopharmacol 25:463–467
Sparks DL, Sabbagh MN, Connor DJ, Lopez J, Launer LJ, Browne P, Wasser D, Johnson-Traver S, Lochhead J, Ziolwolski C (2005) Atorvastatin for the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer disease: preliminary results. Arch Neurol 62:753–757
Alvarez XACR, Laredo M et al (2006) A 24-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of three dosages of cerebrolysin in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Neurol 13:43–54
Peskind ER, Potkin SG, Pomara N, Ott BR, Graham SM, Olin JT, McDonald S (2006) Memantine treatment in mild to moderate Alzheimer disease: a 24-week randomized, controlled trial. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 14:704–715
Winblad B, Kilander L, Eriksson S, Minthon L, Båtsman S, Wetterholm A-L, Jansson-Blixt C, Haglund A (2006) Donepezil in patients with severe Alzheimer’s disease: double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled study. Lancet 367:1057–1065
Black SE, Doody R, Li H, McRae T, Jambor KM, Xu Y, Sun Y, Perdomo CA, Richardson S (2007) Donepezil preserves cognition and global function in patients with severe Alzheimer disease. Neurology 69:459–469
Chappell AS, Gonzales C, Williams J, Witte MM, Mohs RC, Sperling R (2007) AMPA potentiator treatment of cognitive deficits in Alzheimer disease. Neurology 68:1008–1012
Howard RJ, Juszczak E, Ballard CG, Bentham P, Brown RG, Bullock R, Burns AS, Holmes C, Jacoby R, Johnson T, Knapp M, Lindesay J, O'Brien JT, Wilcock G, Katona C, Jones RW, DeCesare J, Rodger M (2007) Donepezil for the treatment of agitation in Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 357:1382–1392
Mintzer JE, Tune LE, Breder CD, Swanink R, Marcus RN, McQuade RD, Forbes A (2007) Aripiprazole for the treatment of psychoses in institutionalized patients with Alzheimer dementia: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled assessment of three fixed doses. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 15:918–931
van Dyck CH, Tariot PN, Meyers B, Malca RE (2007) A 24-week randomized, controlled trial of memantine in patients with moderate-to-severe Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 21:136–143
Winblad B, Cummings J, Andreasen N, Grossberg G, Onofrj M, Sadowsky C, Zechner S, Nagel J, Lane R (2007) A six-month double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of a transdermal patch in Alzheimer’s disease—rivastigmine patch versus capsule. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 22:456–467
Ballard C, Lana MM, Theodoulou M, Douglas S, McShane R, Jacoby R, Kossakowski K, Yu LM, Juszczak E (2008) A randomised, blinded, placebo-controlled trial in dementia patients continuing or stopping neuroleptics (the DART-AD trial). PLoS Med 5:e76
de Jong D, Jansen R, Hoefnagels W, Jellesma-Eggenkamp M, Verbeek M, Borm G, Kremer B (2008) No effect of one-year treatment with indomethacin on Alzheimer’s disease progression: a randomized controlled trial. PLoS One 3:e1475
Streitn JE, Porsteinsson AP, Breder CD, Swanink R, Marcus R, McQuade R, Carson WH (2008) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of aripiprazole for the treatment of psychosis in nursing home patients with Alzheimer disease. Am J Geriatr Psychiatr 16:537–550
Sultzer DL, Davis SM, Tariot PN, Dagerman KS, Lebowitz BD, Lyketsos CG, Rosenheck RA, Hsiao JK, Lieberman JA, Schneider LS (2008) Clinical symptom responses to atypical antipsychotic medications in Alzheimer’s disease: phase 1 outcomes from the CATIE-AD effectiveness trial. Am J Psychiatry 165:844–854
Rafii MS, Walsh S, Little JT, Behan K, Reynolds B, Ward C, Jin S, Thomas R, Aisen PS (2011) A phase II trial of huperzine A in mild to moderate Alzheimer disease. Neurology 76:1389–1394
Fox C, Crugel M, Maidment I, Auestad BH, Coulton S, Treloar A, Ballard C, Boustani M, Katona C, Livingston G (2012) Efficacy of memantine for agitation in Alzheimer’s dementia: a randomised double-blind placebo controlled trial. PLoS One 7:e35185
Herrmann N, Gauthier S, Boneva N, Lemming OM (2013) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of memantine in a behaviorally enriched sample of patients with moderate-to-severe Alzheimer’s disease. Int Psychogeriatr 25:919–927
Schwam EM, Nicholas T, Chew R, Billing CB Jr, Davidson W, Ambrose D, Altstiel LD (2014) A multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of the PDE9A inhibitor, PF-04447943, in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 11:413–421
Cummings JL, Lyketsos CG, Peskind ER, Porsteinsson AP, Mintzer JE, Scharre DW, De La Gandara JE, Agronin M, Davis CS, Nguyen U, Shin P, Tariot PN, Siffert J (2015) Effect of dextromethorphan-quinidine on agitation in patients with Alzheimer disease dementia: a randomized clinical trial. Jama 314:1242–1254
Rosenberg PB, Drye LT, Porsteinsson AP, Pollock BG, Devanand DP, Frangakis C, Ismail Z, Marano C, Meinert CL, Mintzer JE, Munro CA, Pelton G, Rabins PV, Schneider LS, Shade DM, Weintraub D, Newell J, Yesavage J, Lyketsos CG (2015) Change in agitation in Alzheimer’s disease in the placebo arm of a nine-week controlled trial. Int Psychogeriatr 27:2059–2067
Rinne JO, Wesnes K, Cummings JL, Hakulinen P, Hallikainen M, Hänninen J, Murphy M, Riordan H, Scheinin M, Soininen H, Rouru J (2017) Tolerability of ORM-12741 and effects on episodic memory in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement (N Y) 3:1–9
Xiao S, Wang T, Ma X, Qin Y, Li X, Zhao Z, Liu X, Wang X, Xie H, Jiang Q (2015) Efficacy and safety of a novel acetylcholinesterase inhibitor octohydroaminoacridine in mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease: a phase II multicenter randomised controlled trial. Alzheimers Dement 11:P902–PP03
Schneider LS, Dagerman KS, Insel P (2005) Risk of death with atypical antipsychotic drug treatment for dementia: meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. JAMA 294:1934–1943
Lanctôt KL, Boot BP, Bain LJ, Hendrix JA, Carrillo MC (2016) Considering new treatment paradigms for neuropsychiatric symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 12:1031–1032
Wang J, Yu TJ, Wang FH, Meng FX, Wang C, Tan CC, Tan L (2015) Pharmacological treatment of neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 86:101–109
Ito K, Corrigan B, Zhao Q, French J, Miller R, Soares H, Katz E, Nicholas T, Billing B, Anziano R (2011) Disease progression model for cognitive deterioration from Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative database. Alzheimers Dement 7:151–160
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the participants and their study partners who volunteered their time to complete this study.
Funding
This study was supported by the Science and Technology Innovation Action Plan of Shanghai (17401970900), National Major Scientific and Technological Special Project for “Significant New Drugs Development” during the Thirteenth Five-year Plan Period (2018ZX09734-005, 2018ZX09711001-009-011, 2018ZX09731016-001, 2017ZX09304003), and Research Program of Shanghai University of traditional Chinese Medicine (2016YSN15).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 318 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, N., Lv, Y., Li, H. et al. Quantifying placebo responses in clinical evaluation of neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 75, 497–509 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-018-02620-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-018-02620-x