Abstract
Purpose
Idebenone is a synthetic analogue of ubiquinone that may be beneficial in the treatment of Friedreich’s ataxia. Since in previous pharmacokinetic trials only lower doses were studied, it was the aim of this study to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of idebenone in higher doses of up to 2,250 mg/day.
Methods
In this open, randomized trial, 25 healthy male subjects received first either a single oral dose of 150 mg or 750 mg of idebenone, then the same dose given at 8-h intervals for 14 days.
Results
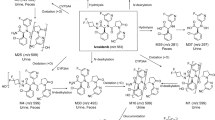
Idebenone and its metabolites appeared in the plasma quickly. Over 99% of parent idebenone was metabolized, indicating a high first-pass effect. Cmax and AUC0−t values for parent idebenone and its metabolites increased in a dose-proportional manner. There was virtually no accumulation of parent drug or metabolites following multiple dosing.
Conclusions
Idebenone exhibited dose-dependent pharmacokinetics in daily doses up to 2,250 mg. In 6/14 subjects, adverse events of mild to moderate severity were observed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Durr A, Cossee M, Agid Y, Campuzano V, Mignard C, Penet C, Mandel JL, Brice A, Koenig M (1996) Clinical and genetic abnormalities in patients with Friedreich’s ataxia. N Engl J Med 335:1169–1175
Campuzano V, Montermini L, Molto MD, Pianese L, Cossee M, Cavalcanti F, Monros E, Rodius F, Duclos F, Monticelli A, Zara F, Canizares J, Koutnikova H, Bidichandani SI, Gellera C, Brice A, Trouillas P, De Michele G, Filla A, De Frutos R, Palau F, Patel PI, Di Donato S, Mandel JL, Cocozza S, Koenig M, Pandolfo M (1996) Friedreich’s ataxia: autosomal recessive disease caused by an intronic GAA triplet repeat expansion. Science 271:1423–1427
Rötig A, Sidi D, Munnich A, Rustin P (2002) Molecular insights into Friedreich’s ataxia and antioxidant-based therapies. Trends Mol Med 8:221–224
Pandolfo M (2008) Friedreich ataxia. Arch Neurol 65:1296–1303
Lodi R, Cooper JM, Bradley JL, Manners D, Styles P, Taylor DJ, Schapira AH (1999) Deficit of in vivo mitochondrial ATP production in patients with Friedreich ataxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:11492–11495
Schulz JB, Dehmer T, Schols L, Mende H, Hardt C, Vorgerd M, Burk K, Matson W, Dichgans J, Beal MF, Bogdanov MB (2000) Oxidative stress in patients with Friedreich ataxia. Neurology 55:1719–1721
Di Prospero NA, Fischbeck KH (2005) Therapeutics development for triplet repeat expansion diseases. Nat Rev 6:756–765
Suno M, Nagaoka A (1984) Inhibition of lipid peroxidation by a novel compound, idebenone (CV-2619). Jap J Pharmacol 35:196–198
Zs-Nagy I (1990) Chemistry, toxicology, pharmacology and pharmacokinetics of idebenone: a review. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 11:177–186
Sugiyama Y, Fujita T (1985) Stimulation of the respiratory and phosphorylating activities in rat brain mitochondria by idebenone (CV-2619), a new agent improving cerebral metabolism. FEBS Lett 184:48–51
Gillis JC, Benefield P, McTavish D (1994) Idebenone. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic use in age-related cognitive disorders. Drugs Aging 5:133–152
Gutzmann H, Hadler D (1998) Sustained efficacy and safety of idebenone in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: update on a 2-year double-blind multicentre study. J Neural Transm Suppl 54:301–310
Thal LJ, Grundman M, Berg J, Ernstrom K, Margolin R, Pfeiffer E, Weiner MF, Zamrini E, Thomas RG (2003) Idebenone treatment fails to slow cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 61:1498–1502
Weyer G, Babej-Dolle RM, Hadler D, Hofmann S, Herrmann WM (1997) A controlled study of 2 doses of idebenone in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychobiol 36:73–82
Buyse G, Mertens L, Di Salvo G, Matthijs I, Weidemann F, Eyskens B, Goossens W, Goemans N, Sutherland GR, Van Hove JL (2003) Idebenone treatment in Friedreich’s ataxia: neurological, cardiac, and biochemical monitoring. Neurology 60:1679–1681
Hausse AO, Aggoun Y, Bonnet D, Sidi D, Munnich A, Rotig A, Rustin P (2002) Idebenone and reduced cardiac hypertrophy in Friedreich’s ataxia. Heart 87:346–349
Mariotti C, Solari A, Torta D, Marano L, Fiorentini C, Di Donato S (2003) Idebenone treatment in Friedreich patients: one-year-long randomized placebo-controlled trial. Neurology 60:1676–1679
Arnold P, Boulat O, Maire R, Kuntzer T (2006) Expanding view of phenotype and oxidative stress in Friedreich’s ataxia patients with and without idebenone. Schweiz Arch Neurol Psychiatr 157:169–176
Artuch R, Aracil A, Mas A, Colome C, Rissech M, Monros E, Pineda M (2002) Friedreich’s ataxia: idebenone treatment in early stage patients. Neuropediatrics 33:190–193
Rustin P, Rötig A, Munnich A, Sidi D (2002) Heart hypertrophy and function are improved by idebenone in Friedreich’s ataxia. Free Radical Res 36:467–469
Di Prospero N, Baker A, Jeffries N, Fischbeck KH (2007) Neurological effects of high-dose idebenone in patients with Friedreich’s ataxia: a randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 6:878–886
Kobayashi T, Yoshida K, Mitani M, Torii H, Tanayama S (1985) Metabolism of idebenone (CV-2619), a new cerebral metabolism improving agent: isolation and identification of metabolites in the rat and dog. J Pharmacobiodyn 8:448–456
Boni J, Maugeri A, Zingali G, Ramelli L, Gherardi S (1992) Steady-state pharmacokinetics of idebenone in healthy volunteers. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 15:197–205
Pisano P, Durand A, Autret E, Desnuelle C, Pinsard N, Serratrice G, Legout V, Joubert M, Blin O (1996) Plasma concentrations and pharmacokinetics of idebenone and its metabolites following single and repeated doses in young patients with mitochondrial encephalomyopathy. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 51:167–169
Torii H, Yoshida K, Kobayashi T, Tsukamoto T, Tanayama S (1985) Disposition of idebenone (CV-2619), a new cerebral metabolism improving agent, in rats and dogs. J Pharmacobiodyn 8:457–467
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interest: P.V. is employee of Santhera Pharmaceuticals, K.W.K. is an independent consultant to Santhera Pharmaceuticals, J.D. received a research grant from Santhera Pharmaceuticals, M.B. and M.D. have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bodmer, M., Vankan, P., Dreier, M. et al. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of idebenone in healthy male subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 65, 493–501 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-008-0596-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-008-0596-1