Abstract
Background
Spinal-cord injury (SCI) is a leading cause of neuropathic pain (NP). Current pharmaceutical treatments for NP in SCI patients are not effective. Two promising options are gabapentin (GP) and pregabalin (PB). Their predominant mechanism of action is believed to be the inhibition of calcium currents, leading in turn to reduced neurotransmitter release and attenuation of postsynaptic excitability. This could explain much of their efficacy in the treatment of both seizure disorders and pain syndromes. However, evidence for their efficacy in attenuating NP of SCI is still controversial.
Objective
To efficiently integrate valid information and provide a basis for rational decision making, through determining PB and GP efficacy in treating NP in SCI.
Methods
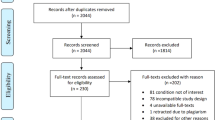
Literature was systematically reviewed. Medline, Embase, CINAHL and Cochrane Database were searched using search terms ‘gabapentin’, ‘pregabalin’, ‘neurontin’, ‘lyrica’, ‘neuropathic pain’ and ‘spinal-cord injury’. Studies were assessed independently by two authors.
Results
Five studies were eligible for inclusion. Two of them studied PB and three GP. Both GP and PB appear to be efficacious for NP in SCI. A clear comparison between the two drugs could not be performed. The literature data suggest that PB is more efficacious than GP in many important variables for NP in SCI, although PB use is followed by more side effects than GP. PB reduced Visual Analogue Score (VAS) in both studies (P < 0.001 and P = 0.016). On the other hand, for GP a maximum dosage of 3,600 mg/day reduced VAS score (P = 0.000), whereas a maximum dosage of 1,200 mg/day failed to do so.
Conclusion
There is a lack of studies comparing GP and PB in treating NP in SCI. This systematic review indicates the possible efficacy of PB and GP in NP of SCI. Recommendations for future research to inform clinical practice should include cost-effectiveness studies and dose-response analysis in order to determine the schema employed and the duration of treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mellegers MA, Furlan AD, Mailis A (2001) Gabapentin for neuropathic pain: systematic review of controlled and uncontrolled literature. Clin J Pain 17:284–295
Jensen TS, Gottrup H, Sindrup SH, Bach FW (2001) The clinical picture of neuropathic pain. Eur J Pharmacol 429:1–11
Belgrade MJ (1999) Following the clues to neuropathic pain. Postgrad Med 106:127–140
Finnerup NB, Jensen TS (2004) Spinal cord injury pain—mechanisms and treatment. Eur J Neurol 11:73–82
Nicholson BD (2004) Evaluation and treatment of central pain syndromes. Neurology 62:30–36
Siddall PJ, McClelland JM, Rutkowski SB, Cousins MJ (2003) A longitudinal study of the prevalence and characteristics of pain in the first 5 years following spinal cord injury. Pain 103:249–257
Siddall PJ, Taylor DA, Cousins MJ (1997) Classification of pain following spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 35:69–75
Cairns DM, Adkins RH, Scott MD (1996) Pain and depression in acute traumatic spinal cord injury: origins of chronic problematic pain? Arch Phys Med Rehabil 77:329–335
Warms CA, Turner JA, Marshall MH, Cardenas CC (2002) Treatments for chronic pain associated with spinal cord injuries: many are tried, few are helpful. Clin J Pain 18:154–163
Rowbotham M, Harden N, Stacey B, Bernstein P, Magnus-Miller L (1998) Gabapentin for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 280:1837–1842
Backonja M, Beydoun A, Edwards KR, Schwartz SL, Fonseca V, Hes M, LaMoreaux L, Garofalo E (1998) Gabapentin for the symptomatic treatment of painful neuropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 280:1831–1836
Hao JX, Xu XJ, Urban L, Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z (2000) Repeated administration of systemic gabapentin alleviates allodynia-like behaviors in spinally injured rats. Neurosci Lett 280:211–214
To TP, Lim TC, Hill ST, Frauman AG, Cooper N, Kirsa SW, Brown DJ (2002) Gabapentin for neuropathic pain following spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 40:282–285
Attal N, Brasseur L, Parker F, Chauvin M, Bouhassira D (1998) Effects of gabapentin on the different components of peripheral and central neuropathic pain syndromes: a pilot study. Eur Neurol 40:191–200
Tai Q, Kirshblum S, Chen B, Millis S, Johnston M, DeLisa JA (2002) Gabapentin in the treatment of neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, crossover trial. J Spinal Cord Med 25:100–105
Levendoglu F, Ogun CO, Ozerbil O, Ogun TC, Ugurlu H (2004) Gabapentin is a first line drug for the treatment of neuropathic pain in spinal cord injury. Spine 29:743–751
Tomson T, Johannessen SI (2000) Therapeutic monitoring of the new antiepileptic drugs. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 55:697–705
Iorio ML, Moretti U, Colcera S, Magro L, Meneghelli I, Motola D, Rivolta AL, Salvo F, Velo GP (2007) Use and safety profile of antiepileptic drugs in Italy. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 63:409–15
Lesser H, Sharma U, LaMoreaux L, Poole RM (2004) Pregabalin relieves symptoms of painful diabetic neuropathy: a randomized controlled trial. Neurology 63:2104–2110
Richter RW, Portenoy R, Sharma U, Lamoreaux L, Bockbrader H, Knapp LE (2005) Relief of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy with pregabalin: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Pain 6:253–260
Rosenstock J, Tuchman M, LaMoreaux L, Sharma U (2004) Pregabalin for the treatment of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Pain 110:628–638
Freynhagen R, Strojek K, Griesing T, Whalen E, Balkenohl M (2005) Efficacy of pregabalin in neuropathic pain evaluated in a 12-week, randomised, double-blind, multicentre, placebo-controlled trial of flexible- and fixed dose regimens. Pain 115:254–263
Dworkin RH, Corbin AE, Young JP Jr, Sharma U, LaMoreaux L, Bockbrader H, Garofalo EA, Poole RM (2003) Pregabalin for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Neurology 60:1274–1283
Dooley DJ, Mieske CA, Borosky SA (2000) Inhibition of K(+)-evoked glutamate release from rat neocortical and hippocampal slices by gabapentin. Neurosci Lett 280:107–110
Dooley DJ, Donovan CM, Pugsley TA (2000) Stimulus-dependent nodulation of [3H] norepinephrine release from rat neocortical slices by gabapentin and pregabalin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 295:1086–1093
Maneuf YP, Hughes J, McKnight AT (2001) Gabapentin inhibits the substance P–facilitated K(+)-evoked release of [3H]glutamate from rat caudal trigeminal nucleus slices. Pain 93:191–196
Siddall PJ, Cousins MJ, Otte A, Griesing T, Chambers R, Murphy TK (2006) Pregabalin in central neuropathic pain associated with spinal cord injury: a placebo-controlled trial. Neurology 67:1792–1800
Vranken JH, Dijkgraaf MG, Kruis MR, van der Vegt MH, Hollmann MW, Heesen M (2007) Pregabalin in patients with central neuropathic pain: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of a flexible-dose regimen. Pain [Epub ahead of print]. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2007.06.033
Gray P (2007) Pregabalin in the management of central neuropathic pain. Expert Opin Pharmacother 8:3035–3041
Rose MA, Kam PC (2002) Gabapentin: pharmacology and its use in pain management. Anaesthesia 57:451–462
Errante LD, Williamson A, Spencer DD, Petroff OAC (2002) Gabapentin and vigabatrin increase GABA in the human neocortical slice. Epilepsy Res 49:203–210
McClelland D, Evans RM, Barkworth L, Martin DJ, Scott RH (2004) A study comparing the actions of gabapentin and pregabalin on the electrophysiological properties of cultured DRG neurons from neonatal rats. BMC Pharmacol 4:14
Fink K, Dooley DJ, Meder WP, Suman-Chauhan N, Duffy S, Clusmann H, Gothert M (2002) Inhibition of neuronal Ca2+ influx by gabapentin and pregabalin in the human neocortex. Neuropharmacology 42:229–236
Taylor CP (2004) The biology and pharmacology of a2-d proteins. CNS Drug Rev 10:183–188
Rintala DH, Holmes SA, Courtade D, Fiess RN, Tastard LV, Loubser PG (2007) Comparison of the effectiveness of amitriptyline and gabapentin on chronic neuropathic pain in persons with spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 88:1547–1560
Kruszewski SP, Shane JA (2007) Pregabalin in central neuropathic pain associated with spinal cord injury: a placebo-controlled trial. Neurology 68:2158–2159
Watson CP (2000) The treatment of neuropathic pain: antidepressants and opioids. Clin J Pain 16:49–55
Katz N, Benoit C (2005) Opioids for neuropathic pain. Curr Pain Headache Rep 9:153–60
Cardenas DD, Warms CA, Turner JA, Marshall H, Brooke MM, Loeser JD (2002) Efficacy of amitriptyline for relief of pain in spinal cord injury: results of a randomized controlled trial. Pain 96:365–373
Gruenthal M, Mueller M, Olson WL, Priebe MM, Sherwood AM, Olson WH (1997) Gabapentin for the treatment of spasticity in patients with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 35:686–689
Priebe MM, Sherwood AM, Graves DE, Mueller M, Olson WH (1997) Effectiveness of gabapentin in controlling spasticity: a quantitative study. Spinal Cord 35:171–175
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tzellos, T.G., Papazisis, G., Amaniti, E. et al. Efficacy of pregabalin and gabapentin for neuropathic pain in spinal-cord injury: an evidence-based evaluation of the literature. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 64, 851–858 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-008-0523-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-008-0523-5