Abstract
Objective
Metronidazole has been reported to cause various drug interactions when co-administered with certain drugs. One possible mechanism for this action is through an inhibition of P-glycoprotein (P-gp). We have assessed the possible inhibitory effects of metronidazole on P-gp-mediated drug disposition in healthy subjects using fexofenadine as a P-gp substrate.
Methods
This was a randomized, placebo-controlled, open-label, two-way crossover study involving 12 healthy male volunteers who were treated with metronidazole 500 mg or placebo three times daily for 7 days. On day 7, a single dose of fexofenadine 120 mg was given orally. Plasma levels of fexofenadine were measured and its pharmacokinetics assessed.
Results
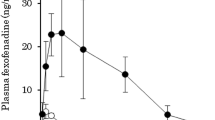
Metronidazole did not affect the plasma concentration profiles and the pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine. The area under the time versus concentration curve of fexofenadine in the metronidazole phase (2075.7 ng h/mL) was similar to that of the placebo phase (1999.2 ng h/mL) (P = 0.356). Additionally, metronidazole did not affect the maximum plasma levels of fexofenadine (304.4 ng/mL for placebo vs. 293.2 ng/mL for metronidazole) (P = 0.423). The elimination half-life and oral clearance of fexofenadine were not affected by metronidazole treatment.
Conclusion
These results show that metronidazole did not have any inhibitory effect on the pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine. The results of the present study provide evidence that metronidazole does not act as an inhibitor of P-gp-mediated disposition in humans.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zylber-Katz E, Rubinger D, Berlatzky Y (1988) Cyclosporine interactions with metronidazole and cimetidine. Drug Intell Clin Pharm 22:504–505
Page RL 2nd, Klem PM, Rogers C (2005) Potential elevation of tacrolimus trough concentrations with concomitant metronidazole therapy. Ann Pharmacother 39:1109–1113
Cooke CE, Sklar GE, Nappi JM (1996) Possible pharmacokinetic interaction with quinidine: ciprofloxacin or metronidazole? Ann Pharmacother 30:364–366
Kounas SP, Letsas KP, Sideris A, Efraimidis M, Kardaras F (2005) QT interval prolongation and torsades de pointes due to a coadministration of metronidazole and amiodarone. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 28:472–473
Patterson BD (1994) Possible interaction between metronidazole and carbamazepine. Ann Pharmacother 28:1303–1304
Herzig K, Johnson DW (1999) Marked elevation of blood cyclosporin and tacrolimus levels due to concurrent metronidazole therapy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 14:521–523
Liu YT, Hao HP, Liu CX, Wang GJ, Xie HG (2007) Drugs as CYP3A probes, inducers, and inhibitors. Drug Metab Rev 39:699–721
Roedler R, Neuhauser MM, Penzak SR (2007) Does metronidazole interact with CYP3A substrates by inhibiting their metabolism through this metabolic pathway? Or should other mechanisms be considered? Ann Pharmacother 41:653–658
Wang JS, Backman JT, Kivisto KT, Neuvonen PJ (2000) Effects of metronidazole on midazolam metabolism in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 56:555–559
Christians U, Schmitz V, Haschke M (2005) Functional interactions between P-glycoprotein and CYP3A in drug metabolism. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 1:641–654
Cvetkovic M, Leake B, Fromm MF, Wilkinson GR, Kim RB (1999) OATP and P-glycoprotein transporters mediate the cellular uptake and excretion of fexofenadine. Drug Metab Dispos 27:866–871
Perloff MD, von Moltke LL, Greenblatt DJ (2002) Fexofenadine transport in Caco-2 cells: inhibition with verapamil and ritonavir. J Clin Pharmacol 42:1269–1274
Kim KA, Park PW, Park JY (2009) Short-term effect of quercetin on the pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine, a substrate of P-glycoprotein, in healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 65:609–614
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (2006) Guidance: drug interaction Studies—study design, data analysis, and implications for dosing and labeling. FDA, Rockville
Nilsson C, Aschan J, Hentschke P, Ringden O, Ljungman P, Hassan M (2003) The effect of metronidazole on busulfan pharmacokinetics in patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 31:429–435
Hassan M, Ehrsson H (1987) Metabolism of 14C-busulfan in isolated perfused rat liver. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 12:71–76
Marchand DH, Remmel RP, Abdel-Monem MM (1988) Biliary excretion of a glutathione conjugate of busulfan and 1, 4-diiodobutane in the rat. Drug Metab Dispos 16:85–92
Gibbs JP, Murray G, Risler L, Chien JY, Dev R, Slattery JT (1997) Age-dependent tetrahydrothiophenium ion formation in young children and adults receiving high-dose busulfan. Cancer Res 57:5509–5516
Pelissier MA, Marteau P, Pochart P (2007) Antioxidant effects of metronidazole in colonic tissue. Dig Dis Sci 52:40–44
Dilger K, Fux R, Rock D, Morike K, Gleiter CH (2007) Effect of high-dose metronidazole on pharmacokinetics of oral budesonide and vice versa: a double drug interaction study. J Clin Pharmacol 47:1532–1539
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, KA., Park, JY. Effect of metronidazole on the pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine, a P-glycoprotein substrate, in healthy male volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 66, 721–725 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-010-0797-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-010-0797-2