Abstract
Objective
The objective of this study was to evaluate genetic and pharmacokinetic factors affecting the initial pharmacotherapeutic effect of paroxetine (PAX) in Japanese patients with panic disorder (PD).
Method
Plasma concentration of PAX was determined by high performance liquid chromatography. Serotonin transporter gene-linked polymorphic region (5-HTTLPR) variants were determined by polymerase chain reaction techniques. PD severity was assessed using the Panic and Agoraphobia Scale (PAS).
Results
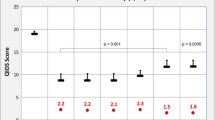
Multiple regression analysis revealed that the plasma concentration of PAX, 5-HTTLPR genotype, and comorbid physical illness were significant factors affecting the initial pharmacotherapeutic effect of PAX in PD and indicated that these factors accounted for 52.4% (R 2 = 0.524) of the variability in the percent reduction in PAS score. The final model was described by the following equation (P = 0.001): percent reduction in PAS score (%) = 68.5 − 1.2 × [plasma concentration of PAX (ng/ml)] − 33.0 × (L/S = 1, S/S = 0) − 21.8 × (with comorbid physical illness = 1, without comorbid physical illness = 0).
Conclusion
The high plasma concentration of PAX, the L/S genotype of 5-HTTLPR, and comorbid physical illness might be associated with a poor response to the initial phase of pharmacotherapy of PD with PAX.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weissman MM, Bland RC, Canino GJ, Faravelli C, Greenwald S, Hwu HG, Joyce PR, Karam EG, Lee CK, Lellouch J, Lepine JP, Newman SC, Oakley-Browne MA, Rubio-Stipec M, Wells JE, Wickramaratne PJ, Wittchen HU, Yeh EK (1997) The cross-national epidemiology of panic disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 54:305–309
Carlbring P, Gustafsson H, Ekselius L, Andersson G (2002) 12-month prevalence of panic disorder with or without agoraphobia in the Swedish general population. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 37:207–211
Crowe RR, Noyes R, Pauls DL, Slymen D (1983) A family study of panic disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 40:065–1069
Harris EL, Noyes R Jr, Crowe RR, Chaudhry DR (1983) Family study of agoraphobia. Report of a pilot study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 40:1061–1064
Skre I, Onstad S, Torgersen S, Lygren S, Kringlen E (1993) A twin study of DSM-III-R anxiety disorders. Acta Psychiatr Scand 88:85–92
Hettema JM, Neale MC, Kendler KS (2001) A review and meta-analysis of the genetic epidemiology of anxiety disorders. Am J Psychiatry 158:1568–1578
Oehrberg S, Christiansen PE, Behnke K, Borup AL, Severin B, Soegaard J, Calberg H, Judge R, Ohrstrom JK, Manniche PM (1995) Paroxetine in the treatment of panic disorder. A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Br J Psychiatry 167:374–379
Lecrubier Y, Bakker A, Dunbar G, Judge R (1997) A comparison of paroxetine, clomipramine and placebo in the treatment of panic disorder. Collaborative Paroxetine Panic Study Investigators. Acta Psychiatr Scand 95:145–152
Lecrubier Y, Judge R (1997) Long-term evaluation of paroxetine, clomipramine and placebo in panic disorder. Collaborative Paroxetine Panic Study Investigators. Acta Psychiatr Scand 95:153–160
Ballenger JC, Wheadon DE, Steiner M, Bushnell W, Gergel IP (1998) Double-blind, fixed-dose, placebo-controlled study of paroxetine in the treatment of panic disorder. Am J Psychiatry 155:36–42
Black DW, Wesner R, Bowers W, Gabel J (1993) A comparison of fluvoxamine, cognitive therapy, and placebo in the treatment of panic disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 50:44–50
Sandmann J, Lorch B, Bandelow B, Hartter S, Winter P, Hiemke C, Benkert O (1998) Fluvoxamine or placebo in the treatment of panic disorder and relationship to blood concentrations of fluvoxamine. Pharmacopsychiatry 31:117–121
Watanabe T, Ueda M, Saeki Y, Hirokane G, Morita S, Okawa M, Akiyama K, Shimoda K (2007) High plasma concentrations of paroxetine impede clinical response in patients with panic disorder. Ther Drug Monit 29:40–44
Meyer JH, Wilson AA, Ginovart N, Goulding V, Hussey D, Hood K, Houle S (2001) Occupancy of serotonin transporters by paroxetine and citalopram during treatment of depression: a [(11)C]DASB PET imaging study. Am J Psychiatry 158:1843–1849
Lesch KP, Bengel D, Heils A, Sabol SZ, Greenberg BD, Petri S, Benjamin J, Muller CR, Hamer DH, Murphy DL (1996) Association of anxiety-related traits with a polymorphism in the serotonin transporter gene regulatory region. Science 274:1527–1531
Heils A, Teufel A, Petri S, Stober G, Riederer P, Bengel D, Lesch KP (1996) Allelic variation of human serotonin transporter gene expression. J Neurochem 66:2621–2624
Deckert J, Catalano M, Heils A, Di Bella D, Friess F, Politi E, Franke P, Nothen MM, Maier W, Bellodi L, Lesch KP (1997) Functional promoter polymorphism of the human serotonin transporter: lack of association with panic disorder. Psychiatr Genet 7:45–47
Hamilton SP, Heiman GA, Haghighi F, Mick S, Klein DF, Hodge SE, Weissman MM, Fyer AJ, Knowles JA (1999) Lack of genetic linkage or association between a functional serotonin transporter polymorphism and panic disorder. Psychiatr Genet 9:1–6
Ishiguro H, Arinami T, Yamada K, Otsuka Y, Toru M, Shibuya H (1997) An association study between a transcriptional polymorphism in the serotonin transporter gene and panic disorder in a Japanese population. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 51:333–335
Olesen OF, Bennike B, Hansen ES, Koefoed P, Woldbye DP, Bolwig TG, Mellerup E (2005) The short/long polymorphism in the serotonin transporter gene promoter is not associated with panic disorder in a Scandinavian sample. Psychiatr Genet 15:159
Perna G, Favaron E, Di Bella D, Bussi R, Bellodi L (2005) Antipanic efficacy of paroxetine and polymorphism within the promoter of the serotonin transporter gene. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:2230–2235
Bandelow B (1995) Assessing the efficacy of treatments for panic disorder and agoraphobia. II. The Panic and Agoraphobia Scale. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 10:73–81
Charlier C, Broly F, Lhermitte M, Pinto E, Ansseau M, Plomteux G (2003) Polymorphisms in the CYP 2D6 gene: association with plasma concentrations of fluoxetine and paroxetine. Ther Drug Monit 25:738–742
Güzey C, Aamo T, Spigset O (2000) Risperidone metabolism and the impact of being a cytochrome P450 2D6 ultrarapid metabolizer. J Clin Psychiatry 61:600–601
Nishida Y, Fukuda T, Yamamoto I, Azuma J (2000) CYP2D6 genotypes in a Japanese population: low frequencies of CYP2D6 gene duplication but high frequency of CYP2D6*10. Pharmacogenetics 10:567–570
Hikida K, Inoue Y, Nouchi E, Ohkura Y (1990) Determination of etizolam in human serum or plasma using automated column-switching high-performance liquid chromatography. Jpn J Clin Chem 19:354–359
Stahl SM (2000) Essential psychopharmacology, 2nd ed. Cambridge University Press, New York
Louie AK, Lewis TB, Lannon RA (1993) Use of low-dose fluoxetine in major depression and panic disorder. J Clin Psychiatry 54:435–438
Gilles M, Deuschle M, Kellner S, Shams M, Krumm B, Hartter S, Heuser I, Hiemke C (2005) Paroxetine serum concentrations in depressed patients and response to treatment. Pharmacopsychiatry 38:118–121
Stahl SM (2002) Independent actions on fear circuits may lead to therapeutic synergy for anxiety when combining serotonergic and GABAergic agents. J Clin Psychiatry 63:854–855
David SP, Murthy NV, Rabiner EA, Munafo MR, Johnstone EC, Jacob R, Walton RT, Grasby PM (2005) A functional genetic variation of the serotonin (5-HT) transporter affects 5-HT1A receptor binding in humans. J Neurosci 25:2586–2590
Simon NM, Fischmann D (2005) The implications of medical and psychiatric comorbidity with panic disorder. J Clin Psychiatry 66(Suppl 4):8–15
Murphy GM Jr, Hollander SB, Rodrigues HE, Kremer C, Schatzberg AF (2004) Effects of the serotonin transporter gene promoter polymorphism on mirtazapine and paroxetine efficacy and adverse events in geriatric major depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 61:1163–1169
Perlis RH, Mischoulon D, Smoller JW, Wan YJ, Lamon-Fava S, Lin KM, Rosenbaum JF, Fava M (2003) Serotonin transporter polymorphisms and adverse effects with fluoxetine treatment. Biol Psychiatry 54:879–883
Takahashi H, Yoshida K, Ito K, Sato K, Kamata M, Higuchi H, Shimizu T, Ito K, Inoue K, Tezuka T, Suzuki T, Ohkubo T, Sugawara K (2002) No association between the serotonergic polymorphisms and incidence of nausea induced by fluvoxamine treatment. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 12:477–481
Kato M, Fukuda T, Wakeno M, Fukuda K, Okugawa G, Ikenaga Y, Yamashita M, Takekita Y, Nobuhara K, Azuma J, Kinoshita T (2006) Effects of the serotonin type 2A, 3A and 3B receptor and the serotonin transporter genes on paroxetine and fluvoxamine efficacy and adverse drug reactions in depressed Japanese patients. Neuropsychobiology 53:186–195
Blaya C, Salum GA, Lima MS, Leistner-Segal S, Manfro GG (2007) Lack of association between the serotonin transporter promoter polymorphism (5-HTTLPR) and panic disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Behav Brain Funct 3:41. doi:10.1186/1744–9081–3–41
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by KAKENHI, Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research, and a Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) (#18591307) and the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) (#19790837 and #18790847). The authors are grateful to Ms. Yoshimi Aoyama for her excellent technical assistance. The authors have no conflicts of interest directly relevant to the content of the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saeki, Y., Watanabe, T., Ueda, M. et al. Genetic and pharmacokinetic factors affecting the initial pharmacotherapeutic effect of paroxetine in Japanese patients with panic disorder. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 65, 685–691 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-009-0633-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-009-0633-8