Abstract
Objective
This study was conducted to retrospectively compare the area under the curve (AUC) and the total clearance of busulfan (Bu) following oral and intravenous (IV) administrations and to determine which intravenous dose generated equivalent exposure to that of the oral form that has been marketed for decades.
Methods
Patient pharmacokinetics were assessed at dose 9 during a conditioning regimen for stem-cell transplantation and included data from 277 patients for oral Bu (71 from fixed-dose studies and 206 from studies with dose adjustment allowed) and 120 patients for IV Bu (fixed dose). AUCs were compared between patients with fixed dose of oral Bu (n = 71, 1 mg/kg) and those of IV Bu (n = 120, 0.8 mg/kg). Total clearances were calculated for all 277 patients with oral Bu and compared to those with IV Bu, with the ratio of IV-to-oral clearance representing the absolute bioavailability of the oral form.
Results
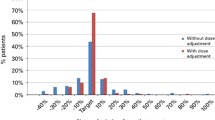
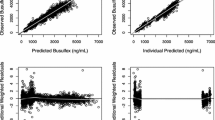
Oral and IV populations differed on disease-type distribution but presented comparable demography parameters. IV Bu dosing was mostly based on the ideal body weight index while actual body weight or adjusted ideal body weight indexes were mostly used for oral. When normalised to comparable indexes, bioequivalent AUCs were achieved between oral and IV populations. Oral Bu bioavailability was about 80% when calculated from the ratio of IV-to-oral total clearances.
Conclusion
This retrospective study carried out on a large set of data showed that similar plasma exposures were achieved with 1.0 mg/kg oral Bu or 0.8 mg/kg IV Bu.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gibbs JP, Liacouras CA, Baldassano RN, Slattery JT (1999) Up-regulation of glutathione S-transferase activity in enterocytes of young children. Drug Metab Dispos 27:1466–1469
Gibbs JP, Murray G, Risler L et al (1997) Age-dependent tetrahydrothiophenium ion formation in young children and adults receiving high-dose busulfan. Cancer Res 57:5509–5516
Hassan M, Ljungman P, Bolme P et al (1994) Busulfan bioavailability. Blood 84:2144–2150
Czerwinsky M, Gibbs JP, Slattery JT (1996) Busulfan conjugation by glutathione S-transferases α, μ, and π. Drug Metab Dispos 24:1015–1019
Nguyen L, Léger F, Lennon S, Puozzo C (2006) Intravenous busulfan in adults prior to haematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a population pharmacokinetic study. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 57:191–198
Ehrsson H, Hassan M, Ehrnebo M, Beran M (1983) Busulfan kinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 34:86–89
Hassan M, Oberg G, Ehrsson H et al (1989) Pharmacokinetic and metabolic studies of high-dose busulphan in adults. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 36:525–530
Grochow LB, Jones RJ, Brundrett RB et al (1989) Pharmacokinetics of busulfan: correlation with veno-occlusive disease in patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 25:55–61
Hassan M, Oberg G, Bekassi AN et al (1991) Pharmacokinetics of high-dose busulphan in relation to age and chronopharmacology. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 28:130–134
Gibbs JP, Gooley T, Borneau B et al. (1999) The impact of obesity and disease on busulfan oral clearance in adults. Blood 93:4436–4440
Schuler U, Schroer S, Kühnle A et al (1994) Busulfan pharmacokinetics in bone marrow transplant patient: is drug monitoring warranted? Bone Marrow Transplant 14:759–765
Committee for Proprietary Medicinal Products (CPMP) (2001) Note for guidance on the investigation of bioavailability and bioequivalence. CPMP/EWP/QWP/1401/98, London
Diletti E, Hauschke D, Steinijans W (1991) Sample size determination for bioequivalence assessment by means of confidence intervals. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol 29:1–8
Grochow LB (1993) Busulfan disposition: the role of therapeutic monitoring in bone marrow transplantation induction regimens. Semin Oncol 20(4 Suppl 4):18–25
Slattery JT, Sanders JE, Buckner CD et al (1995) Graft-rejection and toxicity following bone marrow transplantation in relation to busulfan pharmacokinetics. Bone Marrow Transplant 16:31–42
Andersson BS, Thall PF, Madden T et al (2002) Busulfan systemic exposure relative to regimen-related toxicity and acute graft-versus-host disease: defining a therapeutic window for IV BuCy2 in chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 8:477–485
Slattery JT, Clift RA, Buckner CD et al (1997) Marrow transplantation for chronic myeloid leukaemia: the influence of plasma busulfan levels on the outcome of transplantation. Blood 89:3055–3060
Bostrom B, Enockson K, Johnson A et al (2003) Plasma pharmacokinetics of high-dose Oral busulfan in children and adults undergoing bone marrow transplantation. Ped Transplant 7(Suppl 3):12–18
Lindley C, Shea T, McCune J et al (2004) Intraindividual variability in busulfan pharmacokinetics in patients undergoing a bone marrow transplant: assessment of a test dose and first dose strategy. Anticancer Drugs 15:453–459
Andersson BS, Madden T, Tran HT et al (2000) Acute safety and pharmacokinetics of intravenous busulfan when used with oral busulfan and cyclophosphamide as pretransplantation conditioning therapy: a phase I study. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 6:548–554
Andersson BS, Kashyap A, Gian V et al (2003) Conditioning therapy with intravenous busulfan and cyclophosphamide (IV BuCy2) for hematologic malignancies prior to allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a phase II study. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 8:145–154
Puozzo C, Fuller D, Nguyen L et al (2003) A novel dosing to improve safety / efficacy of a IV BU/CY regimen in children (PEDS) undergoing haematopoietic progenitor cell transplantation (HPCT). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 22:809 Abstract 3252
Santos ES, de Cesare T, Goodman M et al (2004) The efficacy and long-term toxicity of intravenous Busulfan and cyclophosphamide conditioning regimen for stem cell transplantation in advanced lymphoma. Blood 104(11): Abstract 5215
Sobocinski KA, Thall PF, Bekele N et al (2004) Matched pairs analysis of IV vs. PO busulfan as a conditioning agent prior to transplantation. Blood 104:(11) Abstract 2308
Vassal G, Ré M, Gouyette A (1988) Gas chromatographic-mass spectrometry assay for busulfan in biological fluids using deuterated internal standard. J Chromatogr 428:357
Food and Drug Administration (2001) Guidance for industry - statistical approaches to establishing bioequivalence. US Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CEDER), Washington DC
Hassan M, Oberg G, Bekassy AN et al (1991) Pharmacokinetics of high-dose busulphan in relation to age and chronopharmacology. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 28:130
Vassal G, Challine D, Koscielny S et al (1993) Chronopharmacology of high-dose busulfan in children. Cancer Res 53:1534
Schuler US, Ehrsam M, Schneider A et al (1998) Pharmacokinetics of intravenous busulfan and evaluation of the bioavailability of the oral formulation in conditioning for haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 22:241–244
Acknowledgements
The authors express their thanks and gratefully acknowledge the contribution of Professor John T. Slattery who, while at Clinical Research Division of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, kindly provided the PK data of oral busulfan that gave us the opportunity to carry out this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Léger, F., Nguyen, L. & Puozzo, C. Exposure equivalence between IV (0.8 mg/kg) and oral (1 mg/kg) busulfan in adult patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 65, 903–911 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-009-0652-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-009-0652-5